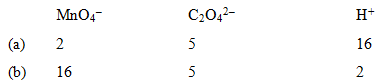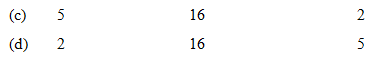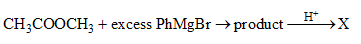IIT JAM Chemistry - MCQ Test 5 - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - IIT JAM Chemistry - MCQ Test 5
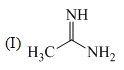
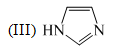
The order of basicity among the following compounds is:
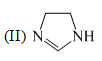
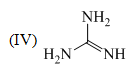

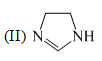

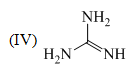
The rate of the reaction A → products, at the initial concentration of 3.24 × 10–2 M is nine times its rate at another initial concentration of 1.2 × 10–3 M. The order of the reaction is:
For the reaction the value of rate of disappearance of 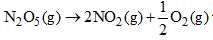 is given as 6.25 × 10–3 mol L–1S–1. The rate of formation of NO2 and O2 is given respectively as:
is given as 6.25 × 10–3 mol L–1S–1. The rate of formation of NO2 and O2 is given respectively as:
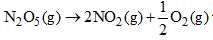 is given as 6.25 × 10–3 mol L–1S–1. The rate of formation of NO2 and O2 is given respectively as:
is given as 6.25 × 10–3 mol L–1S–1. The rate of formation of NO2 and O2 is given respectively as:In the synthesis of ammonia by Haber process, if 60 moles of ammonia is obtained in one hour, then the rate of disappearance of Nitrogen is:
For a first order reaction A → P, the temperature (T) dependent rate constant (k) was found to follow the equation 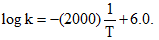 The pre-exponential factor A and the activation energy Ea, respectively, are:
The pre-exponential factor A and the activation energy Ea, respectively, are:
In the case of alkali metals, the covalent character decreases in the order:
Which of the following does not illustrate the anomalous properties of lithium
Which of the following sulphates have the highest solubility in water:
The element that does not show catenation among the following p-block elements is:
A quantity of 0.50 mole of an ideal gas at 20°C expands isothermally against a constant pressure of 2.0 atm from 1.0 L to 5.0 L. Entropy change of the system is:
Given the molecular formula of the hexa-coordinated complexes (A) CoCl3.6NH3 (B) CoCl3.5NH3 (C) CoCl3.4NH3. If the number of coordinated NH3 molecules in A, B and C respectively are 6, 5 and 4 the primary valency in (A), (B) and (C) are:
Which one of the following statement for order of reaction is not correct:
t1/4 can be taken as the time taken for the concentration of a reactant to drop to 3/4 of its initial value. If the rate constant for a first order reaction is K, the t1/4 can be written as:
The compound that undergoes decarboxylation most readily under mild condition is:
Consider the acidity of the carboxylic acids:
(I) PhCOOH
(II) o-NO2C6H4COOH
(III) p-NO2C6H4COOH
(IV) m-NO2C6H4COOH
Which of the following order is correct:
Starting with one mole of a compound A it is found that the reaction is 3/4th complete in one hour. If the reaction is first order, the rate constant is:
Find the organic acid produced from the below reaction:
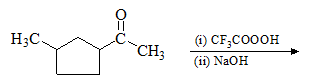
The diketone 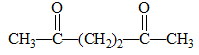 on intramolecular aldol condensation gives the final product.
on intramolecular aldol condensation gives the final product.
Which of the following does not have optical isomer
Which of the following complex ions is expected to absorb visible light:
The reaction [Fe(CNS)6]3– → [FeF6]3– takes place with
The crystal field stabilization energy (CFSE) is the highest for:
An optically active compound having molecular formula C8H16 on ozonolysis gives acetone as one of the products. The structure of the compound is:
The major organic product formed from the following reaction:
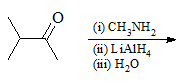
For the redox reaction
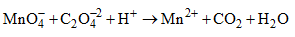
The correct coefficients of the reaction for the balanced reaction are: