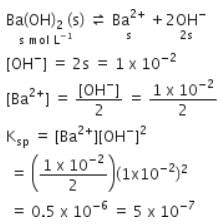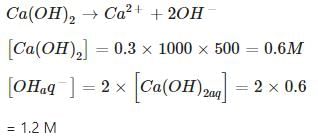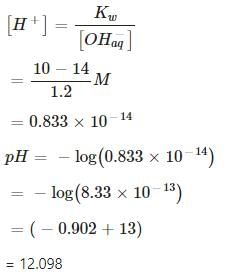Chemistry: Topic-wise Test- 3 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Chemistry: Topic-wise Test- 3
pH of a saturated solution of Ba(OH)2 is 12. The value of solubility product (Ksp) of Ba(OH)2 is
0.3 g of Ca(OH)2 is dissolved in water to give 500 mL of solution. The pH of the solution is
The mass of a gas dissolved in a given mass of a solvent at any temperature is proportional to the pressure of the gas above the solvent.
If Vf is the final volume and Vi is the initial volume and pex the external pressure the work done can be calculated by
Spontaneity in the context of chemical thermodynamics means
Enthalpy of combustion of carbon to CO2is –393.5 kJ mol−1. Calculate the heat released upon formation of 35.2 g of CO2from carbon and dioxygen gas.
The volume of gas is reduced to half from its original volume. The specific heat will
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of polarity
In principle, what is true regarding benzene and 1, 3, 5-cyclohexatriene?
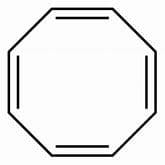
Which is not true regarding 1, 3, 5, 7-cyclooctatetraene?
How many minimum no. of C-atoms are required for position & geometrical isomerism in alkene?
The number of isomers of dibromoderivative of an alkene (molear mass 186 g mol-1) is
Which among the following does not exhibit geometric isomerism?
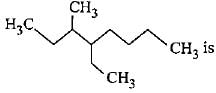
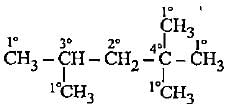
How many primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary carbon atoms are present in the following compound?
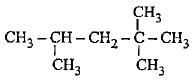
If pKb for fluoride ion at 25°C is 10.83, the ionisation constant of hydrofluoric acid in water at this temperature is :
If K1 & K2 be first and second ionisation constant of H3PO4 and K1 >> K2 which is incorrect.
If 40 ml of 0.2 M KOH is added to 160 ml of 0.1 M HCOOH [Ka = 2 × 10-4]. The pOH of the resulting solution is
The range of most suitable indicator which should be used for titration of X - Na+ (0.1 M, 10 ml) with 0.1 M HCl should be ( Given : kb(X-) = 10-6 )
3 moles of a diatomic gas are heated from 127° C to 727° C at a constant pressure of 1 atm. Entropy change is (log 2.5 = 0 .4)
Given
I. C (diamond) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ; ΔH° = - 91.0 kcdl mol-1
II. C(graphite) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ; ΔH° = - 94.0 kcal mol-1
Q. At 298 K, 2.4 kg of carbon (diamond) is converted into graphite form. Thus, entropy change is
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-14) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q. For an ideal gas, consider only (p -V) work in going from initial state X to the final state Z. The final state Z can be reached either of the two paths shown in the figure. Which of the following choice (s) is (are) correct?
(Take ΔS as change in entropy and W as work done)
[IIT JEE 2012]
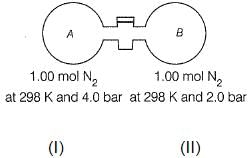
Passage II
The stopcock connecting A and B is of negligible volume. Stopcock is opened and gases are allowed to mix isothermally.
Q. Final pressure set up is