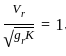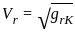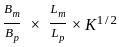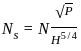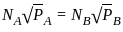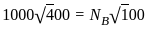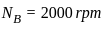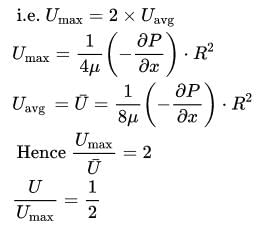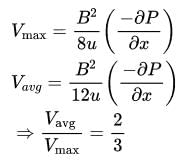BPSC AE Civil Paper 6 (Civil) Mock Test - 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BPSC AE Civil Paper 6 (Civil) Mock Test - 2
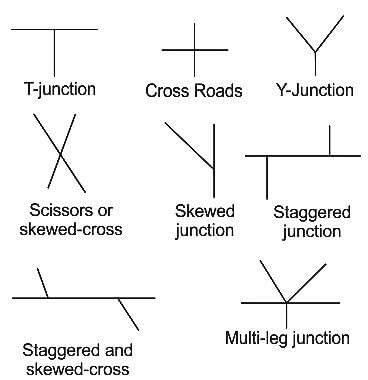
Which of the following is not one of the basic form of at-grade intersections for transport?
A stationary hydraulic jump occurs in a rectangular channel with the initial and sequent depth being equal to 0.20 m and 1.20 m respectively. Estimate the energy loss.
When used in road work, the coefficient of hardness of a stone should be greater than
According to Lacey's theory of channel design, what will be the velocity of flow in the channel corresponding to a discharge of 140 cumec and silt factor 1.0?
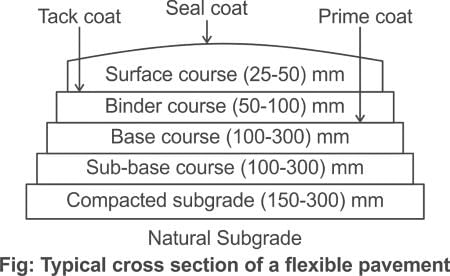
The interface treatment provided to plug in the voids of porous surfaces and to bond loose particles in bituminous pavements is called:
Fill in the blank with the correct option:
__________ refer to the dispersion of solid or liquid particles of microscopic size in the air.
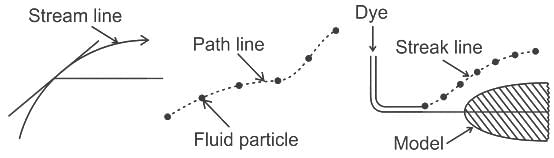
There is no geometrical distinction between streamline, pathline and streakline in the case of:
Which one of the following options is NOT a condition or property for an ideal fluid?
Statement (I): The deeper a lake, the lesser the evaporation in summer and the more in winter.
Statement (II): Heat storage in water bodies affects seasonal evaporation.A barrage on a major river in the Gangetic plains has been designed for a flood discharge 7000 m3/s. It has been provided with a waterway of 360 m length. The looseness factor of this barrage is
The temporary hardness of water is due to presence of:
When assessing the strength of a structure or structural member for the limit state of collapse, the values of partial safety factor for reinforcing steel, should be taken as:
In a model experiment with weir, if the dimension of the model weir are reduced by a factor k, the flow rate through the model weir is the following fraction of the flow rate through the prototype
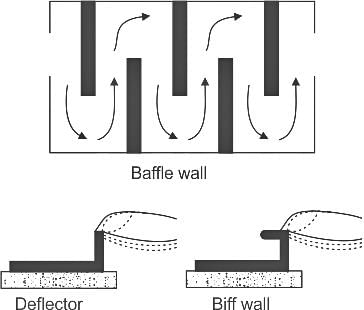
Which of the following function is fulfilled by the biff wall in the channel?
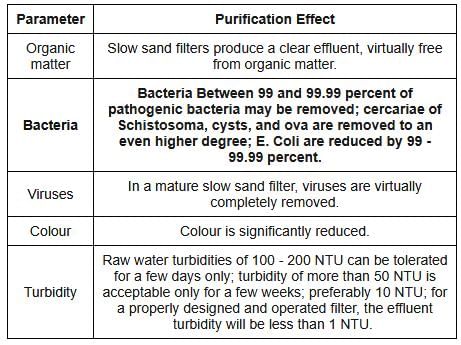
Which of the following statements is NOT correct with respect to the slow sand filter in the drinking water treatment plant?
In the transportation of MSW, Which type of system is ideal for the locations where the waste generation rate is high?
Two Pelton turbines A and B have the same specific speed and are working under the same head. Turbine A produces 400 kW at 1000 rpm. If turbine B produces 100 kW, then its rpm is
If the average centre to centre spacing of vehicles is 30 meters, then the basic capacity of the traffic lane at a speed of 60 kmph is:
Failures in flexible pavements are due to the failure of :
(a) Sub grade
(b) Base course
(c) Wearing Course
Which is the best hydraulic section of the following open channel cross-sections?
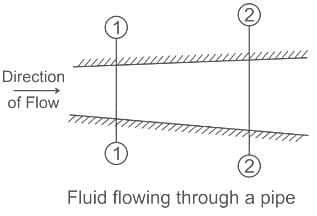
In steady flow through a pipe the density, velocity and area of a section are 3 kg/m3, 8m/s and 0.5m2 respectively. The velocity at another section having area of 1m2 and density of 4 kg/m3 will be
The ratio of average velocity to maximum velocity for steady laminar flow in circular pipes is
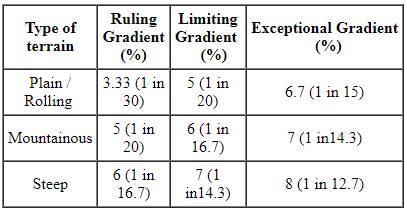
Exceptional gradient in plains as per IRC
In an ogee shaped spillway, the discharge is proportional to


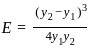
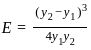
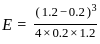
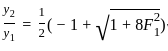

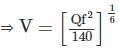
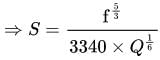
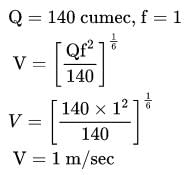
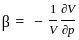
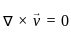
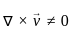

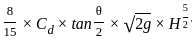
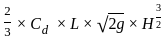
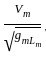 =
= 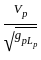 ……..(i)
……..(i)