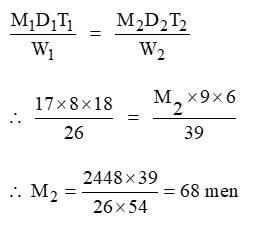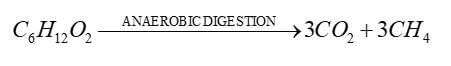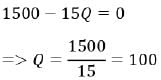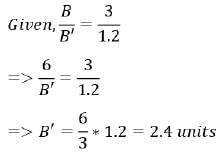GATE Architecture and Planning Mock Test - 8 (Planning) - GATE Architecture and Planning MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - GATE Architecture and Planning Mock Test - 8 (Planning)
If an ascending order of intensity is indicated, then the relationship between the terms [sick → infirm → moribund] is similar to that of [silly → _______ → daft].
Which of the provided options is most suitable to complete the blank?
Which of the provided options is most suitable to complete the blank?
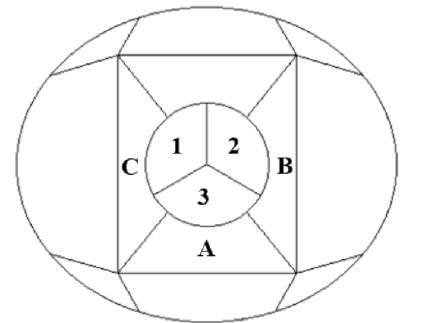
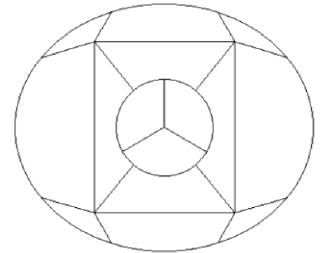
The 15 sections of the illustrated figure need to be colored in such a way that no two adjacent sections sharing boundaries (excluding corners) have the same color. What is the minimum number of colors that are required?

What is the reflection of the text shown above with respect to the x-axis?

If 17 men can excavate a ditch that is 26 m long in 18 days while working for 8 hours each day, how many additional men are required to dig a ditch that is 39 m long in 6 days, assuming each man works for 9 hours daily?
The phrase ‘turn marketing on its ear’ could be substituted with which of the following?
What is meant by the term gentrification?
In the activated sludge process, the combination of untreated wastewater and activated sludge found in the aeration tank is known as:
The concept of ‘Anastylosis’ in the context of preserving ancient structures pertains to:
A water basin is a component of
According to the Census of India, 2011, the population of a Class I city must be no less than:
The measurement unit for the Damp-proof course in the construction of buildings is
Which gases are generated during the anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge?
Which of the following combinations represent the fundamental principles for creating an urban built environment that is friendly to people?
Which combination of colour coding for urban land uses is/are correct according to URDPFI?
Which of the following abbreviations are matched correctly?
Identify the options in which the definitions related to Urban Design are accurately stated.
Identify the options in which the theories or concepts related to urban planning are accurately matched with their respective authors or theorists.
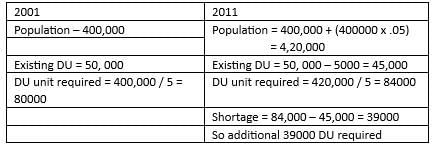
In the year 2001, a town had a population of 4,00,000 and 50,000 housing units. If by 2011, 5,000 dwelling units will become uninhabitable, determine the extra number of dwelling units (DU) needed by 2011 to avoid a housing shortage. Assume a 5% decadal increase in population and a household size of 5.
A university campus covering 100 hectares allocates 25% of its area for student accommodation, 30% for staff residences, and 15% for major roadways (with 50% of the roadways located within the academic zone). The campus supports 6000 students and 2000 faculty and staff members, each with an average family size of 5.0. Calculate the overall residential population density of the campus in dwelling units per hectare.
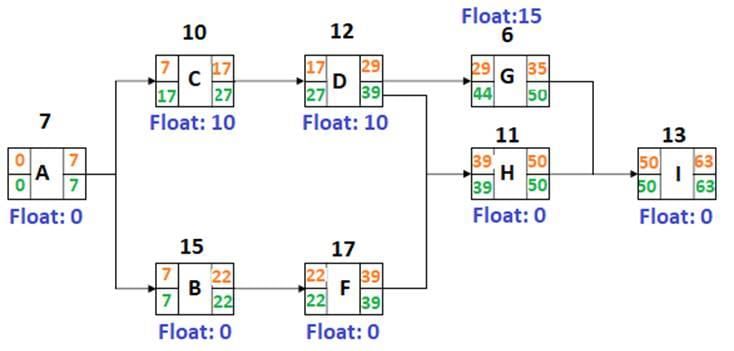
The table below outlines the details of the activities involved in a project.
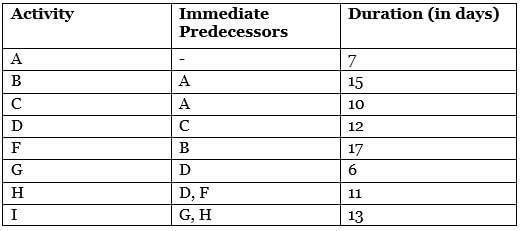
The total float for activity ‘G’, measured in days, will be ______
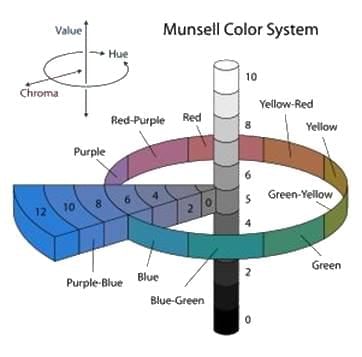
In the Munsell colour system, the value assigned to Grey on the central axis is ______.
A cuboidal building has dimensions of 50m in length, 30m in breadth, and 4m in height. The front facade features a structural glazing area of 50m x 4m. The remaining three sides of the walls require painting with enamel paint. The area that needs to be painted is _________(Answer in whole number)
The most optimistic duration, the least optimistic duration, and the duration considered most probable for a task are 5, 14, and 6 days respectively. What is the variance associated with this task?
Determine the abbreviation that has been inaccurately listed for the terms associated with project delivery methods.
Who holds the authority to approve the perspective plan?
An area represented on a map with a scale of 1: 16000 has a measurement of 82 sqcm. What is the corresponding actual area of this site in hectares?
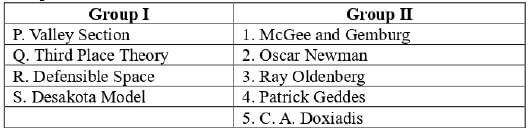
Pair the planning theories/concepts listed in Group-I with their respective proponents in Group-II.
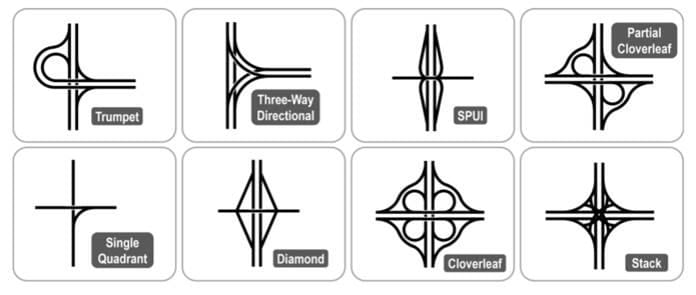
Which of the following graphical depictions of road junctions are NOT accurately labeled?
The estimated demand for a EcoCity theme park is given by the equation P = 1500 - 7.5Q, where P (in Indian Rupees) represents the price of a single entry ticket, and Q (as an integer) indicates the number of tickets sold each hour. What is the maximum revenue per hour along the demand curve, expressed in Indian Rupees, represented as _____________ (in integer)?
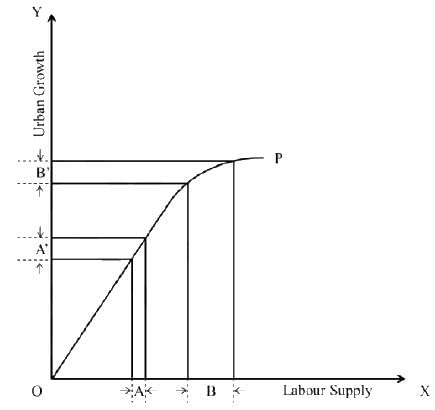
The relationship between labour supply and urban growth is illustrated on the X and Y axes in the figure below. Curve OP depicts this relationship. The ratios A : A’ and B : B' are 1 : 1.2 and 3 : 1.2, respectively. If 6 units of labour are provided at point B, what will be the corresponding units of urban growth at B' _____________ (rounded to one decimal place)?