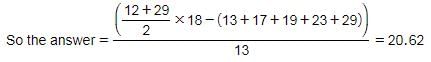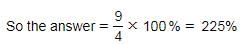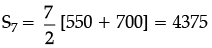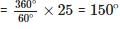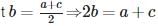HTET TGT Maths Mock Test - 2 - HTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - HTET TGT Maths Mock Test - 2
If you are planning to conduct an exam particularly for the backward children, then the exam would be
You have been regularly noticing in the classroom that there exists an individual difference among your students. Being a teacher, what should be your role in meeting the individual differences?
"A young child responds to a new situation on the basis of the response made by him/ her in a similar situation as in the past". This is related to:
Assertion (A): A teacher records the pace of development of the students in his class, and finds that the pace of development is not equal for all the students.
Reason (R): Development varies from person to person because it follows the principle of individual differences.
Which of the following is NOT a form of non-discursive communication?
Choose the correct meaning of the given proverb/idiom.
To make clean breast of
In questions given below out of four alternatives, choose the one which can be substituted for the given word/sentence.
Q. A person pretending to be somebody he is not
Directions to Solve
In each of the following questions find out the alternative which will replace the question mark.
Question -
8 : 24 :: ? : 32
What is the average of all the composite numbers between 11 and 30?
A, B and C can complete a work in 40, 20 and 90 days respectively. The efficiency of A is what percentage of the efficiency of C?
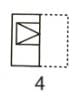
Direction: If a Paper (Transparent Sheet) is folded in a manner and a design or pattern is drawn. When unfolded this paper appears as given below in the answer figure. Choose the correct answer figure given below.
Find out from the four alternatives as how the pattern would appear when the transparent sheet is folded at the dotted line.
Question Figure

Read the following text and answer the following questions.
A manufacturer of TV sets produced 600 sets in the third year and 700 sets in the seventh year, assuming that the production increases uniformly by a fixed number every year.
Q. Find the total production in the first 7 years.
Find the measure of the angle which is complement of itself.
If x + 2 is a factor of x3 – 2ax2 + 16, then value of a is
In the adjoining figure, the side AC of ABC is produced to E such that CE = 1/2 AC. If D is the midpoint of BC and ED produced meets AB at F, and CP, DQ are drawn parallel to BA, then FD is
Find the greatest number of 5 digits, that will give us remainder of 5, when divided by 8 and 9 respectively.
The positive solution of equation ax + by + c = 0 always lie in the:
The marks obtained by 9 students in Mathematics are 59, 46, 30, 23, 27, 44, 52, 40 and 29. The median of the data is
A beam 9 m long, 40 cm wide and 20 cm deep is made up of iron which weighs 50 kg per cubic metre.
The weight of the beam is :
The angle described b the minute hand between 4.00 pm and 4.25 pm is
The 11th and 13th terms of an AP are 35 and 41 respectively, its common difference is
If a, b and c are in A.P., then the relation between them is given by
The maximum number of zeroes that a polynomial of degree 3 can have is