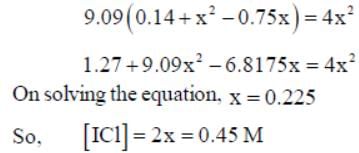Equilibria - Phase, Chemical & Ionic - GATE Chemistry MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test GATE Chemistry Mock Test Series - Equilibria - Phase, Chemical & Ionic
If K < Q. where, K = equilibrium constant.
Q = reaction quotient
The reaction move in which direction to achieve equilibrium
Q = reaction quotient
The reaction move in which direction to achieve equilibrium
For the reaction, 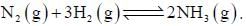 On increasing pressure equilibrium shift to
On increasing pressure equilibrium shift to
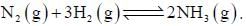 On increasing pressure equilibrium shift to
On increasing pressure equilibrium shift to The effect of which variable is ignored for the study of two-component system
A sample of propane (C3H8) placed in a closed vessel together with an amount of O2, that is 3-times the amount needed to completely oxidize the propane to CO2 and H2O at constant temperature. Calculate the mole of fraction of each component in the resulting mixture after oxidation assuming that the H2O is present as a gas?
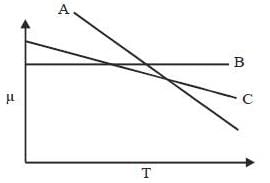
For the below diagram, which statement is correct
A solution is 0.1M in CI- and 0.001M in CrO2-4. If solid AgNO3, is gradually added to this solution, the one which precipitate first is
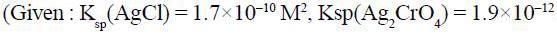
At 39.9°C. a solution of ethanol 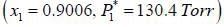 and iso-octane
and iso-octane 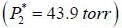 foms a vappour phase with Y1 = 0.6667 at a total pressure of 185.9 torr. The activity coefficient of ethanol is __________ (Hint: X1 = mole fraction in solution, Y1 = mole fraction vapour phase) (Round off to two decimal places).
foms a vappour phase with Y1 = 0.6667 at a total pressure of 185.9 torr. The activity coefficient of ethanol is __________ (Hint: X1 = mole fraction in solution, Y1 = mole fraction vapour phase) (Round off to two decimal places).
Phase-diagram that shown below represents the congruent melting point. Which of the following statements are not correct?
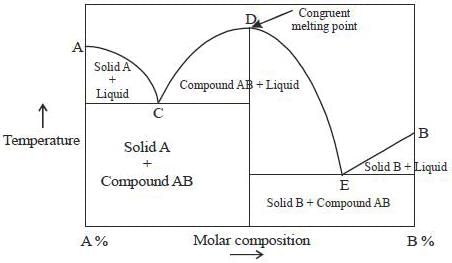
(A) There will be three freezing point curves
(B) Congruent melting point always lies above the melting point of pure components
(C) Congruent melting point diagram always contains equimolar amounts of A and B
(D) There are two eutectic point (in above figure)
In an ideal solution of A and B 3.50 mol are in the liquid phase and 4.75 mol are in the gaseous phase. The overall composition of the system is ZA = 0.300 and XA = 0.250. The mole fraction in vapour phase of YA is ____________(round off to two decimal places).
The degree of freedom for a two component system, at congruent melting point is
For an indicator, the value of pH is 2 when half of the indicator is present in unionised form. The percentage of indicator in unionised form in a solution of 4.0x10-3 M hydrogen ion concentration is
For a system A (s) + B(g)  C(l) + D(s). The number of phases are
C(l) + D(s). The number of phases are
A solution is made-up of 184.2g of ethanol and 108.1 g of H2O, if the volume of the solution is 333.4 cm3 and the partial molar volume of H2O, is 17 cm3. What is the partial molar volume of ethanol under these conditions?
The number of component for the reaction,
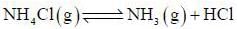
in vacuum is
The pH of a solution made by adding 0.001 mole of NaOH to 100cm3 of a solution which is 0.50 M in CH3COOH and 0.50 M in CH3COONa is _________________ (pkCH3cooH = 4.744) (Round off to two decimal places).
The vapour pressure of solid and liquid chlorine is given by
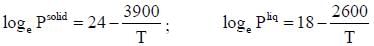
where Psolid and p liquid are vapour pressure (in Torr) of solid and liquid chlorine near the triple point absolute temperature. The ratio of slope of solid-gas curve to the slope of liquid-gas curve at the trip the P-T diagram is ______(Round off to one decimal places).
At a certain temperature, kC = 0.11 for the reaction,
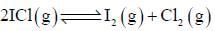
The equilibrium concentration of IC1 if 0.75 mole of I2 and 0.75 mol of CI2 are initially mixed in 2L flask is ___mol/L. (Round off to two decimal places).
|
20 docs|37 tests
|



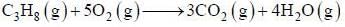
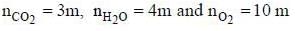
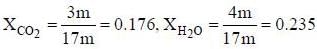
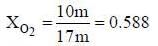
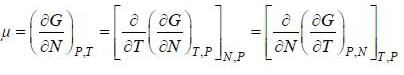
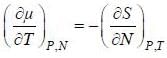
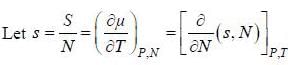
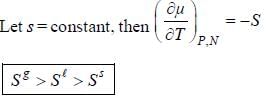
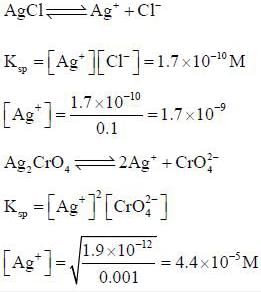
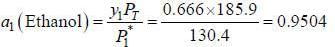
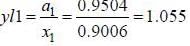
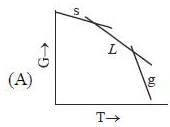
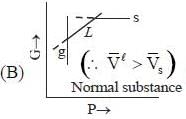
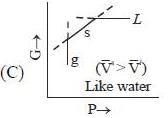
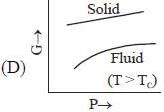
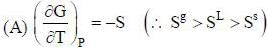
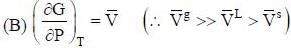
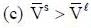 ( a temperature lower than the triple point temperature)
( a temperature lower than the triple point temperature)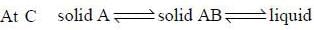
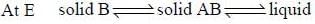
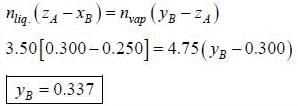
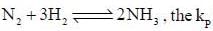 is expressed as
is expressed as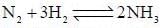
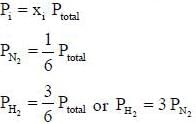
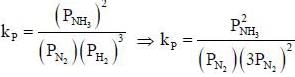

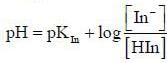
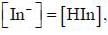 pH = 2
pH = 2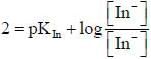
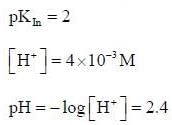
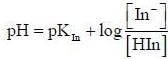
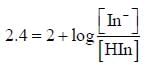
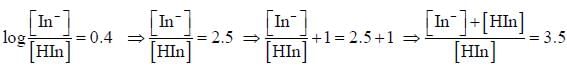
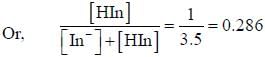
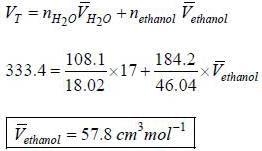
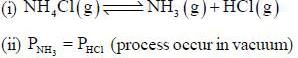

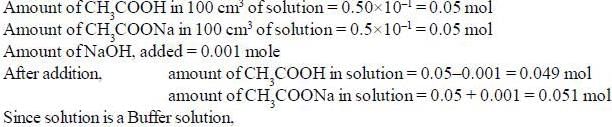
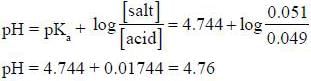
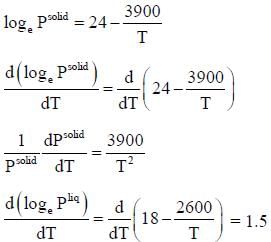
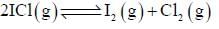 kc = 0.11
kc = 0.11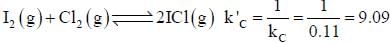

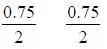 0
0