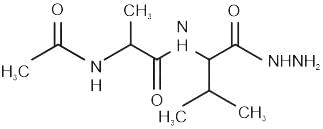
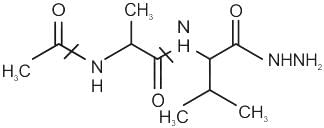
Chemistry: CUET Mock Test - 7 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 - Chemistry: CUET Mock Test - 7
Aromatic diazonium salts are stable at _____ temperatures.
Match list I with list II
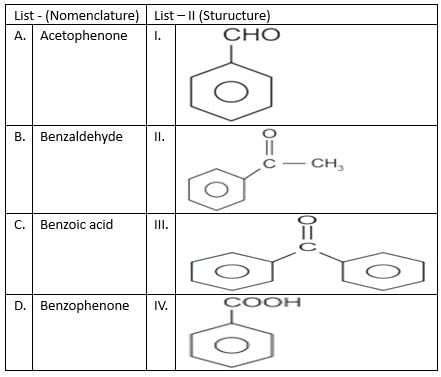
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
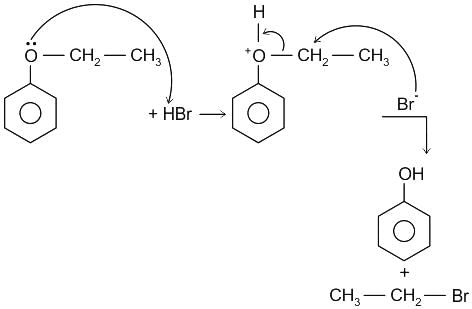
Which simple chemical test is used to distinguish between ethanal & propanal?
What is the main characteristic of transition metals that is discussed in the passage?
What factor can enhance the stability of transition metal complexes?
Which of the following is a key application of transition metal complexes as mentioned in the passage?
In the compound [Fe(CN)6]4-, what oxidation states can iron exist in?
What distinguishes lanthanides and actinides from transition metals?
Which of the following is a characteristic of lanthanides?
What is the primary use of actinides like uranium and thorium?
What oxidation state is most common for lanthanides?
Why do actinides exhibit more varied oxidation states than lanthanides?
Consider the following statements regarding activation energy:
(A) Activation energy is the minimum energy required for reactants to undergo a chemical reaction.
(B) A higher activation energy increases the reaction rate.
(C) The Arrhenius equation relates the rate constant to activation energy.
(D) Catalysts reduce the activation energy of a reaction.
Choose the correct statements:
Consider the following statements about half-life in reactions:
(A) The half-life for a first-order reaction is constant and independent of initial concentration.
(B) The half-life for a second-order reaction depends on the initial concentration of reactants.
(C) The half-life of a reaction is the time required for the concentration of reactants to reach half its initial value.
(D) For zero-order reactions, the half-life is directly proportional to the initial concentration.
Choose the correct statements:
Consider the following statements about the integrated rate equations:
(A) The integrated rate law for a first-order reaction is linear when plotted as ln[A] vs time.
(B) For a zero-order reaction, the integrated rate law is linear when plotted as [A] vs time.
(C) For a second-order reaction, the integrated rate law is linear when plotted as 1/[A] vs time.
(D) The integrated rate law for a first-order reaction is linear when plotted as [A] vs time.
Choose the correct statements:
Statement 1: Transition metals have incomplete d-subshells in their neutral atoms or ions.
Statement 2: Zinc is considered a transition metal because it has a partially filled d-orbital.
Statement 3: Lanthanoids and actinoids are part of the f-block elements in the periodic table.
Statement 4: The f-block elements are placed at the bottom of the periodic table to separate them from the d-block.
Choose the correct statements:
Statement 1: Transition metals are known for exhibiting multiple oxidation states due to their incomplete d-orbitals.
Statement 2: Manganese shows oxidation states ranging from +2 to +7.
Statement 3: The transition elements are not magnetic.
Statement 4: The stability of oxidation states varies across the transition metals.
Choose the correct statements:
Which of the following diazonium salts is insoluble in water?
Which of the following properties is suitable for all diazonium salts?
If the bond length of C-Cl bond in chloromethane is 178pm, what will be the probable bond length of C-Br bond in bromomethane?
The donation of lone pair of electrons of CO carbon into the vacant orbital of metal atom results in _________ bond.
What was the term proposed by Werner for the number of groups bound directly to the metal ion in a coordination complex?
If the secondary valence in CoCl3.4NH3 is six, the solution conductivity in silver nitrate corresponds to ________ electrolyte.
Given that 1 mol of NiCl2.6H2O with excess AgNO3 precipitates 2 mols of AgCl, what is the secondary valence of Ni?
What is the sum of the oxidation number of cobalt in [Co(H2O)(CN)(en)2]2+and [CoBr2(en)2]+?
|
39 docs|145 tests
|


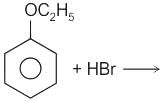

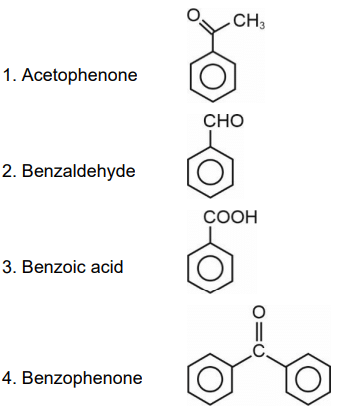
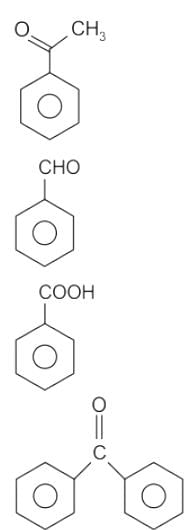
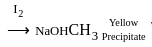
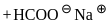
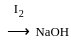 No characteristic change
No characteristic change