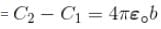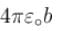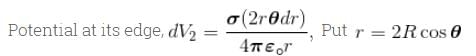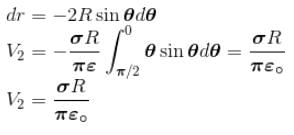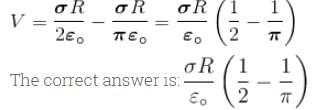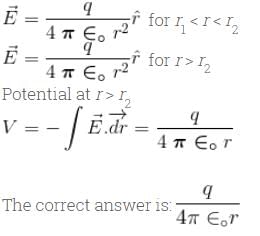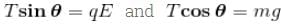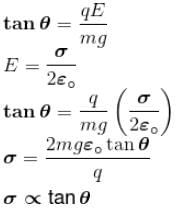Electric Flux And Field Due To Charge Distribution MCQ - Physics MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Topic wise Tests for IIT JAM Physics - Electric Flux And Field Due To Charge Distribution MCQ
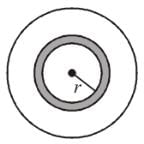
Two concentric sphere of radii R and r have similar charges with equal surface charge density σ. The electric potential at their common centre is
A long string with a charge of λ per unit length passes through an imaginary cube of edge l. The maximum possible flux of electric field through the cube will be
Force of attraction between the plate of a parallel plate capacitor is
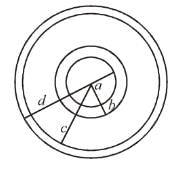
Consider two concentric conducting spherical shell with inner and outer radii a, b, c and d as shown in the figure. Both the shell are given Q amount of positive charges. The electric field in different regions are
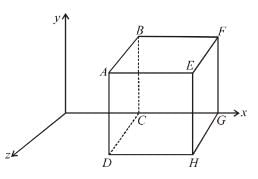
Electric field in the region is given by 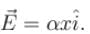 Here, α is a constant of proper dimensions. The total flux passing through a cube bounded by the surfaces x = l , x = 2l, y = 0, y = l, z = 0, z = l.
Here, α is a constant of proper dimensions. The total flux passing through a cube bounded by the surfaces x = l , x = 2l, y = 0, y = l, z = 0, z = l.
A spherical condenser has inner and outer sphere of radii a and b respectively. The space between the two is filled with air. The difference between the capacities of two condensers formed when outer sphere is earthed and when inner sphere is earthed will be
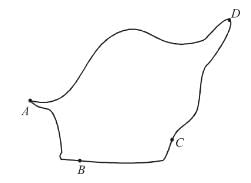
A diagram of an irregularly shaped charged conductor is shown at the right figure. Four location along the surface are labeled A, B, C, D. Rank these locations in increasing order of the strength of their electric field beginning with the smallest electric field.
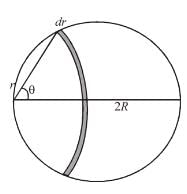
A positively charge non-conducting disc having uniform surface change density α coulomb/m2. The difference in the potential at its centre and at its edge is given by.
A metallic sphere of radius r and carrying a charge q is enclosed by a dielectric shell of thickness δ outer radius r2 and relative permittivity ε The medium elsewhere is air. The potential V(r) for r > r2 is
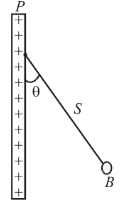
A charged ball B hangs from a silk thread S, which make an angle θ and a large conducting sheet P as shown in the figure. The surface charge density σ of the sheet is proportional to


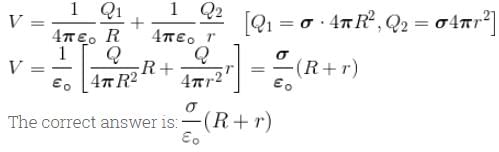
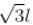
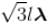
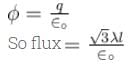
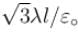


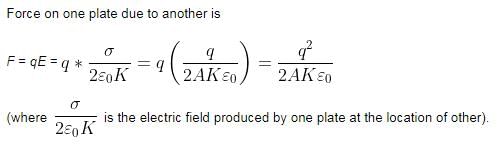
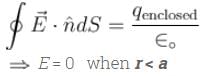

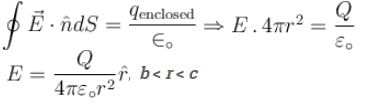
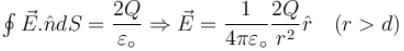
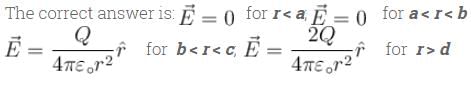
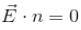 for all the faces as
for all the faces as 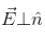
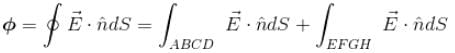
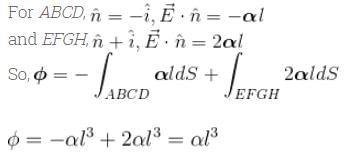
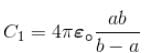
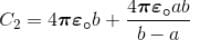 Difference in their capacity
Difference in their capacity