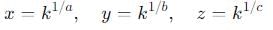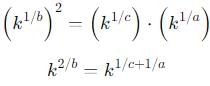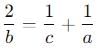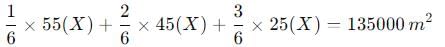GATE Architecture and Planning Mock Test - 3 (Planning) - GATE Architecture and Planning MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - GATE Architecture and Planning Mock Test - 3 (Planning)
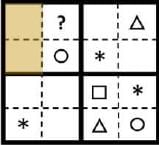
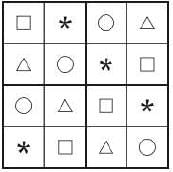
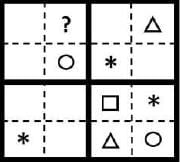
The symbols Ο, ✱, △, and □ are to be filled, one in each box, as shown below. The rules for filling in the four symbols are as follows.
- Every row and every column must contain each of the four symbols.
- Every 2×2 square delineated by bold lines must contain each of the four symbols.
Which symbol will occupy the box marked with ‘?’ in the partially filled figure?

Planting is to Seed as Raising is to _____ (By word meaning)
If xa = yb = zc and y2 = z x, then what is the value of (1 / a + 1 / c)?
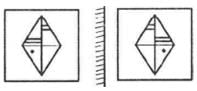
What will the reflection of the figure shown below look like?
4. Problem figure
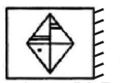
Answer Figures
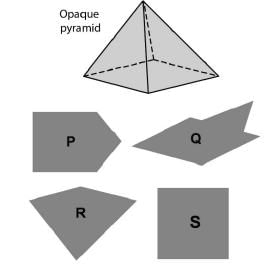
A non-transparent pyramid (illustrated below) features a square base and isosceles triangular faces. It is positioned in the path of a parallel light beam, casting a shadow onto a screen that is perpendicular to the light's direction. The pyramid can be adjusted to face any direction within the beam of light. Given these conditions, which of the shadows P, Q, R, and S is NOT achievable?
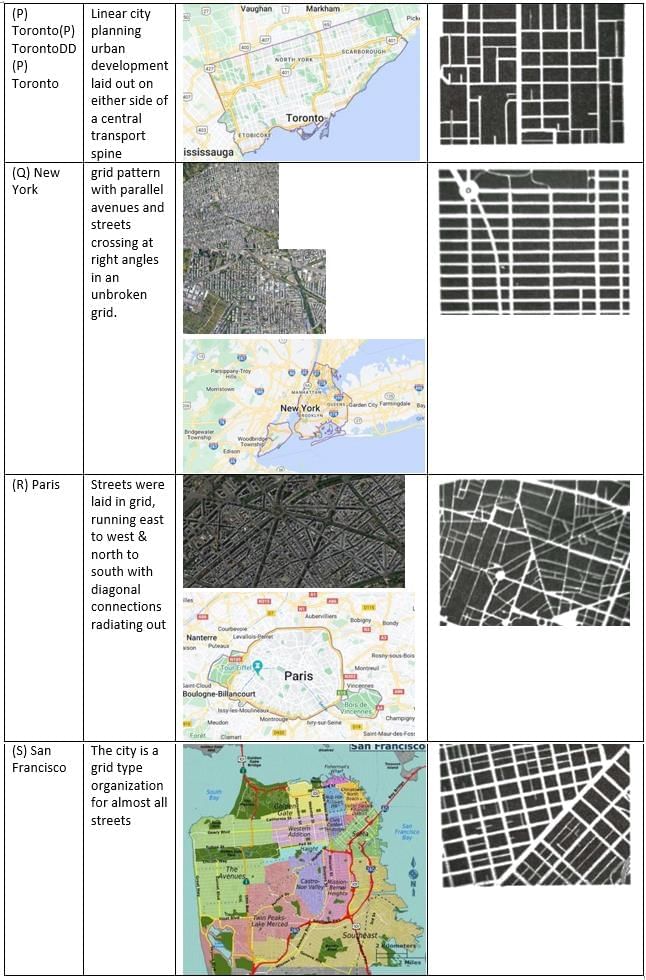
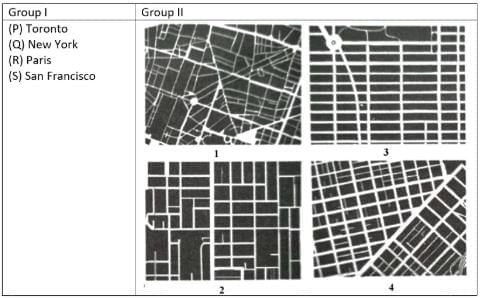
Pair the cities listed in Group I with their corresponding figure-ground representations in Group II.
According to the National Building Code, the minimum height for a kitchen should be no less than ____
According to the Burra Charter (2013), 'Cultural Significance' refers to __________ for past, present, or future generations.
Lowry’s Metropolis model (1964) incorporates two _____________ models of spatial interaction.
Identify the Act that specifies a prohibited zone of 100 m surrounding centrally protected monuments in India.
What is the hydraulic radius (in mm) of a full-flowing circular pipe with a diameter of 450 mm?
Determine the volume of air needed (in cubic meters per minute) to eliminate 400 p.p.m of B.O.D from 10 million liters of sewage daily.
A housing development project covers a total land area of 50 hectares, with the portions allocated for community facilities, common open spaces, and roads being 8%, 25%, and 15% respectively. The total number of saleable plots, each measuring 260 sq m, will be ______.
In a construction project, typically 50% of the overall project expenditure is associated with
The Sustainable Development Goal 10, which is supported by the UN, aims to address:
Which of the following statements are accurate concerning PERT, the tool used for project management planning?
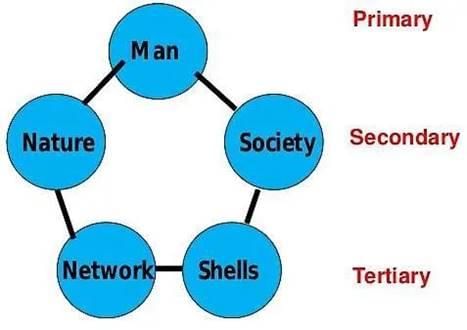
Which of the following principles are included in the four fundamental concepts of Ekistics?
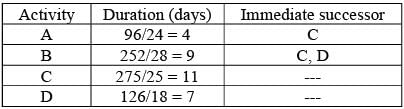
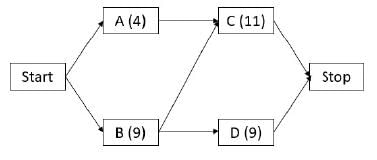
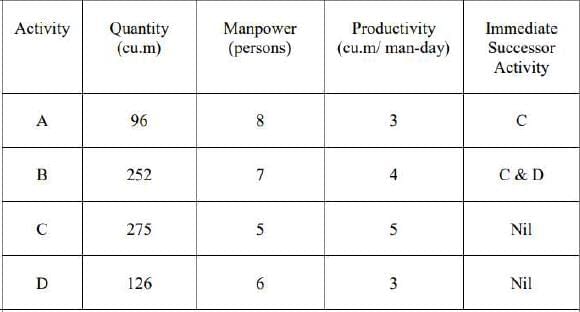
A construction undertaking involves four distinct activities. The details regarding the amount of work, required manpower, and productivity levels for each activity are outlined in the table below. Additionally, the interdependencies among these activities are provided in the same table. The commencement date for the construction project is January 29. Assume that there will be no holidays throughout the project's duration. The completion date of the project will be February _____ [insert date in numeric form].
In a particular town, the yearly precipitation measured is 400 mm. Rainwater is collected from the flat roof of a structure, treated to meet potable standards, and then stored. The water losses occurring due to evaporation, transmission, and treatment amount to 40 percent of the total volume harvested. The area of the roof is 500 sq.m. There are 3 residents, with an average daily water requirement of 200 liters per person per day (lpcd). The amount of collected rainwater will sustain the household's daily usage for ________ days [in integer].
A residential development is planned on a plot of land measuring 1 hectare. The parking area for vehicles is evenly divided between the ground floor and the basement. Based on the information provided below, the total number of cars that can be accommodated in the basement will be ____________ [in integer].
Data:
FAR utilized = 2.0
The car parking area is excluded from the built-up area for FAR calculations.
One parking space is allocated for every 100 sq.m of built-up area.
Space needed for each car on the ground floor = 15 sq.m
Space needed for each car in the basement = 25 sq.m
If earth excavation is performed manually, the cost is Rs. 120 per cubic meter (cum). In contrast, a machine incurs a fixed expense of Rs. 40,000 along with a variable cost of Rs. 20 per cum for excavation. Determine the volume of earth (in cum) for which the excavation cost using the machine will match the cost incurred through manual excavation.
A primary school consists of 8 classrooms, each with internal dimensions measuring 15m × 10m × 4m (height). Only the internal walls of all classrooms will be painted. It is assumed that there will be a 10% deduction from the internal wall area due to doors, windows, and other openings. The specifications recommend applying two coats of paint. The coverage rates for the chosen paint during the base coat and finish coat are 4.5 l/sq.m and 2.5 l/sq.m, respectively. The total amount of paint (in liters) necessary for this task will be _______ [in integer]
A housing development is planned on a site measuring 4.5 hectares. The maximum allowable Floor Area Ratio (FAR) is 3, and the highest permitted ground coverage is 55%. The distribution of dwelling units (DU) for Middle Income Group (MIG), Lower Income Group (LIG), and Economically Weaker Sections (EWS) follows a ratio of 1: 2: 3, with respective sizes of 55, 45, and 25 square meters. What is the maximum number of DUs that can be accommodated on the site?
The concentration of MLSS in an aeration tank is 2000 mg/l, and after 30 minutes of settling in a 1000 ml graduated cylinder, the sludge volume measures 180 ml. What will be the approximate value of the sludge density index (SDI) (in gm/ml)?
Which of the following represents the National Electronic Toll Collection System that has been established by the National Payment Corporation of India?
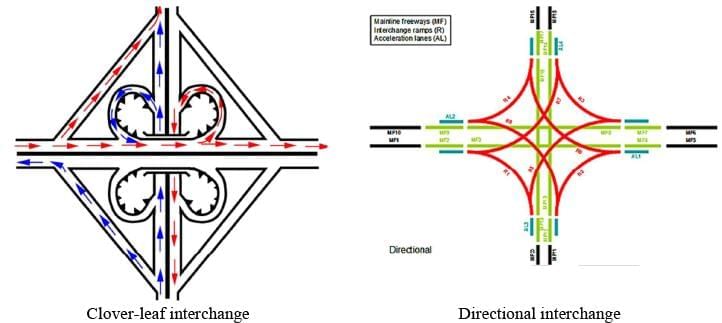
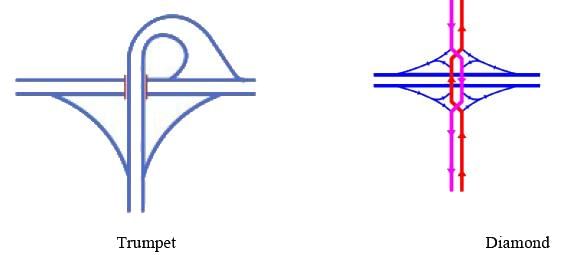
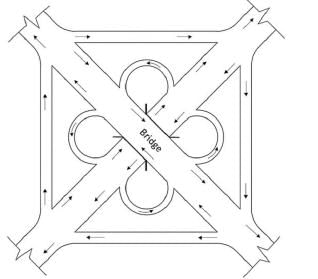
Determine the type of traffic interchange depicted in the image below.
Which of the following represents the model(s) of Public-Private Partnership (PPP) utilized for infrastructure projects?
The proper sequence of the processes involved in the 'Four step travel demand model' is
(i) Trip generation
(ii) Mode choice
(iii) Trip distribution
(iv) Traffic assignment
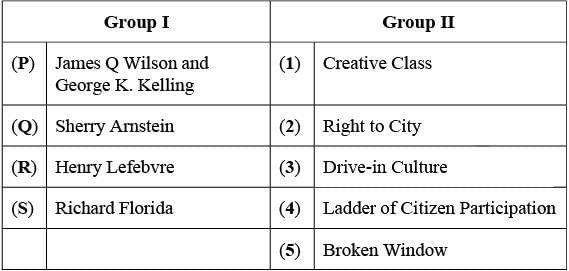
Relate the individuals in Group I to their respective theories in Group II.
A property owner has expressed interest in a Town Planning Scheme. According to the information provided in the following Table, the projected Net Benefit to the property owner following land development (in Indian Rupees, as an integer) is ____.