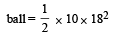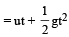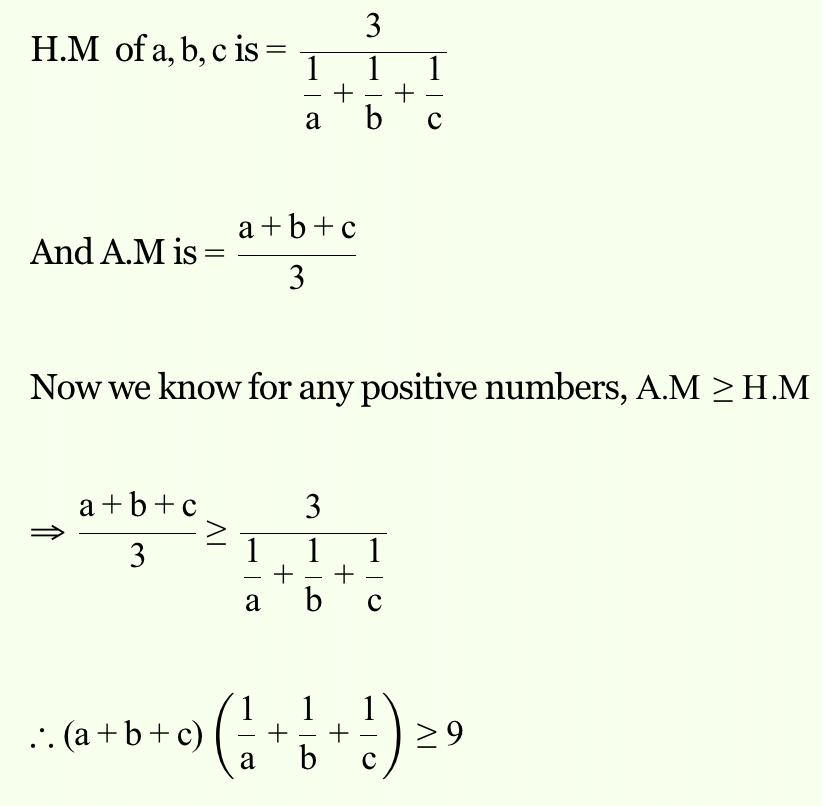Indian Air Force Agniveer Science Subject Mock Test - 6 - Indian Air Force Agniveer Vayu MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Indian Air Force Agniveer Vayu Group X Mock Test Series 2025 - Indian Air Force Agniveer Science Subject Mock Test - 6
Who discovered ultra-short radio waves?
A ball is dropped from a high rise platform at t = 0 starting from rest. After 6 seconds another ball is thrown downwards from the same platform with a speed v. The two balls meet at t = 18s.What is the value of v? [2010] (take g = 10 m/s2)
Two billiard balls A and B. each of mass 50 g and moving in opposite directions with speed of 5 m s-1 each, collide and rebound with the same speed. The impulse imparted to each ball is
All the points of a rigid body rotating about the given axis have same :
Which of the following represents Hooke’s Law?
In which of the following processes is heat transfer equal to zero?
Hot coffee in a thermos flask is shaken vigorously, considering it as a system which of the statement is not true?
Which of the following is not correct about cyclotron?
Emission line spectra of different elements
Which of the following is the universal gate?
The distance of the point (3, 4, 5) from X-axis is:
If the coefficients of (r +1)th term and (r + 3)th term in the expansion of (1+x)2n be equal then
The distance between the parallel lines 3x + 4y + 13 = 0 and 3x + 4y – 13 = 0 is
The equation of circle of radius 5 units touches the coordinates axes in the second quadrant is:
Determine the direction cosines of the normal to the plane and the distance from the origin. Plane z = 2
The slope of the tangent to the curve x = a sin t, y = a at the point ‘t’ is
If a, b, c be any three positive numbers, then the least value of (a + b + c) 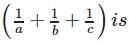
Read the each sentence to find out whether there is any grammatical error in it. The error, if any will be in one part of the sentence. The letter of that part is the answer. If there is no error, the answer is 'D'. (Ignore the errors of punctuation, if any).
Civilisation means outward….(21)… whereas culture means inward perfection. We may be…(22)...today, but we are not cultured. We have trains, aeroplanes and all the modern modes and ….(23).. . This is…(24)…on the road of materialism but we have lost our finer emotions. Civilisation has…..(25)…mystery and romance out of the heart of nature and …..(26)… her beauty and magic. It has placed…..(27)….power in the hands of man, making him a….(28)….. With a single atom or hydrogen bomb, he can rain death and ..(29)…… in millions of innocent creatures. Thus, he is out to….(30)…..himself with his own hands.
Q. Find the word most appropriate for Blank No. 29
Civilisation means outward….(21)… whereas culture means inward perfection. We may be…(22)...today, but we are not cultured. We have trains, aeroplanes and all the modern modes and ….(23).. . This is…(24)…on the road of materialism but we have lost our finer emotions. Civilisation has…..(25)…mystery and romance out of the heart of nature and …..(26)… her beauty and magic. It has placed…..(27)….power in the hands of man, making him a….(28)….. With a single atom or hydrogen bomb, he can rain death and ..(29)…… in millions of innocent creatures. Thus, he is out to….(30)…..himself with his own hands.
Find the word most appropriate for Blank No. 30
Recently discovered gravitational lensing around certain proximate stars stronglysuggests that the nine planets of our solar system are a common phenomenonin the universe rather than developing incidentally from a unique galactic phenomenon several billion years ago.
Directions: Rearrange the following five sentences in the proper sequence to form a coherent paragraph, and then answer the question given below.
(i) If no evil had existed in this world, man would never have dreamt of those numerous divinities to which he has rendered such various modes of worship.
(ii) The man, always contented, would only have occupied himself with satisfying his wants; with enjoying the present, with feeling the influence of objects, that would unceasingly warn him of his existence in a mode that he must necessarily approve; nothing would alarm his heart; everything would be analogous to his existence.
(iii) These feelings can only be the consequence of some troublesome sensation, which must have previously affected him, or which by disturbing the harmony of his machine, has interrupted the course of his happiness; which has shown him he is naked.
(iv) He would neither know fear, experience distrust, nor have in quietude for the future.
(v) If nature had permitted him easily to satisfy all his regenerating wants, if she had given him none but agreeable sensations, his days would have uninterruptedly rolled on in perpetual uniformity; he would never have discovered his own nakedness.
Q. Which of the following should be the FIFTH sentence after rearrangement?
Directions: Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
There is now no denying that the new government takes office amid a clear economic slowdown. The first macro data set released showed an under-performing economy with GDP growth falling to 5.8% in the fourth quarter of 2018-19 and pulling down the overall growth for the fiscal to a five-year low of 6.8%. Growth in gross value added (GVA), which is GDP minus taxes and subsidies, fell to 6.6% in 2018-19, pointing to a serious slowdown. If further confirmation were needed, the growth in core sector output — a set of eight major industrial sectors — fell to 2.6% in April, compared to 4.7% in the same month last year. And finally, unemployment data, controversially suppressed by the Union government so far, showed that joblessness was at a 45-year high of 6.1% in 2017-18. These numbers highlight the challenges ahead in drafting the Budget for 2019-20. The economy is beset by a consumption slowdown as reflected in the falling sales of everything from automobiles to consumer durables, even fast-moving consumer goods. Private investment is not taking off, while government spending, which kept the economy afloat during the last NDA government, was cut back in the last quarter of 2018-19 to meet the fiscal deficit target of 3.4%.
The good news is that inflation is undershooting the target and oil prices are on the retreat again. But the rural economy remains in distress, as seen by the 2.9% growth in agriculture last fiscal; the sector needs a good monsoon this year to bounce back. Overall economic growth in the first quarter of this fiscal is likely to remain subdued, and any improvement is unlikely until the late second quarter or the early third. There are not too many options before the new Finance Minister. In the near term, she has to boost consumption, which means putting more money in the hands of people. That, in turn, means cutting taxes, which is not easy given the commitment to rein in the fiscal deficit. In the medium term, Ms. Sitharaman has to take measures to boost private investment even as she opens up public spending again. These call for major reforms, starting with land acquisition and labour, corporate taxes by reducing exemptions and dropping rates, and nursing banks back to health. On the table will be options such as further recapitalisation of the ailing banks, and consolidation. The question, though, is where the money will come from. With tax revenues likely to be subdued owing to the slowdown, the Centre will have to look at alternative sources such as disinvestment. There may be little choice but to go big on privatisation. A rate cut by the Reserve Bank of India, widely expected this week, would certainly help boost sentiment. But it is the Budget that will really set the tone for the economy
Q. Which of the following, as per the passage, indicate a slowdown in the Indian economy?
I. Fall in sale levels of consumer durables
II. Negative growth in the core sector output
III. Fall in inflations levels
Directions: Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
There is now no denying that the new government takes office amid a clear economic slowdown. The first macro data set released showed an under-performing economy with GDP growth falling to 5.8% in the fourth quarter of 2018-19 and pulling down the overall growth for the fiscal to a five-year low of 6.8%. Growth in gross value added (GVA), which is GDP minus taxes and subsidies, fell to 6.6% in 2018-19, pointing to a serious slowdown. If further confirmation were needed, the growth in core sector output — a set of eight major industrial sectors — fell to 2.6% in April, compared to 4.7% in the same month last year. And finally, unemployment data, controversially suppressed by the Union government so far, showed that joblessness was at a 45-year high of 6.1% in 2017-18. These numbers highlight the challenges ahead in drafting the Budget for 2019-20. The economy is beset by a consumption slowdown as reflected in the falling sales of everything from automobiles to consumer durables, even fast-moving consumer goods. Private investment is not taking off, while government spending, which kept the economy afloat during the last NDA government, was cut back in the last quarter of 2018-19 to meet the fiscal deficit target of 3.4%.
The good news is that inflation is undershooting the target and oil prices are on the retreat again. But the rural economy remains in distress, as seen by the 2.9% growth in agriculture last fiscal; the sector needs a good monsoon this year to bounce back. Overall economic growth in the first quarter of this fiscal is likely to remain subdued, and any improvement is unlikely until the late second quarter or the early third. There are not too many options before the new Finance Minister. In the near term, she has to boost consumption, which means putting more money in the hands of people. That, in turn, means cutting taxes, which is not easy given the commitment to rein in the fiscal deficit. In the medium term, Ms. Sitharaman has to take measures to boost private investment even as she opens up public spending again. These call for major reforms, starting with land acquisition and labour, corporate taxes by reducing exemptions and dropping rates, and nursing banks back to health. On the table will be options such as further recapitalisation of the ailing banks, and consolidation. The question, though, is where the money will come from. With tax revenues likely to be subdued owing to the slowdown, the Centre will have to look at alternative sources such as disinvestment. There may be little choice but to go big on privatisation. A rate cut by the Reserve Bank of India, widely expected this week, would certainly help boost sentiment. But it is the Budget that will really set the tone for the economy
Q. Which of the following is the closest in meaning to the word beset?