BPSC AE Civil Paper 6 (Civil) Mock Test - 3 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BPSC AE Civil Paper 6 (Civil) Mock Test - 3
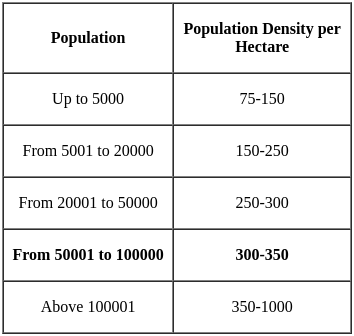
As per public health and environmental engineering organization, for 50,000 - 100,000 population, density of population per hectare will be ________.
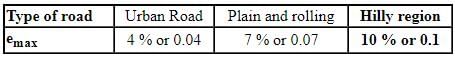
Which of the statement is/are true about superelevation ?
(i) For mixed traffic condition, superelevation is calculated corresponding to 75 % design speed.
(ii) For hilly terrain, maximum superelevation is 7 %.
(iii) In equilibirium superelevation, effect of coefficient of friction is considered.
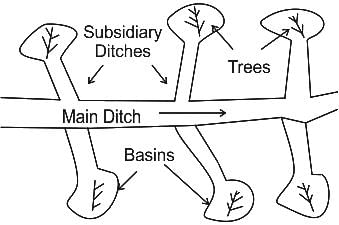
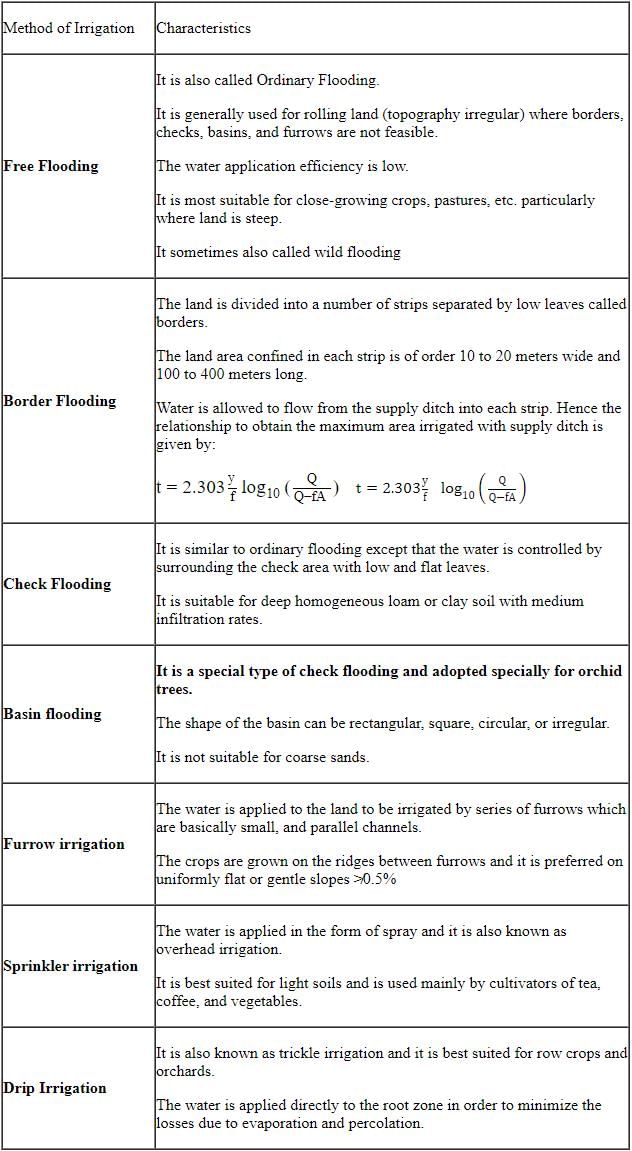
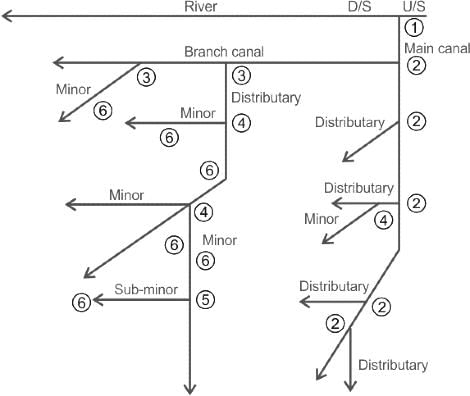
What type of irrigation does this diagram represent?

Verify whether the following functions are valid potential functions.
(i) ϕ = A(X2 - y2)
(ii) ϕ = Acos x
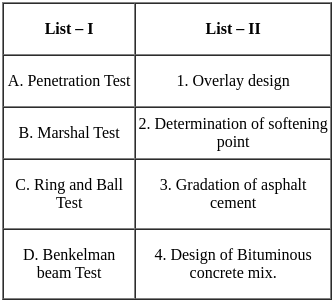
Match list I with list II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the list.
An IUH is a direct runoff hydrograph ?
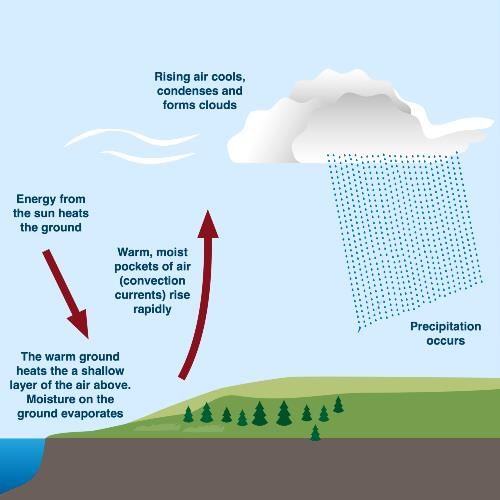
The precipitation caused by natural rising of warmer lighter air in colder and denser surrounding is called
Among the following flow measuring equipments, identify the equipment which cannot be used for measuring the discharge through pipes.
For an irrigation module, the sensitivity was calculated to be 0.5. What would be percent variation in outlet discharge caused, if the percent variation in canal water depth and percentage change in discharge of distributary channel is 50 and 40 respectively.
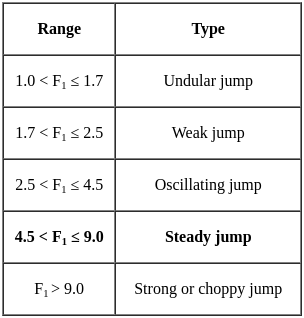
If the Froude number of hydraulic jump is 5.5 it can be classified as
A real fluid in which the shear stress is NOT proportional to the velocity gradient is known as a/an:
The minimum area of steel required per meter width of a slab with overall depth of 100 mm consisting of steel grade Fe500 is
In which of the following system is the sewage allowed to sprinkle over a bed of coarse, rough and hard filter media, and it is then collected through the under drainage system?
Water is flowing through a pipe of 50 mm diameter under a pressure of 29.43 × 104 N/m2. What will be the pressure head?
Study the given statements with respect to turbidity of water and select the correct answer.
Statement A : Turbidity of water is not imparted by the dissolved matter present in water.
Statement B : Jackson's turbid meter is a laboratory apparatus which is used to measure the turbidity of water.
Which of the following method uses Ca(OH)2 (slaked lime) for water softening?
A continuous beam shall be deemed to be deep beam when, the ratio of effective span to overall depth is less than:
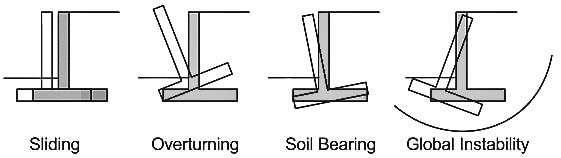
Factor of safety against sliding of the footing when dead load, live load and earth pressure are considered for shallow foundation
The Tie bars in cement concrete pavements are provided across
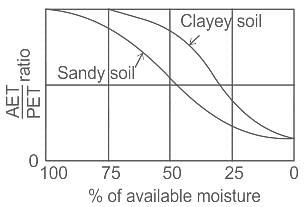
The ratio of actual evapotranspiration to potential evapotranspiration is in the range
Analysis of a surge in open channels is done by using
(i) continuity equation
(ii) energy equation
(iii) momentum equation
The correct answer is
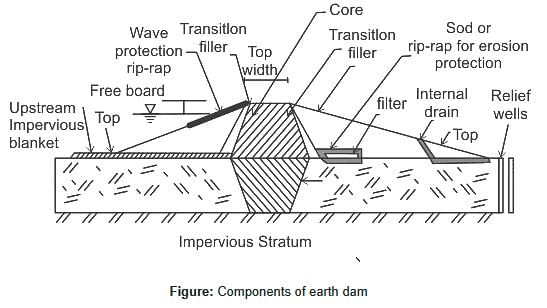
Which one of the following problems is required to be studied in the design of earth dams ?
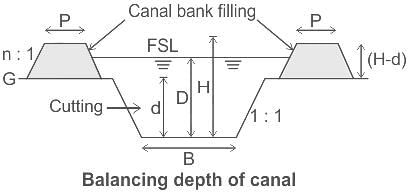
In canal formation, the term ‘balancing depth’ is used to indicate
What is the hydraulic radius of a stable canal carrying a discharge of 27 m3/s using Lacey's method ? (Assume silt factor is 1.0)
The dimension of the Chezy's coefficient (c) are :


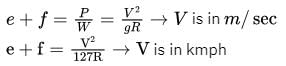

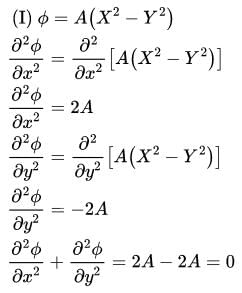
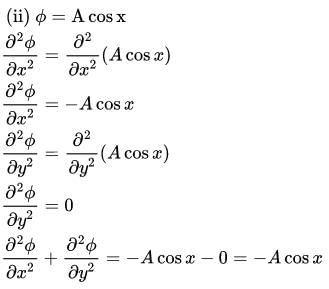
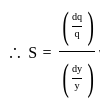
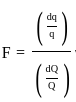
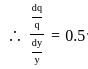
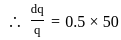
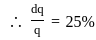
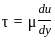
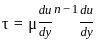
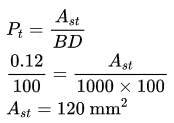
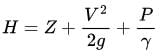
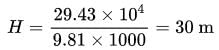
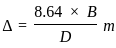
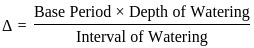
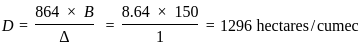
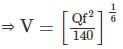
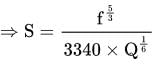
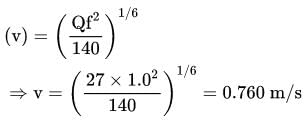
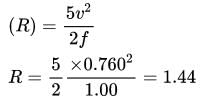
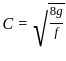
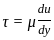 where μ is shear viscosity of the fluid
where μ is shear viscosity of the fluid










