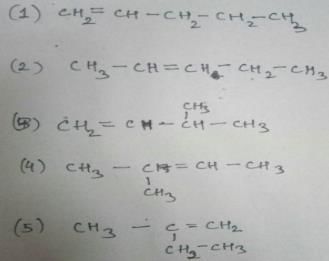Chemistry: Topic-wise Test- 7 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Chemistry: Topic-wise Test- 7
The frequency of light emitted for the transition n = 4 to n = 2 of He+ is equal to the transition in H atom corresponding to which of the following
The maximum number of atomic orbitals associated with a principal quantum number 5 is
The radius of the second Bohr orbit for the hydrogen atom is :
(Planck’s constant, h = 6.262×10-34Js: Mass of electron = 9.1091×10-31kg; Charge of electron e = 1.60210×10-19C; permittivity of vacuum ε0 = 8.854185×10-12kg-1m-3A2)
(Planck’s constant, h = 6.262×10-34Js: Mass of electron = 9.1091×10-31kg; Charge of electron e = 1.60210×10-19C; permittivity of vacuum ε0 = 8.854185×10-12kg-1m-3A2)
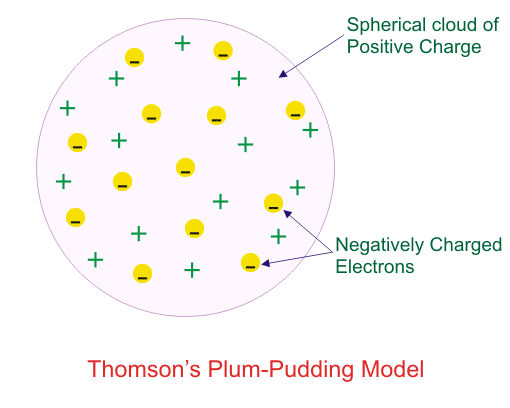
Which model describes that there is no change in the energy of electrons as long as they keep revolving in the same energy level and atoms remains stable?
A sub-shell with n = 6 , l = 2 can accommodate a maximum of
Which of the following conclusions could not be derived from Rutherford’s α -particle scattering experiment?
Passage II
For the following,
Q.
pH of the solution in the half-cell containing 0.02 HA is(HA is a weak monobasic acid)
Passage II
For the following,
Q.
pKa of the weak monobasic acid is
One Integer Value Correct Type
This section contains 3 questions, when worked out will result in an integer value from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q.
For the following cell with metal X electrodes,
Ecell = -0.028 V at 298 K, if there is no liquid juncton potential,valency of X is.......
Passage II
Given molar conductance of 0.001 M NH4OH solution at 298K = 3.0 x 10-3Sm2mol-1.
Limiting molar conductance of
aq. NH4CI = 1.50 x 10-2Sm2mol-1
aq. NaCl = 1.26 x 10-2Sm2 mol-1
and aq. NaOH = 2.48 x 10-2 Sm2 mol-1
Q.
Degree of dissociation of NH4OH at 298 K is
Passage II
Given molar conductance of 0.001 M NH4OH solution at 298K = 3.0 x 10-3Sm2mol-1.
Limiting molar conductance of
aq. NH4CI = 1.50 x 10-2Sm2mol-1
aq. NaCl = 1.26 x 10-2Sm2 mol-1
and aq. NaOH = 2.48 x 10-2 Sm2 mol-1
Q.
pKb of NH4OH is
The internationally recommended unit for conductance is
Matching List Type
Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct
Q.
The standard reduction potential data at 298 K is given below:
Match E° of a redox pair in Column I with the values given in Column II and select the corect answer using the codes given below:
Passage II
Given,
ΔG0f(AgCl) = -109kJmol-1, ΔG0f(Cl-) = -129kJmol-1
ΔG0f(Ag+) = 77kJmol-1,
Thus E°cell of the cell reaction is
Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) → AgCl(s) is
Passage II
Given,
ΔG0f(AgCl) = -109kJmol-1, ΔG0f(Cl-) = -129kJmol-1
ΔG0f(Ag+) = 77kJmol-1,
Q.
Ksp of AgCl is thus,
Using Cr2O72- aqueous, solution
E0red = 1.33V and ΔG0 = -770.07 kJmol-1
What is the valency of the ion formed after reduction?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-18) This section contains 18 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q.
How many diffrent alkenes exist for C5H10 which are structural isomeres ?
Which of the following compounds will exhibit cis-trans isomerism?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-18) This section contains 18 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q.
The correct statement regarding a chiral compound is
The correct statement regarding elements of symmetry and chirality of compound is
The number of optically active optical isomers of the compound is:
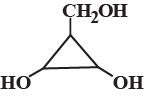
Find the number of stereoisomers for CH3 – CHOH – CH = CH – CH3.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains 13 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q.
Which among the following defines Meso forms of isomers
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 6) This section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q.
A pure enantiomer with molecular formula C6H13OBr, when reacted with PBr3, an achiral product C6H12Br2 is obtained that has no chiral carbon. The compound which satisfy this condition could be (no bond to chiral carbon is broken during the reaction)
Optical rotation of a newly synthesised chiral compound is found to be +60°. Which of the following experiment can be performed to establish that optical rotation is not actually -300°?
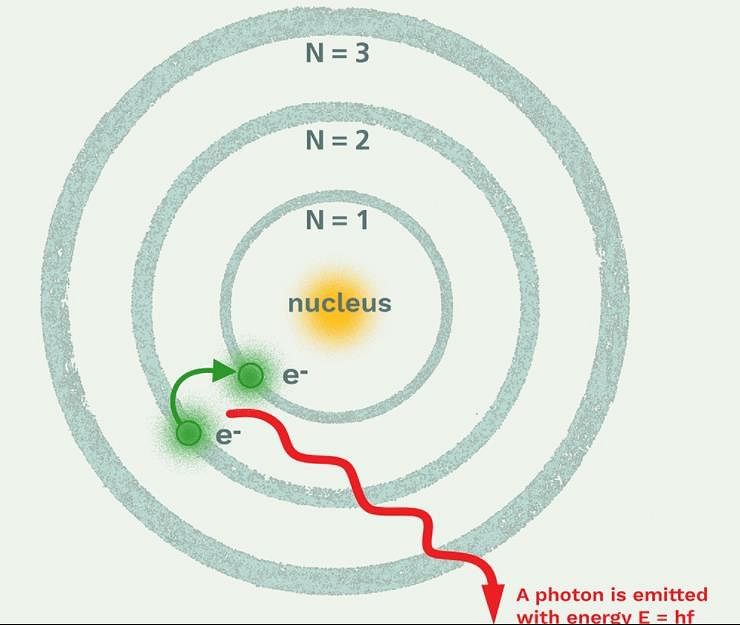
If the ionisation energy of hydrogen atom is 13.6 eV, the energy required to excite it from ground state to the next higher state is approximately
Direction (Q. Nos. 10-14) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c), and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE is correct.
Q.Consider the following molecule
The correct statement concerning the above molecule is/are




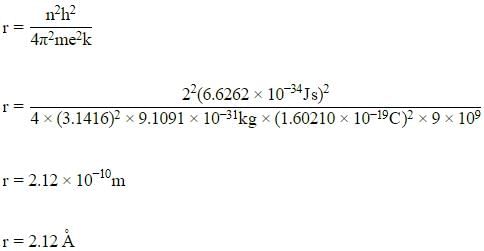
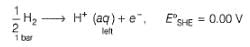
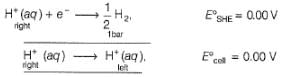
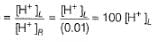

 Ag+ + Cl- E0 = -0.59V
Ag+ + Cl- E0 = -0.59V