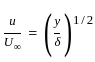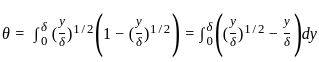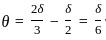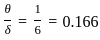HPCL Civil Engineer Mock Test - 2 - HPSC (Haryana) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - HPCL Civil Engineer Mock Test - 2
A and B enter into a partnership, with A putting in three times what B has put in. However, B is the working partner and entitled to a salary of Rs. 50,000 per month to be paid from the gross profit, which is in addition to his share of the profit. If the gross profit at the end of the year is Rs. 30 lakh, what is the total money received by B?
In this question, two statements are followed by two conclusions, numbered I and II. Find out which conclusion (s) is / are definitely true, based on the given statements.
Statement : D > B ≥ W, Y > W > M
Conclusions :
I. B ≥ M
II. M < D
Which of the following options is sixth to the left of the nineteenth letter from the left in a forward alphabet series?
Select the most appropriate option that can substitute the underlined words in the given sentence.
The new restaurant is more better than the old one.
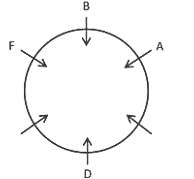
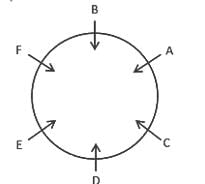
A, B, C, D, E and F are at a restaurant sitting around a circular table. D is sitting is opposite to B and second to the left of A. F is a neighbour of B. E is not a neighbour of A. Who is sitting second to the left of C?
Two pipes A and B can fill a tank in 10 hours and 15 hours respectively. Another pipe C can empty the same tank in 18 hours. Pipes A and C are opened together for the first hour and followed by pipe B alone for an hour alternatively. Find the time taken (in hours) to fill the empty tank.
Select the option that can be used as a one-word substitute for the underlined group of words.
Ms. Scarlet was indifferent to pain and pleasure, she never complained.
A sum of money becomes Rs. 39930 in 3 years and Rs. 36300 in 2 years when kept at compound interest (compounding annually). What is the sum?
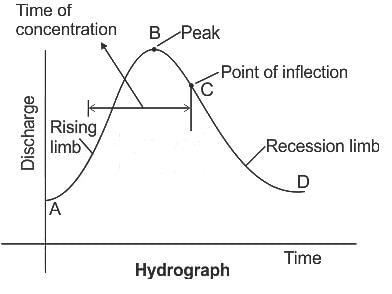
Which of the following statement is correct for Hydrograph?
A) It is the graphical representation of measured discharge of stream.
B) Discharge is plotted in abscissa.
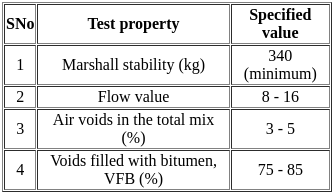
Consider the following criteria for the Marshall mix design for bituminous concrete
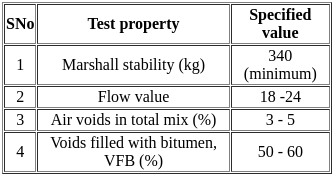
Which of the design criteria is/are true?
A 4-hours rainfall in a catchment of 250 km2 produces rainfall depths of 6.2 cm and 5.0 cm in successive 2-hour unit periods. Assuming the φ index of the soil to be 1.2 cm/hour, the runoff volume in ha-m will be
Indian Standards classifies bitumen into grades such as 65/25, 85/40 etc. The first and second numbers respectively represent:
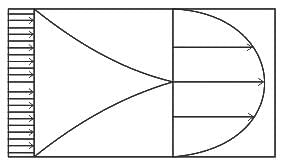
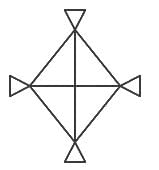
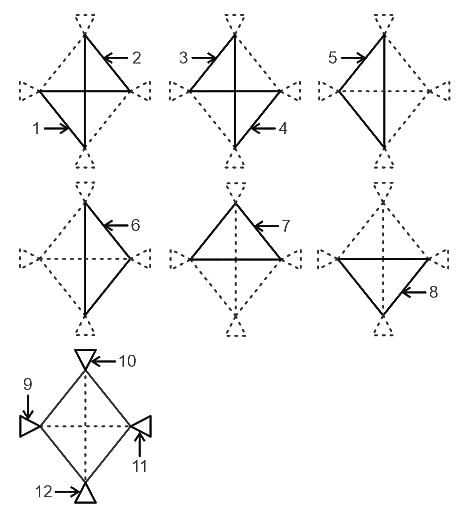
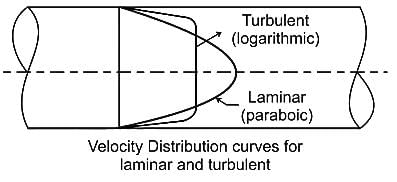
What can definitely be said about the tube-flow in the diagram below?
What is the ratio of momentum thickness to the boundary layer thickness δ when the layer velocity profile is given by 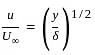
Where u is velocity at height y above surface and 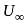 is free stream velocity of flow.
is free stream velocity of flow.
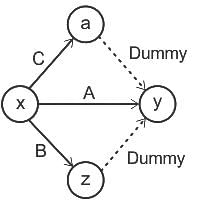
There are three parallel paths in a part of a network between a bursting node and the next merging node with only one activity in each path. The minimum number of dummy arrows needed will be
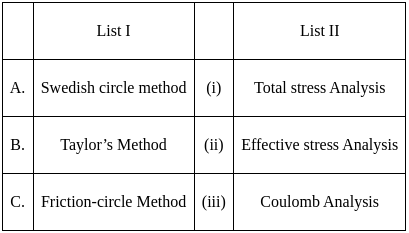
Match List I (Method of finite slope analysis) with List II (basis of these methods) and select the correct code from the list given:
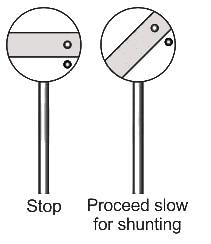
In railways, the disc signals are provided for the purpose of:


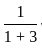 =
= 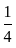
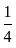 = Rs. 6 lakh.
= Rs. 6 lakh.
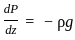

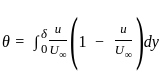
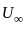 is free stream velocity of flow
is free stream velocity of flow