HP Judicial Services (Prelims) Mock - 3 (Criminal Law) - Judiciary Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - HP Judicial Services (Prelims) Mock - 3 (Criminal Law)
How many types of punishments have been prescribed under the Indian Penal Code, 1860?
A instigates B to instigate C to murder Z. B accordingly instigates C to murder Z and C commits that offence in consequence of B's instigation. A is liable:
For an assembly to be unlawful, it must have a common object of the kind specified in:
In which of the following cases is the offence of 'house-breaking' committed?
Consider the following statements.
(a) Every murder is culpable homicide.
(b) Every culpable homicide is murder.
(c) Every robbery is either theft or extortion.
(d) Every extortion is robbery.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
'A' was sentenced to a fine of rupees one thousand and in case of default, to suffer simple imprisonment for six months. He did not pay the fine and was taken in custody. After six weeks, an amount of rupees one hundred was realised through warrant for recovery and he further deposited rupees four hundred, the balance remaining unpaid. 'A' would be
Which of the following options correctly represents the above statement?
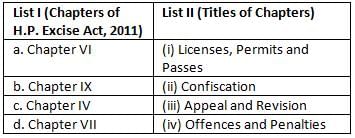
Match List I with List II and give the correct answer by using the codes given below:
'A' & 'B' orally agree to sell an estate. 'A' dishonestly induces 'B' to make advance payment of Rs.5 lacs and make final payment at the execution of conveyance. 'B' pays advance amount. Later on, at the request of 'B' to execute the conveyance, 'A' denies the agreement as well as the receipt of any amount. What offence has been committed by 'A'?
'A' shoots at 'B' with intention to kill him. 'B' survives from the injury. Here 'A' is liable under Indian Penal Code for the offence of














