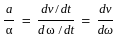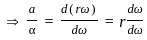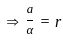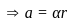BPSC AE Civil Paper 4 (General Engineering) Mock Test - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BPSC AE Civil Paper 4 (General Engineering) Mock Test
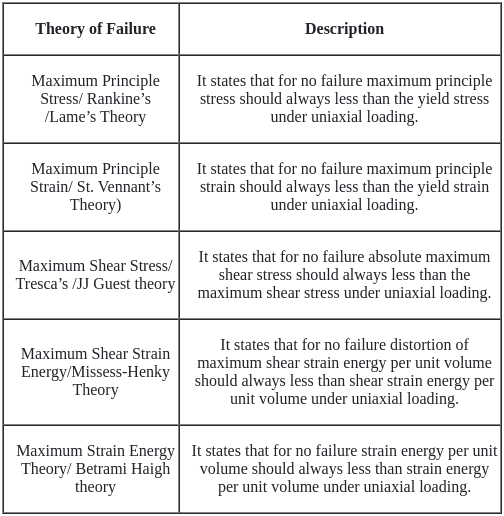
If the bulk modulus and shear modulus are 1 and 2 respectively, what is the value of young's modulus of elasticity?
In a simply supported beam of span L subjected to central concentrated load, the central deflection is 24 mm. Then the slope at supports is:
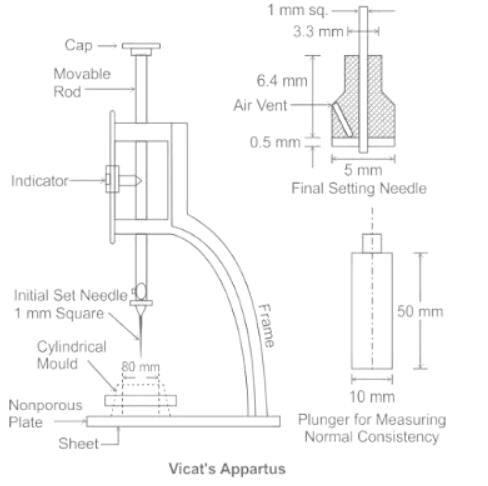
The diameter of plunger used in Vicat apparatus is of
Cast iron contains carbon approximately
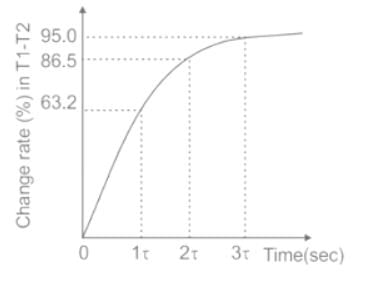
The time constant of a thermocouple is the time taken
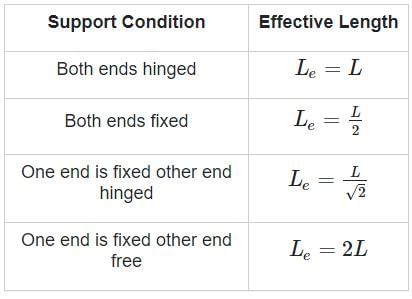
A column with highest equivalent length has-
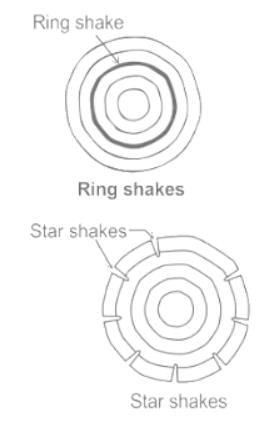
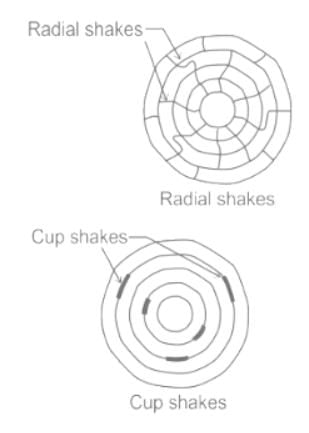
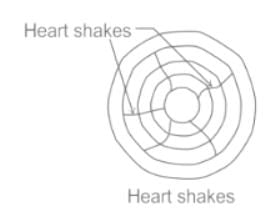
The cracks usually occurs when tree is exposed to sun for seasoning after being fall down are called as
Select the air pollutant that does NOT belong to the category of secondary air pollutants.
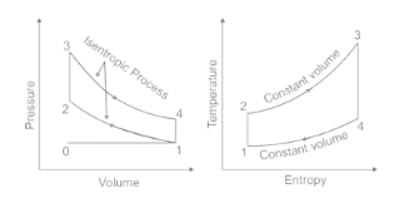
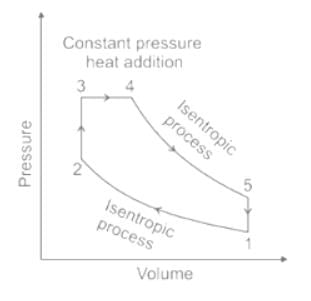
An air-standard diesel cycle consists of
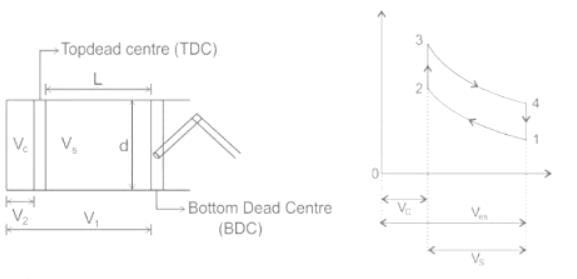
Compression ratio of an internal combustion engine is defined as _______.
[VS = Swept volume, VC = Clearance volume]
Calculate the total impedance for a circuit having the following values:
Resistance = 5 Ω
Inductance reactance = 20 Ω
Capacitance reactance = 8 Ω
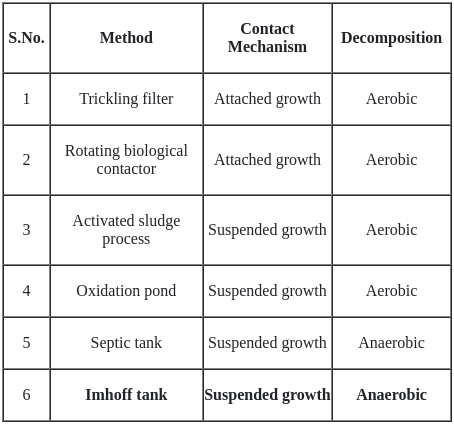
Which of the following unit works in anaerobic conditions?
The example for continuous flow type equipments is
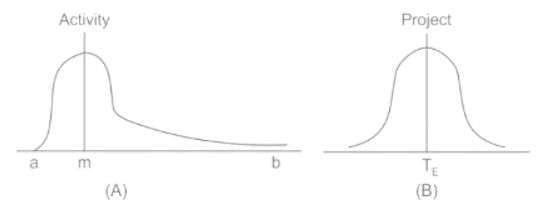
The frequency distribution of duration of an individual activity takes the shape of ______ as per the PERT analysis.
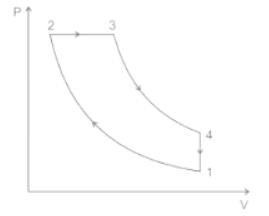
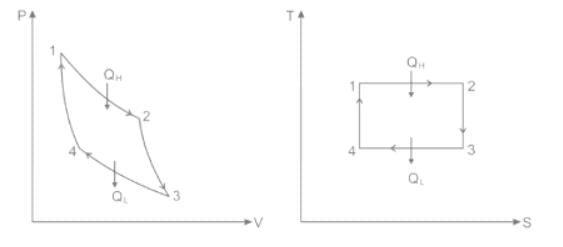
Carnot cycle consists of the following process -
Consider a 390 V, 50 Hz circuit. This inductive circuit has a current of 13 A, lagging 30 degrees. Find the inductive reactance.
Which of the following pairs is not correctly matched?
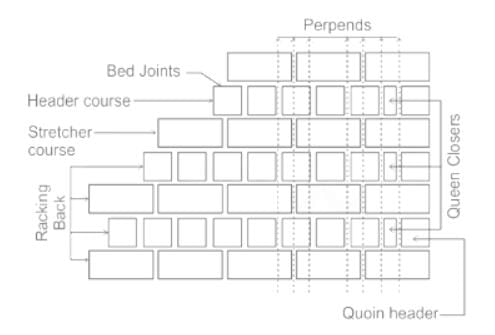
The portions made by cutting standard bricks across their width are known as
Consider the motion of a point on a circular trajectory. The acceleration in a linear motion (a) and the acceleration in angular motion (α), are related as : (Take r as the radius of circular trajectory)
Which of the following classifications are correct with reference to the various types of imperfections in a semi-conductor?
1. Substitutional
2. Vacancies
3. Interstitial
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
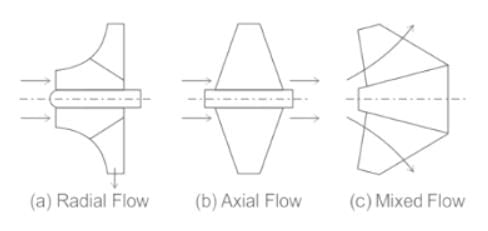
Which of the following is NOT a type of centrifugal pump ?
_________ is the correct formula to determine the elevation difference (dZ) between two points on the ground using a total station.
(VD = Vertical difference, HI = Instrument height and HR = Reflector height)
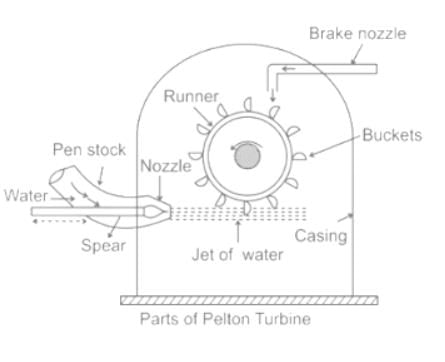
Pelton wheel is which type of turbine?
The quick lime as it comes from kilns is called as-


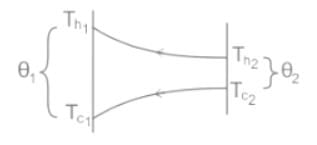
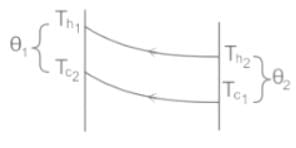
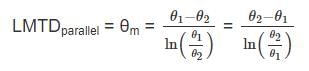
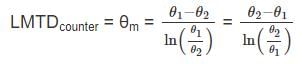
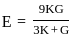
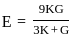
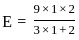

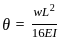
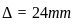 ,
,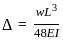
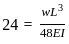
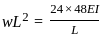
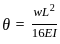
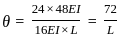
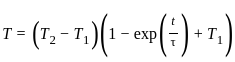
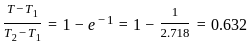
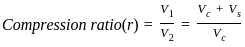
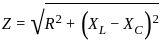
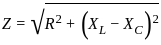
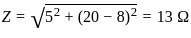
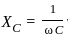
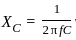
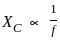
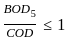
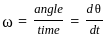
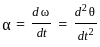
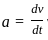 (where v is the linear velocity)
(where v is the linear velocity)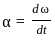 (where ω is the angular velocity)
(where ω is the angular velocity)