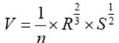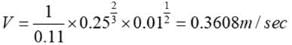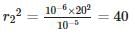GATE Architecture and Planning Mock Test - 10 (Architecture) - GATE Architecture and Planning MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - GATE Architecture and Planning Mock Test - 10 (Architecture)
A man traveling at a speed of 30 km/hr arrives at his destination 10 minutes late, whereas if he travels at 42 km/hr, he arrives 10 minutes early. What is the distance that he travels ______?
Rational individuals manage to live _____ their financial means. (Use the correct Preposition)
Select the word or phrase that you believe is closest in meaning to the term: Discern
A vehicle can operate on two different fuels, A and B. When using fuel A, it can cover 200 km using 10 litres over a duration of 5 hours. Fuel B provides an additional average of 2 km per litre compared to A, although the speed decreases by 25%. It is also possible to use a combination of both fuels, where the speed and fuel efficiency are directly proportional to the quantities of each fuel in the mixture. Given that 1 litre of fuel A is priced at Rs.20 and 1 litre of fuel B at Rs.25, what is the minimum expenditure required for the car to travel 212 km utilizing 10 litres of fuel within a time limit of less than 6 hours and 25 minutes?
Which of the following does not represent a method related to the environmental aspect of sustainability?
BMS is responsible for overseeing and managing a building's mechanical and electrical systems. What does BMS represent?
In Hazen William's Nomogram, the term 'loss of head' is associated with which of the following?
According to the 2011 Census of India, non-notified slums are classified as:
Which of the plans should not be consulted regarding land ownership?
Which of the following books is/are associated with urban design?
Statement I - The act of preservation involves maintaining something in its existing condition.
Statement II - Adaptive reuse refers to the process of repurposing a historic building for functions different from its original use.
Which of the following represents the traits of Good Governance?
The vertical difference in invert levels of two pits that are 25 meters apart horizontally is 550 mm. If the gradient between the pits is represented as 1 in ‘n’, what is the value of ‘n’? (Round your answer to two decimal places)
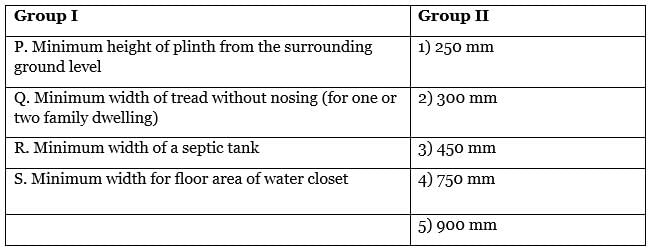
Align the requirements of the components of a Building listed in Group I with their corresponding standards according to NBC 2016 from Group II.
Which of the following does NOT qualify as a magnet in the urban model proposed by Ebenezer Howard?
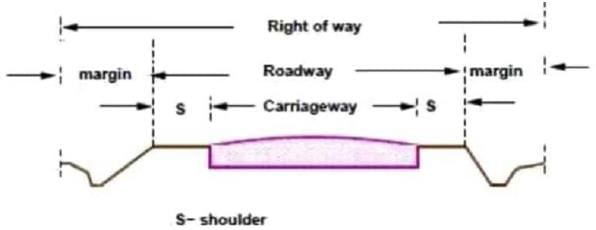
Which of the following constitutes the component(s) of the Right of Way (RoW) for a roadway?
According to the National Building Code of India 2016, what are the terminologies related to firefighting within a building?
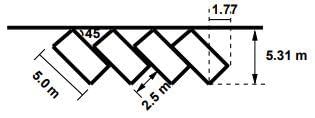
Given the standard dimensions of a car according to the IRC, how many vehicles can be accommodated in a 45-degree parking configuration along a curb that measures 44.25 meters in length?
A project’s critical path consists of three tasks, A, B, and C. The optimistic time estimates for A, B, and C are 1, 2, and 3 weeks, respectively. The pessimistic time estimates for B and C are 14 and 15 weeks, respectively. The most likely time estimate and expected completion time estimate for A are 1 and 2 weeks, respectively. What is the standard deviation of the critical path in weeks?
A plot of agricultural land yields a total annual rent of 72,000 Rupees. Given that the years’ purchase is 10 years and the total annual expenses amount to 8,000 Rupees, what will be the capitalized value of the land parcel, measured in lakh rupees? Please provide your answer rounded to two decimal places.
A stormwater drain with a semi-circular cross-section has a radius of 50 cm and is installed at a slope of 1 in 100. Given a Manning’s roughness coefficient of 0.11, what is the flow velocity in the open stormwater drain, in m/sec, _______ [Rounded-off to two decimal places]
A site plan of a building indicates a terrace area of 10 sq. cm. The runoff coefficient for the terrace's top surface is 0.8. The average rainfall measured at the building's location is 80 cm/hr. Given that the scale of the site plan is 1 : 700, calculate the total volume of water collected from the terrace (in cubic meters) due to continuous rainfall over a period of 72 minutes.
How much parking space (in ECS) is required for a cinema hall in Delhi, which has a built-up area of 5000 Sq. m, given that the parking standard for cinemas is 1.67 ECS for every 100 square meters of built-up area? (up to one decimal)
The velocity head (in meters) for a flow with a velocity of 20 m/sec will be ________. [Assuming the acceleration due to gravity is 10 m/sec2]
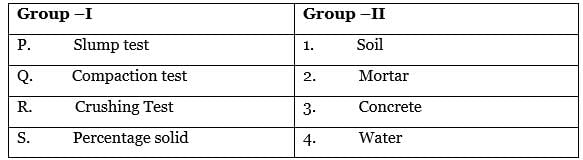
Pair the test from Group – I with the corresponding construction material in Group - II.
Which of the following pairs are matched correctly?
Which of the following factors does the rate of ventilation rely on?
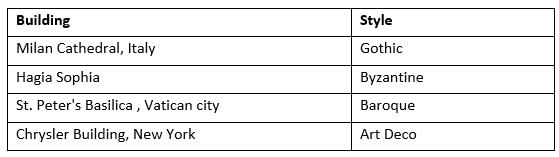
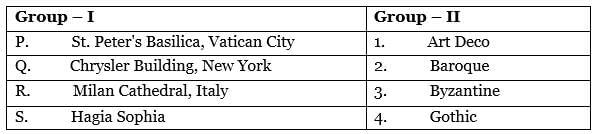
Identify the buildings in Group – I and match them with their corresponding architectural styles in Group - II.
What is the shear force at point C, measured in N?
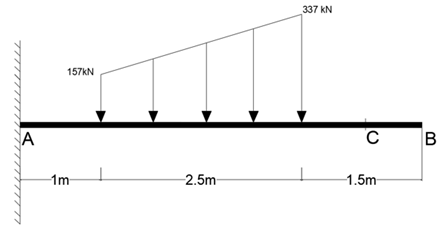
(Provide your answer as a whole number)
A sound source positioned at point B generates an intensity level of 60 dB at point A. The separation between points A and B is 20 meters. What is the distance from point B at which the source needs to be placed, along the line connecting B and A, in order to achieve an intensity level of 70 dB? (Round your answer to two decimal places)


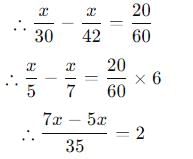

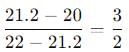
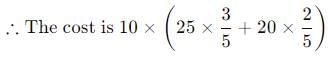
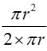 = r/2 = 25 cm = 0.25cm
= r/2 = 25 cm = 0.25cm