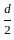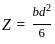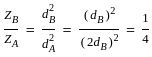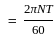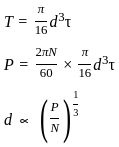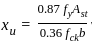BPSC AE Civil Paper 5 (Civil) Mock Test - 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BPSC AE Civil Paper 5 (Civil) Mock Test - 1
What is the main advantage of using the double integration method over other methods for analyzing slopes and deflections?
As per IS: 1892 – 1979; what should be the maximum thickness of cutting edge of sampling tube of 70 mm external diameter which is required for sampling in undisturbed stiff clay soil?
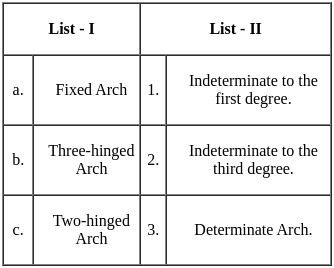
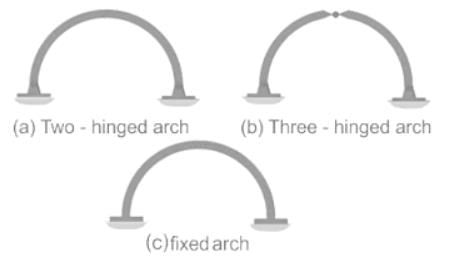
Match List-I (Type of Arch) with List-II (Indeterminacy) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:

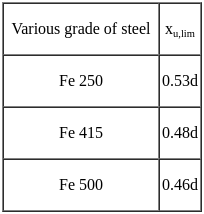
The minimum cement content (kg/m3) for a pre-specified strength of concrete (using standard notations) premised on 'free water-cement ratio' will be as
In plate girders, the web plate is provided with stiffness when the ratio of clear depth to thickness of web is greater than
For a soil void ratio = 0.7 and specific gravity of solids 2.7, the head required to cause quicksand over a column of 5 m high sand will be:
Identify FALSE statement from the following:
_______ is the phenomenon of a material failing under very little stress due to repeated cycles of loading.
Drainage is not permitted during application of cell pressure (before application of deviator stress) in:
(1) Unconsolidated undrained test
(2) Consolidated undrained test
(3) Consolidated drained test
Out of these statements:
If E, G, K, and μ represent the elastic modulus, shear modulus, bulk modulus, and Poisson’s ratio respectively of a linear elastic, isotropic and homogeneous material, and if you need to express the stress-strain relationships completely for this material, at least:
In order to account for shear deformation effects, the effective slenderness ratio of laced columns shall be taken as________ time(s) the actual maximum slenderness ratio.
What is the stiffness factor for a beam simply supported at both ends?
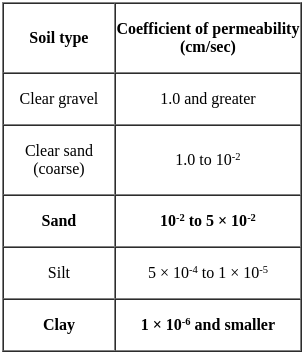
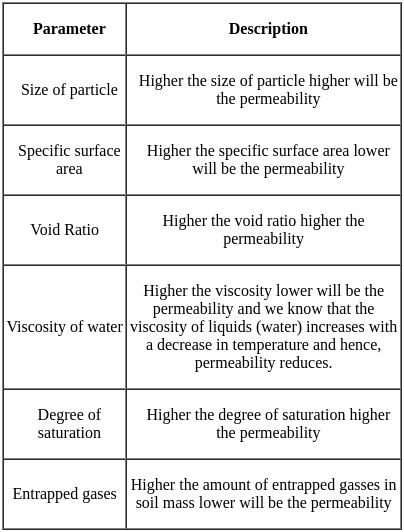
The coefficient of permeability of clay is not more than
Which one of the following statements is NOT correct related to the earthquake resistant design?
Pick up the incorrect statement from the following.
What largest internal pressure can be applied to a cylindrical tank of 2 m diameter and 10 mm wall thickness? (Ultimate tensile strength of steel is 480 MPa and a factor of safety is 8.)
Two beams have the same width but the first beam has double the depth of the second beam. The elastic strength of the first beam compared to the second beam will be
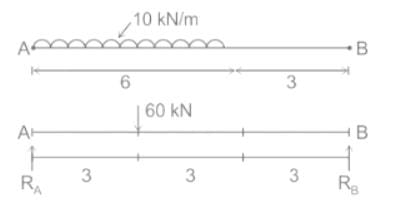
A simply supported beam AB of length 9 m, carries a uniformly distributed load of 10 N/m for a distance of 6 m from end A. What are the reaction forces at A and at B?
For a shaft transmitting power 'P' at rpm N, the diameter of shaft would be proportional to
The phenomenon for the internal transfer of forces from one leg to the other is
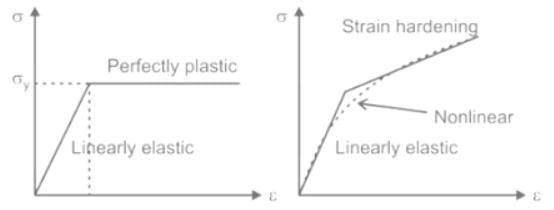
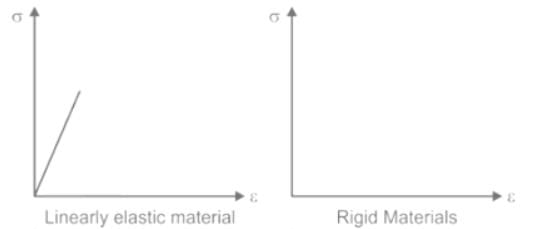
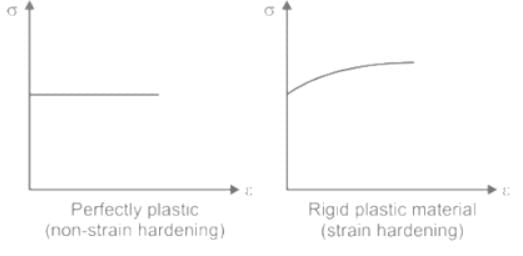
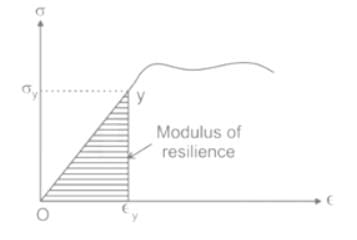
The graph which represents stress (σ) vs strain (ε) characteristics of a Elastic Perfectly Plastic material is:
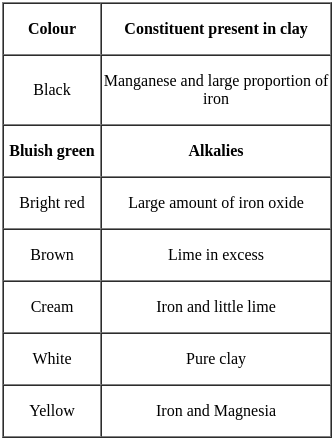
Portland cement is manufactured by burning which of the following materials in a kiln?


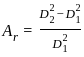
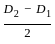
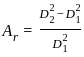

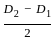
 = 3.05 mm
= 3.05 mm 
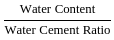
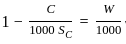 is used to find out the absolute volume of aggregates, where C and W are cement and water content respectively and Sc is specific gravity of cement.
is used to find out the absolute volume of aggregates, where C and W are cement and water content respectively and Sc is specific gravity of cement.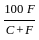 is used to determine the percentage of pulverized ash content in cementing material.
is used to determine the percentage of pulverized ash content in cementing material.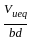
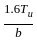 , (For LSM)
, (For LSM)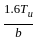
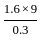 = 68 kN
= 68 kN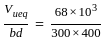
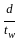 < 85
< 85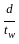 > 85
> 85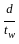 > 200
> 200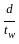 > 250
> 250 > 400
> 400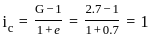
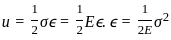



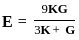
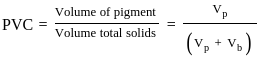 Where, Vp = Volume of pigment, and Vb = Volume of binder.
Where, Vp = Volume of pigment, and Vb = Volume of binder.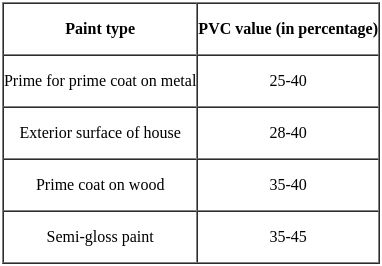
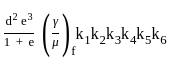

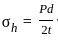
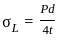
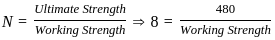
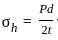
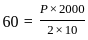
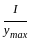
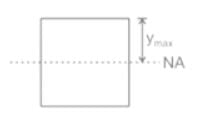
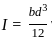 and ymax =
and ymax =