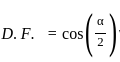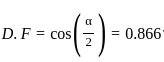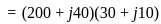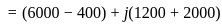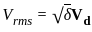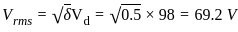HPCL Electrical Engineer Mock Test - 3 - PSSSB Clerk MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - HPCL Electrical Engineer Mock Test - 3
The perimeter of a triangle is 36 cm and the inradius of the triangle is 5.5 cm. Then the area of the triangle is:
A road roller takes 750 complete revolutions to move once over to level a road. The diameter of the road roller is 84 cm and its length is 1 m. Then, the area of the road, that is being levelled, is: [ use π = 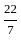 ]
]
The following series is provided and you need to answer the question accordingly:
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P R S T U V W X Y Z
In this series find the letter which is fifth to the left from the thirteenth letter from your right.
Choose the word that is opposite in meaning to the given word.
Ignominy
Directions: Each item in this section has a sentence with three underlined parts, labelled as (a), (b) and (c). Read each sentence to determine whether there is any error in any underlined part and indicate your response on the Answer Sheet against the corresponding letter, i.e., (a) or (b) or (c). If you find no error, your response should be indicated as (d).
He suffered (a)/ from fever when he was interviewed (b)/ for the job. (c)/ No error (d)
Directions: Each item in this section has a sentence with three underlined parts, labelled as (a), (b) and (c). Read each sentence to determine whether there is any error in any underlined part and indicate your response on the Answer Sheet against the corresponding letter, i.e., (a) or (b) or (c). If you find no error, your response should be indicated as (d).
The politicians (a)/ parted ways (b)/ due towards ideological differences. (c)/ No error (d)
R, N, O, W, Q and C are sitting around a circular table facing inside the center. R is sitting immediately to the left to the W, who is facing O, O is sitting immediately to the left to the N. C is not an immediate neighbor of W. Who is sitting to the left of Q?
The following question consists of a statement followed by two arguments I and II. You have to decide which of the arguments is a STRONG argument:
Statement: Should new big industries be started in Mumbai?
Arguments:
I. Yes. It will create job opportunities.
II. No. it will further add to the pollution of the city.
Find the missing numbers (X and Y) in the series and find the value of Y + X:
20, 22, 24, 26, X, 32, 36, Y
If 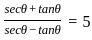 and θ is an acute angle, then the value of
and θ is an acute angle, then the value of 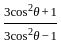 is:
is:
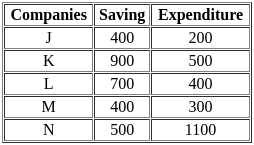
The table given below shows the saving and expenditures of 5 companies.
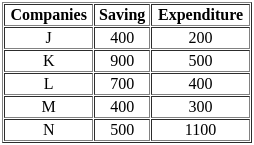
The total expenditure of all the companies is how much percent less than the total savings?
Choose the word that means the same as the given word.
Edacious
Without warning, the volcano _______ a large amount of ash, forcing the residents to _______ the area.
Read the question below followed by two statements. Study them and decide which statement(s) is/are sufficient to answer the question.
Question: P, Q, R, S, and T have different heights. Who among the following is tallest?
Statements:
I) Neither P nor R is the tallest. S is taller than P.
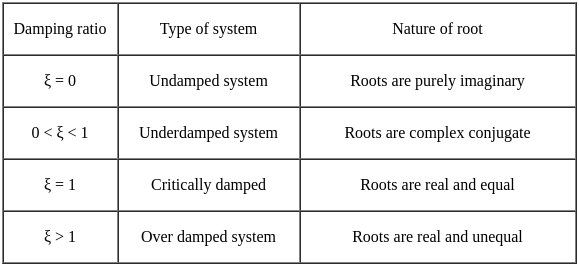
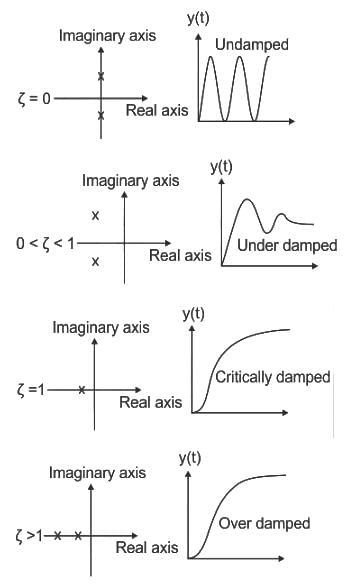
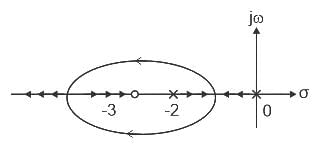
II) P is taller than R and T. S is taller than Q who is not shorter than P.The root locus of the open loop transfer function G(s)H(s) = 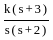 is
is
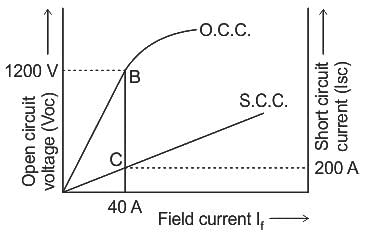
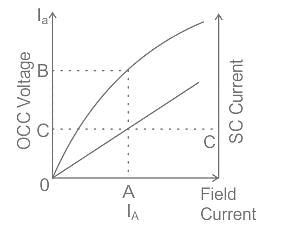
The effective resistance of a 2200-V, 50-Hz, 440-kVA, 1-phase alternator is 0.5 Ω. On short circuit, a field current of 40 A gives a full load current of 200 A. The open circuit EMF for the same field excitation is 1200 V. Find the synchronous impedance.
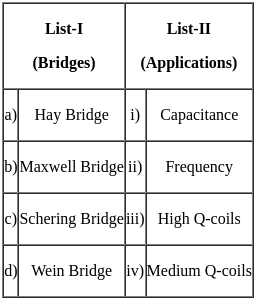
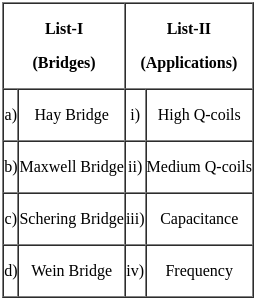
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer from the following options :

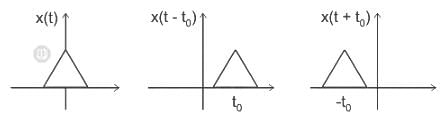
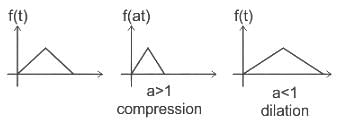
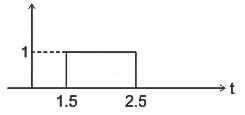
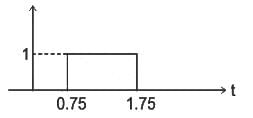
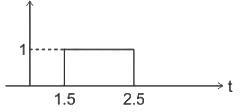
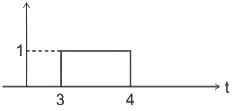
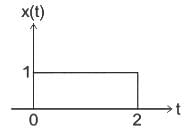
Identify the signal x(2t - 3) given x(t) as
A single-phase semi-converter is operated from 120 V, 50 Hz AC supply at a firing angle of α degrees. The load is such that the load current is continuous and ripple-free. The displacement factor of the converter is 0.866. Then the value of sin α is _______.
Match List-I (Power device) with List-II (Property) and select the correct answer:

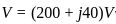 and
and 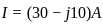 . The active and reactive power of the circuit are respectively
. The active and reactive power of the circuit are respectively





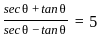
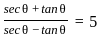
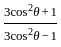
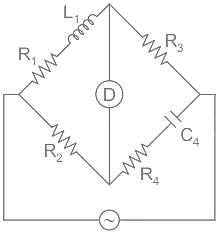
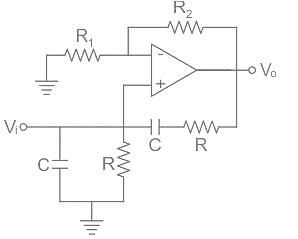
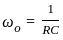
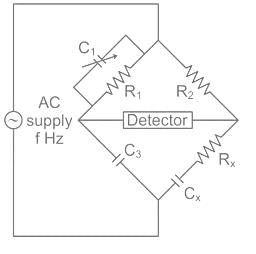
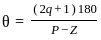
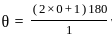
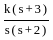
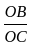 Ω
Ω