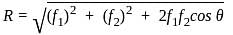HPCL Civil Engineer Mock Test - 3 - HPSC (Haryana) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - HPCL Civil Engineer Mock Test - 3
If mode of a series exceeds its median by 10 then mode exceeds the mean by:
Two persons start running towards each other, one from A to B and the other from B to A. They cross each other in one hour. The first person reaches B 16/15 hours before the second person reaches A. If the distance between A and B is 8 km, then find the speed of the faster man.
In a single throwing of a dice, the probability of getting more than 4 is 1/3 then probability of getting 4 or less than 4 will be
Three statements are given, followed by three conclusions numbered I, II and III. Assuming the statements to be true, even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts, decide which of the conclusions logically follow(s) from the statements.
Statement :
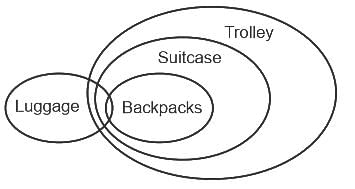
All backpacks are suitcase.
All suitcases are trolley.
Some Backpacks are Luggage.
Conclusions:
(I) Some Suitcases are Luggage.
(II) Some Backpacks are Trolley.
(III) All Trolleys are Luggage.
In the question given below Statement is followed by two arguments I and II. You have to decide which of the arguments is a 'strong' argument:
Statement: Should a cricket team have more than one captain during a match?
Arguments:
(I) No one needs to make decisions on the spot and there won't be time to resolve conflicting ideas between the captains on the field if such a scenario emerges.
(II) Yes, it is always better to have more brains coming to an understanding before taking a decision.
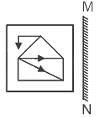
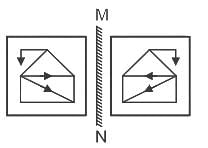
Select the correct mirror image of the given figure which will be formed when the mirror is placed on MN as shown below.
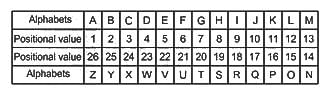
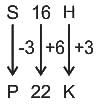
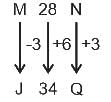
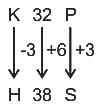
S16H is related to P22K in a certain way. In the same way, M28N is related to J34Q. To which of the following is K32P related following the same logic?
Directions: Select the most appropriate ANTONYM of the given word.
Sabotage
Read the question below followed by two statements and decide which statement(s) is/are sufficient to answer the question.
Question:
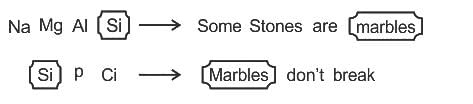
How is 'MARBLES' coded in the code language?
Statements:
I. 'Na Mg Al Si' means 'Some stones are marbles' and 'Si P CI' means 'Marbles don't break'.
II. 'Na Mg Al Si' means 'Some stones are marbles' and 'Si Al Ar' means 'Marbles are strong'.
Select the word-pair in which the two words are related in the same way as are the two words in the given pair.
Hole : snakeA question is given, followed by two statements labelled I and II. Identify which of the statements is/are sufficient to answer the question.
Question:
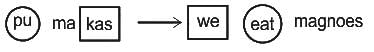
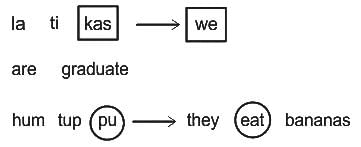
In a certain code language, "pu ma kas' means 'we eat mangoes'. What is the code of 'mangoes'?
Statements:
I. 'la ti kas' means 'we are graduate'.
II. 'hum tup pu' means 'they eat bananas'.
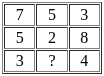
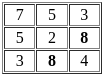
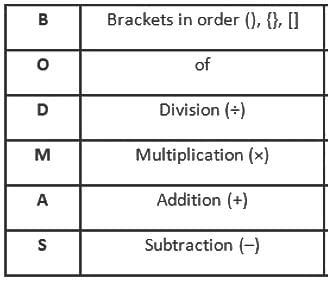
The value of 60 ÷ 16 × 2 - [76 ÷ 5 of 19 - 15 ÷ 8 × (21 - 25) - 3] ÷ 53 is:
Choose the word that means the same as the given word.
Edacious
Study the given bar graph and answer the question that follows.
The bar graph shows the production of table fans in a factory during one week.
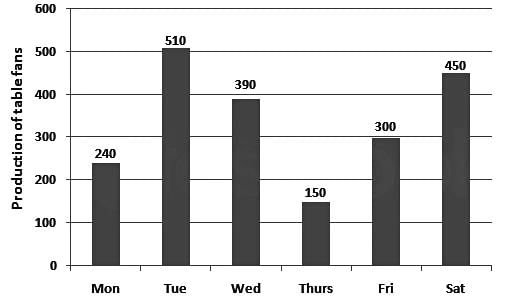
The average production of table fans on Friday and Saturday exceeds the average production of table fans during the week by:
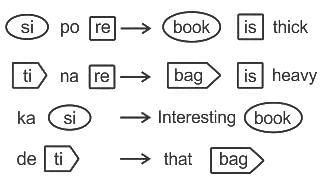
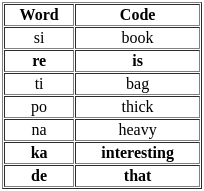
In a certain code language, ‘si po re’ means ‘book is thick’, ‘ti na re’ means ‘bag is heavy’, ‘ka si’ means ‘interesting book’ and ‘de ti’ means 'that bag’. What should stand for ‘that is interesting’ in that code language?
Which two numbers (not the digits of the numbers) and two signs should be interchanged to make the given equation correct?
19 - 2 + 4 ÷ 5 × 4 = 27
Direction: In the following question assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion among given some conclusion is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly:
Statements:
M ≥ Z ≥ B > R < T ≤ V
Conclusions:
I. M > R
II R < V
The domestic sewage of a town was tested for total solids and following results were obtained :
Weight of sample of sewage =1000 gm
Weight of solids after evaporation of liquid = 0.952 gm
Weight of dry residue after ignition = 0.516 gm
Then Weight of Volatile Solids after Ignition = ?
In case of unequal angle section oriented with longer leg vertical, axis parallel to shorter leg of the angle and passing form centroid of cross-section is______
During the analysis of bars of composite sections as shown in the given figure. The modular ratio is defined as ________.
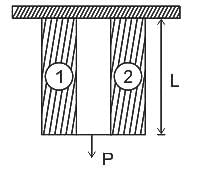
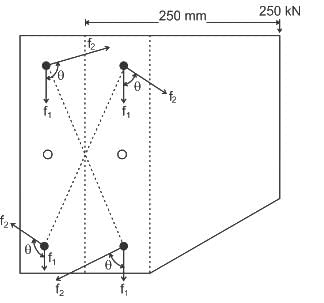
The rivets in an eccentrically loaded riveted joint are shown in figure below,
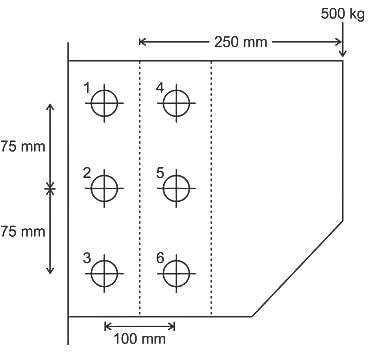
Which rivets will be stressed to maximum?
According to IS 456: 2000, What is the permissible stresses (N/mm2) in steel reinforcement for mild steel bars under compression in column




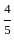 -
- 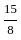 × -4 - 3] ÷ 53
× -4 - 3] ÷ 53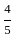 +
+ 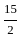 - 3] ÷ 53
- 3] ÷ 53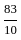 - 3] ÷ 53
- 3] ÷ 53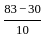 ] ÷ 53
] ÷ 53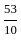 ] ÷ 53
] ÷ 53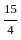 × 2 -
× 2 - 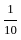
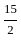 -
- 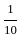
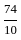 =
= 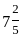
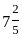 .
.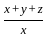
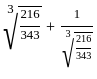
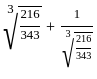
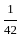
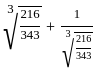 is 2
is 2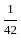
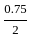 times the area of reinforcement provided the mid-span in the same direction shall be provided.
times the area of reinforcement provided the mid-span in the same direction shall be provided.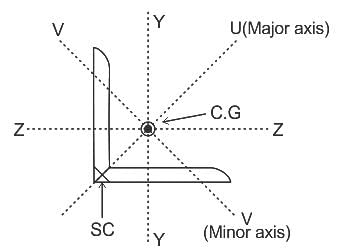
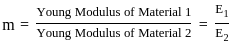
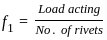
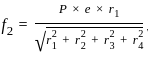 for rivet 1 and similarly for other rivets by changing r2, r3 and r4 in the numerator.
for rivet 1 and similarly for other rivets by changing r2, r3 and r4 in the numerator.