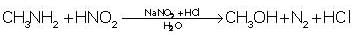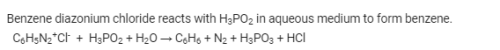Chemistry: Topic-wise Test- 6 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Chemistry: Topic-wise Test- 6
Which of the following electrodes will act as anodes, when connected to Standard Hydrogen Electrode?
A metal in a compound can be displaced by another metal in the uncombined state. Which metal is a better reducing agent in such a case?
In which of the following complexes, the nickel metal is in the highest oxidation state?
Which of the following can be termed as mixed complex?
Which of the following ligand gives chelate complexes?
Arrange the following alcohols, hydrocarbon and ether in order of their increasing boiling points Pentan – 1 – ol, n – butane, pentanal, ethoxyethane.
We can obtain ethylamine by Hoffmann bromamide reaction. The amide used in this reaction is:
Nitro compounds are reduced to amines. The catalyst that is preferred is:
The following reaction takes place in the presence of
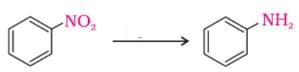
Nitro compounds are reduced by iron scrap and hydrochloric acid to yield one of the following compounds.
Which one of the following is used to increase blood pressure
Aniline on treatment with sodium hypochlorite gives:
Which of the following amine liberates nitrogen gas on reaction with HNO2 ?
Benzene diazonium chloride when reacts with hypophosphorus acid produces
p-amino azo benzene is obtained by treating diazoniumchloride with:
A standard hydrogen electrode has zero electrode potential because



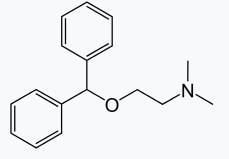
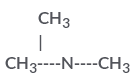 is a tertiary amine having IUPAC name as:
is a tertiary amine having IUPAC name as: