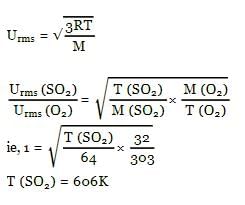Gaseous - Thermodynamic - Thermochemistry - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Gaseous - Thermodynamic - Thermochemistry
For one mole of an ideal gas, increasing the temperature from 10°C to 20°C ______.
With increase of pressure, the mean free path:
At what temperature the RMS velocity of SO2 be same as that of O2 at 303 K
An ideal gas obeying kinetic theory of gases can be liquefied if:
For the process
H2O(l) → H2O(g)
At T = 100°C and 1 atmosphere pressure, the correct choice is:
One mole of a monoatomic ideal gas expands adiabatically at initial temperature T against a constant external pressure of 1 atm from 1L to 3L. The final temperature of the gas is:
The enthalpies of combustion of carbon and carbon monoxide are –393.5 and –283 kJ mol–1, respectively. The enthalpy of formation of carbon monoxide per mole is:
The Maxwell's relationship derived from the equation dG = VdP – SdT is:
For a closed system consisting of a reaction N2O4(g) → 2NO2(g), the pressure:
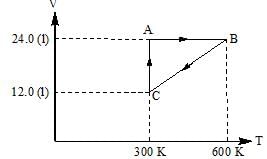
One mole of an ideal gas is put through a series of changes as shown in the graph in which A, B, C mark the three stages of system. Calculate the pressure at three stages of the system & provide the sum value (PA + PB + PC)
If at 298 K the bond energies of C—H, C—C, C=C and H—H are, respectively, 414, 347, 615 and 435 kJ mol–1, the value of enthalpy change for the reaction CH2=CH2(g) + H2(g) → H3C—CH3(g) at 298 K will be:
2 mole 'He' is mixed with 2gm of H2. The molar heat capacity at constant pressure for mixture is:
An ideal gas is allowed to expand both reversibly and irreversibly in an isolated system. If Ti is the initial temperature and Tf is the final temperature, which of the following statement is correct:
An inventor claims to have constructed an engine that has an efficiency of 75% when operated between the boiling and freezing points of water. Which of the following is true?
If C1, C2, C3........ represent the speeds of n1, n2, n3....... molecules, then the root mean square speed is:
A bubble of air is underwater at temperature 15°C and the pressure 1.5 bar. If the bubble rises to the surface where the temperature is 25°C and the pressure is 1.0 bar, what will happen to the volume of the bubble?
0.5 mole of each of H2, SO2 and CH4 are kept in a container. A hole was made in the container. After 3 hours, the order of partial pressures in the container will be:
Volume of air that will be expelled from a vessel of 300 cm3 when it is heated from 27oC o 37oC at the same pressure will be
Two separate bulbs contain ideal gases A and B. The density of gas A is twice that of gas B. The molecular mass of A is half that of gas B. The two gases are at the same temperature. The ratio of the pressure of A to that of gas B is:
The molar entropy of crystalline CO at absolute zero is:
The plot that describes a Carnot cycle is:
The rate of evaporation of a liquid is always faster at a higher temperature because:
For the process,
1 Ar (300 K, 1 bar) → 1Ar (200 K, 10 bar) assuming ideal gas behaviour, the change in molar entropy is:
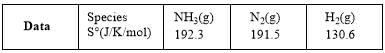
For the reaction, N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
Compute the entropy change (in J/K/mol) for the process and comment on the sign of the property.
For the reaction,
2Cl(g) → Cl2(g)
The thermodynamic properties
The standard enthalpies of formation of CO2(g), H2O(l) and glucose(s) at 25°C are –400 kJ mol–1,
–300 kJ mol–1 and –1300 kJ mol–1, respectively. The standard enthalpy of combustion per gram of glucose at 25°C is:
For an ideal gas, which of the following is true:
Assuming that water vapour is an ideal gas, the internal energy change (∆U) when 1 mol of water is vaporized at 1 bar pressure and 100°C will be (given that molar enthalpy of vaporisation of water at 1 bar and 373 K is 41 kJ mol–1 K–1)
For a system of constant composition, the pressure (P) is given by: