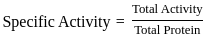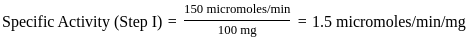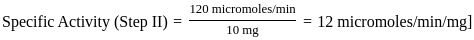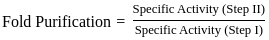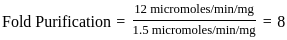CSIR NET Life Sciences Mock Test - 1 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CSIR NET Exam Mock Test Series 2025 - CSIR NET Life Sciences Mock Test - 1
A dishonest shopkeeper professes to sell pulses at the cost price, but he uses a false weight of 950gm for a kg. Find his gain percent.
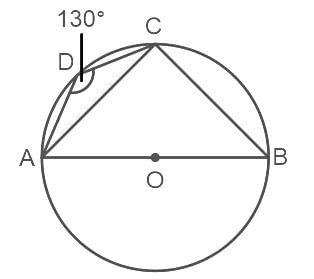
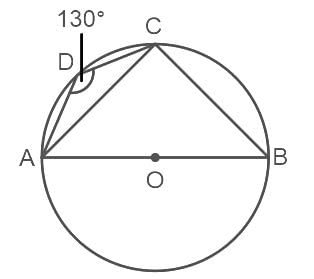
In the given figure, ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral whose side AB is a diameter of the circle through A, B, C and D. If ∠ADC = 130°, then find ∠CAB.

The chart shows forest cover as percentages of total areas of 6 countries over the period 1990-2022 and their land areas (in million km2).
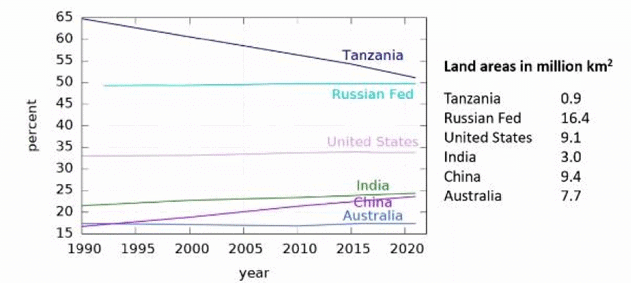
The maximum change in forest area in absolute terms among these countries took place in

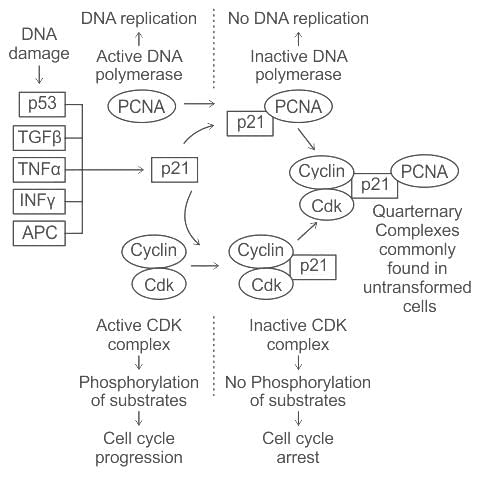
How does p53 contribute to cell cycle regulation when DNA damage is detected?
Which of the following conditions is a peroxisomal disorder?
Which molecule is most likely to diffuse across the cell membrane rapidly without assistance?
In the extrinsic apoptotic pathway, which initiator caspase is primarily activated upon the binding of FasL to the Fas receptor?
The first and foremost assumption of the optical forging theory is
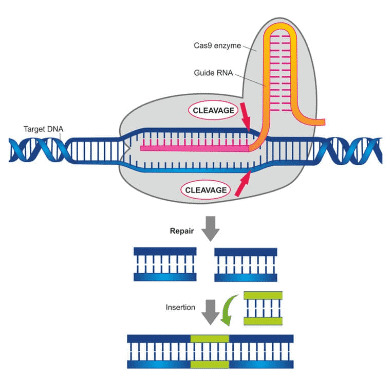
Which principle is utilized in CRISPR-Cas9 technology for gene editing?
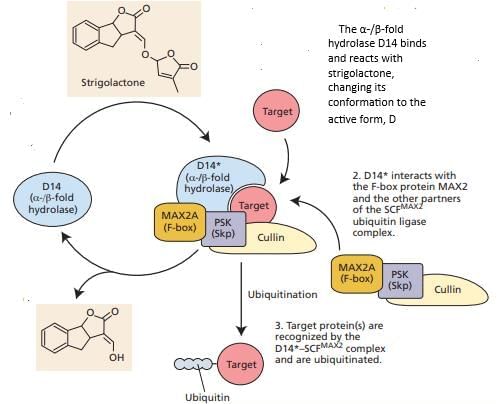
Which of the following statements accurately describes an aspect of strigolactones, a class of plant hormones, concerning their biosynthesis, transport, or mode of action?
For sequencing DNA by Sanger’s method, the chain elongation is terminated by:
If a cell has an adequate supply of adenine nucleotides but requires more guanine nucleotides for protein synthesis, which out of these statements are false:
Molecular mass of a protein CANNOT be determined by:
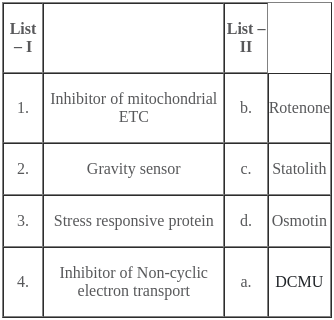
Match the following :
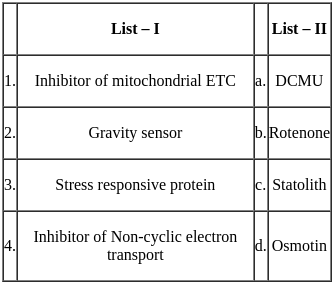
The correct match is :
10 g of a plant material is extracted in 100mL of a suitable buffer. On performing an assay for amylase activity, 100μl extract produced 6 μmoles glucose in 30 minutes of incubation. One unit of amylase activity is defined as the amount of enzyme required to produce 1μmole of glucose per minute. The amylase activity (units / g) of the material is:
You analyze a cell line deficient in Apaf-1 and observe resistance to apoptosis upon UV radiation. Which of the following proteins is most likely still functioning normally in this cell line?
In an animal experiment;
(i) Electrical stimulation of an area in the brain (A) increased a function (F) which was prevented by systemic injection of adrenergic antagonistic, prazosin.
(ii) Injection of carbachol (cholinergic agonist) into A also increased function F which was, however, not prevented by systemic injection of adrenergic antagonistic, prazosin.
The results are likely to be due to the stimulation of
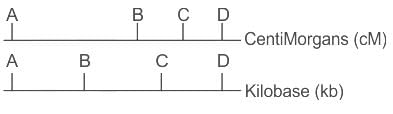
The figure below shows the location of four genes on the genetic map of an organism; the lower panel shows the location of the same group genes on a physical map derived from the nucleotide sequence of the DNA of that organism.What is the reason for the maps to be NOT identical ?
In 'TaqMan' assay for detection of base substitutions (DNA variant), probes (oligonucleotides) with fluorescent dyes at the 5'-end and a quencher at 3'-end are used. While the probe is intact, the proximity of the quencher reduces the fluorescence emitted by reporter dye. If the target sequences (wild type or the variant) are present, the probe anneals to the target sequence, downstream to one of the primers used for amplifying the DNA sequence flanking the position of the variants. For an assay two flanking PCR primers, two probes corresponding to the wild type and variant allele and labelled with two different reporter dyes and quencher were used. During extension the probe may be cleaved by the Taq-polymerase separating the reporter dye and the quencher. Three individuals were genotyped using this assay. Sample for individual I shows maximum fluorescence for the dye attached to the wild type probe, sample for individual II shows maximum fluorescence for the dye attached to variant probe and sample for individual III exhibits equal fluorescence for both the dyes. Which of the following statement is correct?
Certain statements are made concerning nucleic acids and their properties:
A. RNA molecules can exhibit catalytic activity and act as enzymes, known as ribozymes.
B. All DNA polymerases require a primer to initiate DNA synthesis, which can be either DNA or RNA.
C. A-DNA is the biologically active form that exists under physiological conditions.
D. DNA methylation in eukaryotes occurs predominantly on cytosine bases adjacent to guanine bases, a pattern known as CpG methylation.
E. 5' capping and 3' polyadenylation are modifications specific to eukaryotic tRNA to stabilize it and prevent degradation.
Choose the correct statements.
Purification data for an enzyme is given below:
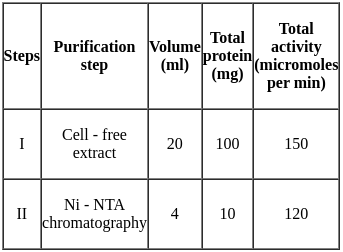
What is the fold - purification?
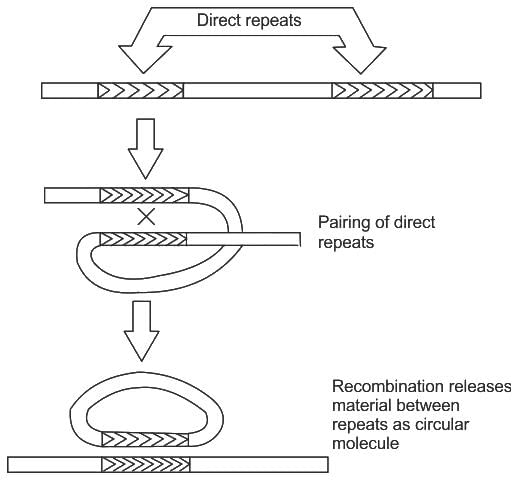
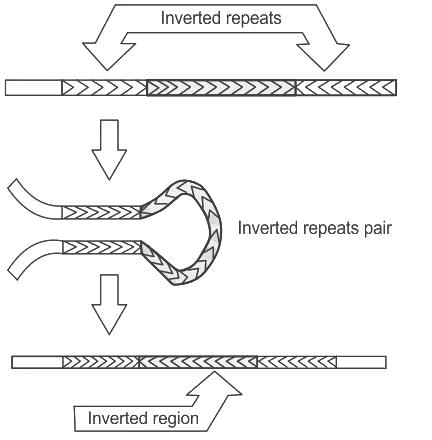
Conservative site specific recombination involves
i. Recombination between inverted repeats leads to inversion of genes
ii. Recombination between direct repeats leads to inversion of genes
iii. Conservation DNA synthesis by doubling of genes by ser-recombinase
iv. Conservation of energy by recombinase
v. Involves both single strand and double strand breakage
AP1 (APETALA) is one of the floral meristem-identifying genes. In wild type Arabidopsis thaliana plants, transformed with AP1:: GUS beta glucoronidase activity is seen in the floral meristem only after the commitment of flowering. Ectopic expression of AP1 :: GUS in the embryonic flower (EF) mutant background results in GUS activity throughout the shoots in four-day-old seedlings; these observations suggest that AP1 is:
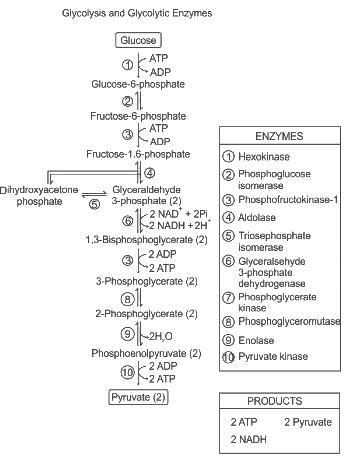
Which of the following molecules are involved in the formation of ATP by substrate level phosphorylation during glycolysis?
A. 1, 3 - bisphosphoglycerate
B. Glucose 6 - phosphate
C. Phosphoenolpyruvate
D. Fructose 1, 6 - bisphosphate
The following statements pertain to enzymes and their applications in advanced molecular biology techniques:
A. FEN cleaves the RNA strand in RNA-DNA hybrids, facilitating the synthesis of complementary DNA (cDNA).
B. DNA polymerase I from E. coli has 3' to 5' exonuclease activity but lacks 5' to 3' exonuclease activity.
C. T4 DNA polymerase is commonly used for end-repair of DNA fragments during library preparation for next-generation sequencing (NGS).
D. Cas9 is an RNA-guided endonuclease that introduces double-strand breaks at specific locations in the genome.
Which one of the following options represents the correct combination of statements?
The characteristic morphological change(s) in cells undergoing apoptosis is/are
A. formation of blebs on cell surface
B. swelling and bursting of cells
C. collapse of the cytoskeleton
D. condensation and fragmentation of nuclear chromatin