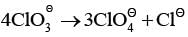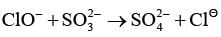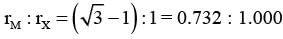JEE Advance 2020 with Solution: Paper - 1 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advance 2020 with Solution: Paper - 1
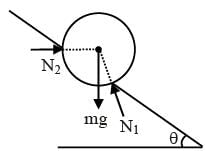
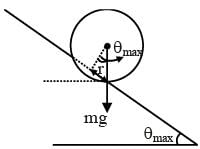
A football of radius R is kept on a hole of radius r (r < R) made on a plank kept horizontally. One end of the plank is now lifted so that it gets tilted making an angle θ from the horizontal as shown in the figure below. The maximum value of θ so that the football does not start rolling down the plank satisfies (figure is schematic and not drawn to scale) -
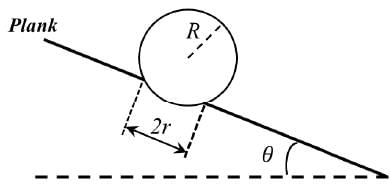

A light disc made of aluminium (a nonmagnetic material) is kept horizontally and is free to rotate about its axis as shown in the figure. A strong magnet is held vertically at a point above the disc away from its axis. On revolving the magnet about the axis of the disc, the disc will (figure is schematic and not drawn to scale)-
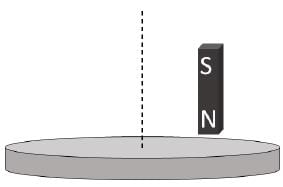

A small roller of diameter 20 cm has an axle of diameter 10 cm (see figure below on the left). It is on a horizontal floor and a meter scale is positioned horizontally on its axle with one edge of the scale on top of the axle (see figure on the right). The scale is now pushed slowly on the axle so that it moves without slipping on the axle, and the roller starts rolling without slipping. After the roller has moved 50 cm, the position of the scale will look like (figures are schematic and not drawn to scale)-
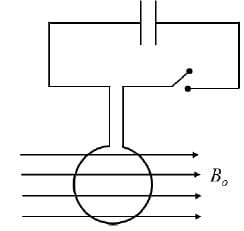
A circular coil of radius R and N turns has negligible resistance. As shown in the schematic figure, its two ends are connected to two wires and it is hanging by those wires with its plane being vertical. The wires are connected to a capacitor with charge Q through a switch. The coil is in a horizontal uniform magnetic field Bo parallel to the plane of the coil. When the switch is closed, the capacitor gets discharged through the coil in a very short time. By the time the capacitor is discharged fully, magnitude of the angular momentum gained by the coil will be (assume that the discharge time is so short that the coil has hardly rotated during this time)-
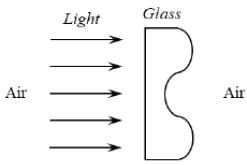
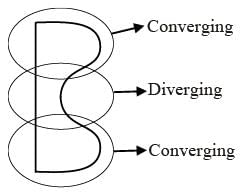
A parallel beam of light strikes a piece of transparent glass having cross section as shown in the figure below. Correct shape of the emergent wavefront will be (figures are schematic and not drawn to scale)-
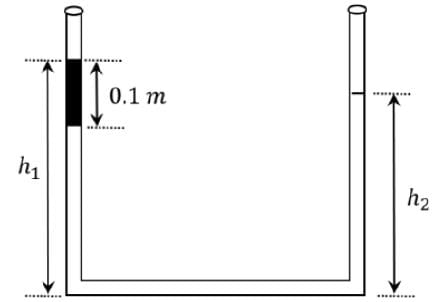
An open-ended U-tube of uniform cross-sectional area contains water (density 103kg m−3). Initially the water level stands at 0.29 m from the bottom in each arm. Kerosene oil (a water-immiscible liquid) of density 800 kg m−3 is added to the left arm until its length is 0.1 m, as shown in the schematic figure below. The ratio (h1/h2) of the heights of the liquid in the two arms is-
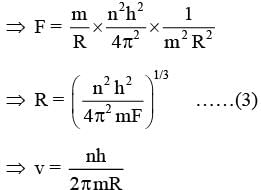
A particle of mass m moves in circular orbits with potential energy V(r)=Fr, where F is a positive constant and r is its distance from the origin. Its energies are calculated using the Bohr model. If the radius of the particle’s orbit is denoted by R and its speed and energy are denoted by v and E, respectively, then for the nth orbit (here h is the Planck’s constant)-
The filament of a light bulb has surface area 64 mm2. The filament can be considered as a black body at temperature 2500 K emitting radiation like a point source when viewed from far. At night the light bulb is observed from a distance of 100 m. Assume the pupil of the eyes of the observer to be circular with radius 3 mm. Then (Take Stefan-Boltzmann constant = 5.67 × 10−8 Wm−2 K−4, Wien’s displacement constant = 2.90 × 10−3 m-K, Planck’s constant = 6.63 × 10−34 Js, speed of light in vacuum= 3.00 × 108 ms−1)-
Sometimes it is convenient to construct a system of units so that all quantities can be expressed in terms of only one physical quantity. In one such system, dimensions of different quantities are given in terms of a quantity X as follows: [position] = [Xα]; [speed] = [Xβ]; [acceleration] =[Xp]; [linear momentum] = [Xq]; [force] = [Xr]. Then -
A uniform electric field, 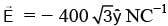 is applied in a region. A charged particle of mass m carrying positive charge q is projected in this region with an initial speed of
is applied in a region. A charged particle of mass m carrying positive charge q is projected in this region with an initial speed of 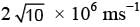 . This particle is aimed to hit a target T, which is 5 m away from its entry point into the field as shown schematically in the figure. Take q/m = 1010 Ckg-1. Then-
. This particle is aimed to hit a target T, which is 5 m away from its entry point into the field as shown schematically in the figure. Take q/m = 1010 Ckg-1. Then-
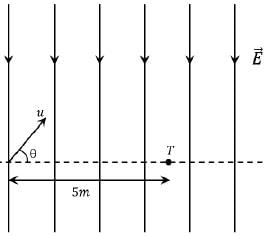
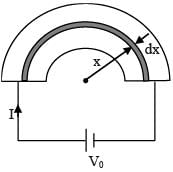
Shown in the figure is a semicircular metallic strip that has thickness t and resistivity ρ. Its inner radius is R1 and outer radius is R2. If a voltage V0 is applied between its two ends, a current I flows in it. In addition, it is observed that a transverse voltage ΔV develops between its inner and outer surfaces due to purely kinetic effects of moving electrons (ignore any role of the magnetic field due to the current). Then (figure is schematic and not drawn to scale)-
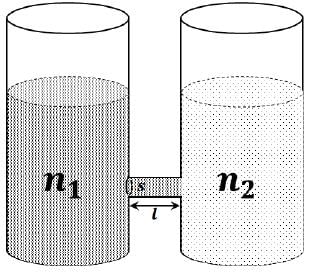
As shown schematically in the figure, two vessels contain water solutions (at temperature T) of potassium permanganate (KMnO4) of different concentrations n1 and n2 (n1 > n2) molecules per unit volume with Δn = (n1 - n2) << n1. When they are connected by a tube of small length l and cross-sectional area S, KMnO4 starts to diffuse from the left to the right vessel through the tube. Consider the collection of molecules to behave as dilute ideal gases and the difference in their partial pressure in the two vessels causing the diffusion. The speed v of the molecules is limited by the viscous force -βv on each molecule, where β is a constant. Neglecting all terms of the order (Δn)2, which of the following is/are correct? (kB is the Boltzmann constant)-
Put a uniform meter scale horizontally on your extended index fingers with the left one at 0.00 cm and the right one at 90.00 cm. When you attempt to move both the fingers slowly towards the center, initially only the left finger slips with respect to the scale and the right finger does not. After some distance, the left finger stops and the right one starts slipping. Then the right finger stops at a distance ��R from the center (50.00 cm) of the scale and the left one starts slipping again. This happens because of the difference in the frictional forces on the two fingers. If the coefficients of static and dynamic friction between the fingers and the scale are 0.40 and 0.32, respectively, the value of ��R (in cm) is ______.-
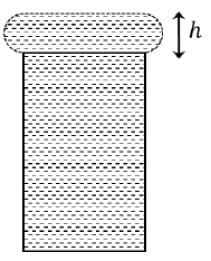
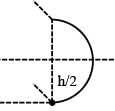
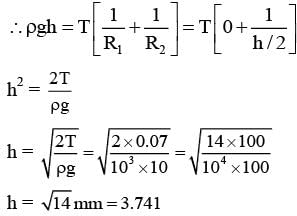
When water is filled carefully in a glass, one can fill it to a height h above the rim of the glass due to the surface tension of water. To calculate h just before water starts flowing, model the shape of the water above the rim as a disc of thickness h having semicircular edges, as shown schematically in the figure. When the pressure of water at the bottom of this disc exceeds what can be withstood due to the surface tension, the water surface breaks near the rim and water starts flowing from there. If the density of water, its surface tension and the acceleration due to gravity are 103kg m−3, 0.07 Nm−1 and 10 ms−2, respectively, the value of h (in mm) is _________.-
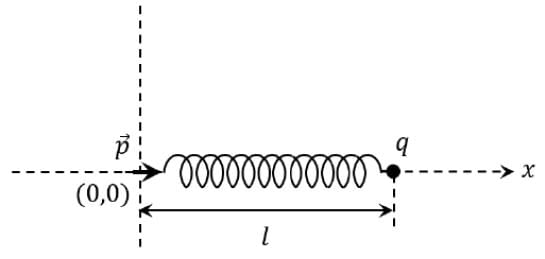
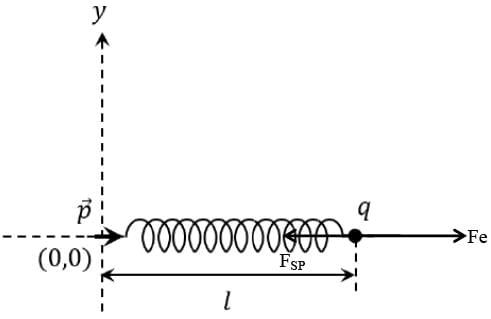
One end of a spring of negligible unstretched length and spring constant k is fixed at the origin (0,0). A point particle of mass m carrying a positive charge q is attached at its other end. The entire system is kept on a smooth horizontal surface. When a point dipole 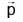 pointing towards the charge q is fixed at the origin, the spring gets stretched to a length l and attains a new equilibrium position (see figure below). If the point mass is now displaced slightly by Δl << l from its equilibrium position and released, it is found to oscillate at frequency
pointing towards the charge q is fixed at the origin, the spring gets stretched to a length l and attains a new equilibrium position (see figure below). If the point mass is now displaced slightly by Δl << l from its equilibrium position and released, it is found to oscillate at frequency 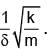 The value of δ is ______.
The value of δ is ______.
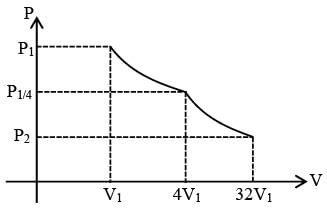
Consider one mole of helium gas enclosed in a container at initial pressure P1 and volume V1. It expands isothermally to volume 4V1. After this, the gas expands adiabatically and its volume becomes 32V1. The work done by the gas during isothermal and adiabatic expansion processes are Wiso and Wadia, respectively. If the ratio 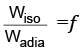 ln 2, then �� is ________.
ln 2, then �� is ________.
A stationary tuning fork is in resonance with an air column in a pipe. If the tuning fork is moved with a speed of 2 ms−1 in front of the open end of the pipe and parallel to it, the length of the pipe should be changed for the resonance to occur with the moving tuning fork. If the speed of sound in air is 320 ms−1, the smallest value of the percentage change required in the length of the pipe is ____________.
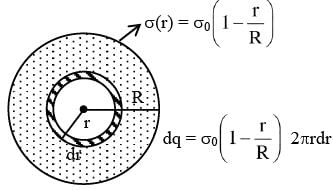
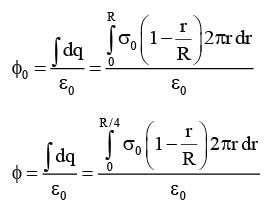
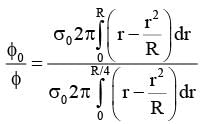
A circular disc of radius R carries surface charge density 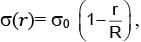 where σ0 is a constant and r is the distance from the center of the disc. Electric flux through a large spherical surface that encloses the charged disc completely is φ0. Electric flux through another spherical surface of radius R/4 and concentric with the disc is φ. Then the ratio
where σ0 is a constant and r is the distance from the center of the disc. Electric flux through a large spherical surface that encloses the charged disc completely is φ0. Electric flux through another spherical surface of radius R/4 and concentric with the disc is φ. Then the ratio 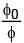 is ......
is ......
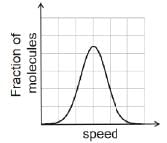
If the distribution of molecular speeds of a gas is as per the figure shown below, then the ratio of the most probable, the average and the roots mean square speeds, respectively, is
Which of the following liberates O2 upon hydrolysis?
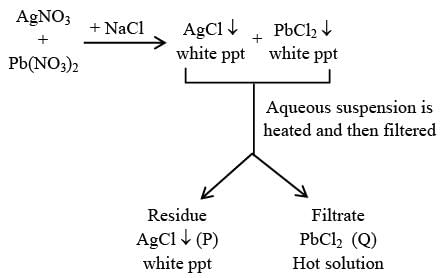
A colorless aqueous solution contains nitrates of two metals, X and Y. When it was added to an aqueous solution of NaCl, a white precipitate was formed. This precipitate was found to be partly soluble in hot water to give a residue P and a solution Q. The residue P was soluble in aq. NH3 and also in excess sodium thiosulfate. The hot solution Q gave a yellow precipitate with KI. The metals X and Y, respectively, are
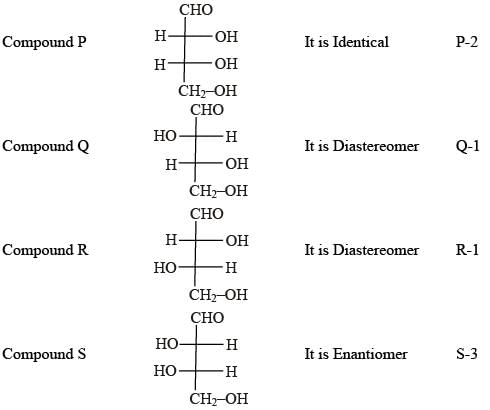
Newman projections P, Q, R and S are shown below :
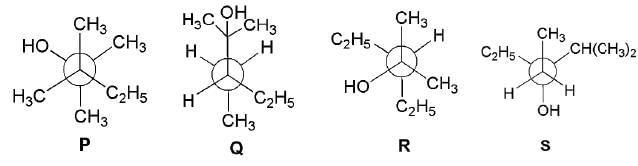
Which one of the following options represents identical molecules?
Which one of the following structures has the IUPAC name
3-ethynyl-2-hydroxy-4-methylhex-3-en-5-ynoic acid?
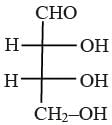
The Fischer projection of D-erythrose is shown below.
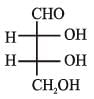
D-Erythrose
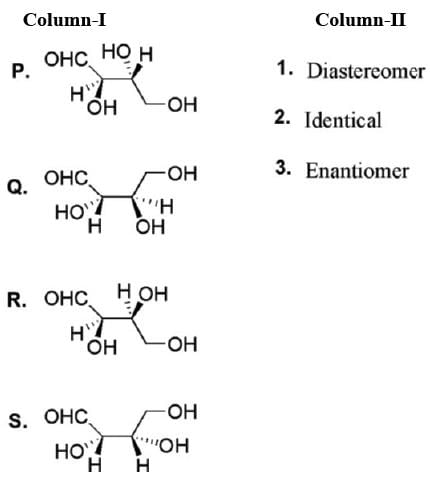
D-Erythrose and its isomers are listed as P, Q, R, and S in Column-I. Choose the correct relationship of P, Q, R, and S with D-erythrose from Column II.
In thermodynamics the P-V work done is given by
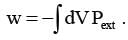
For a system undergoing a particular process, the work done is ,
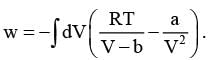
This equation is applicable to a
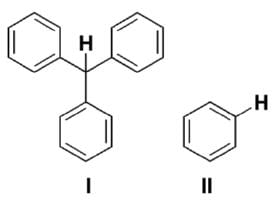
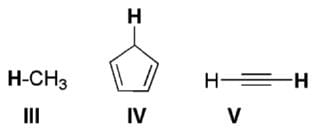
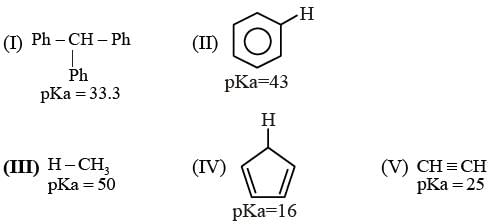
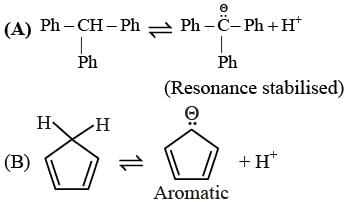
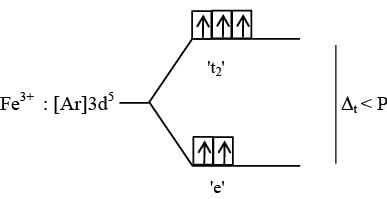
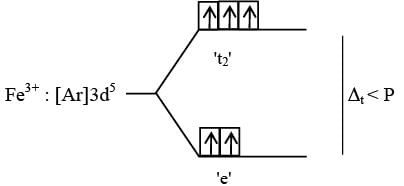
With respect to the compounds I-V, choose the correct statement(s).
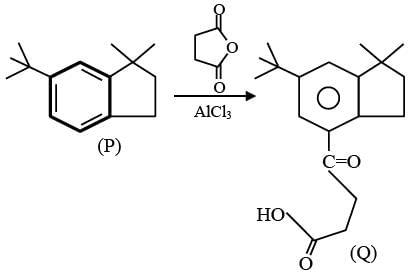
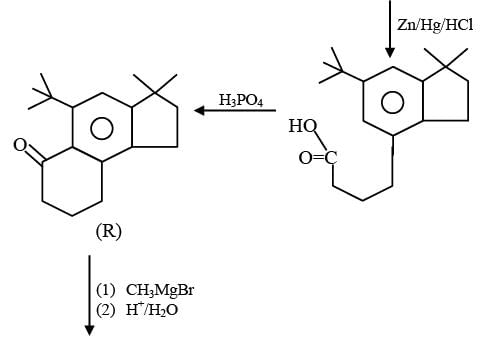
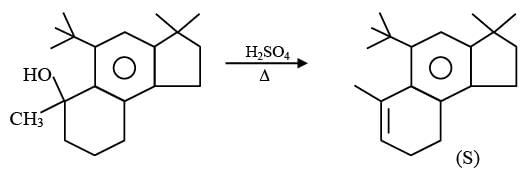
In the reaction scheme shown below Q, R and S are the major products.
The correct structure of
Choose the correct statement(s) among the following :
With respect to hypochlorite, chlorate and perchlorate ions, choose the correct statement(s).
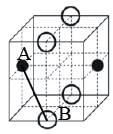
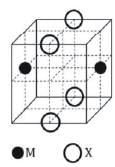
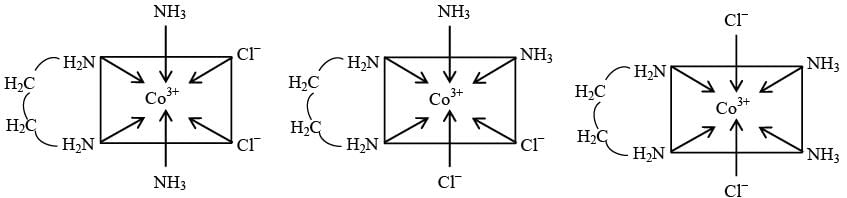
The cubic unit cell structure of a compound containing cation M and anion X is shown below. When compared to the anion, the cation has smaller ionic radius. Choose the correct statement(s).


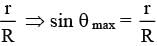

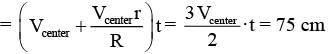
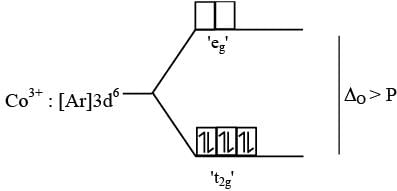
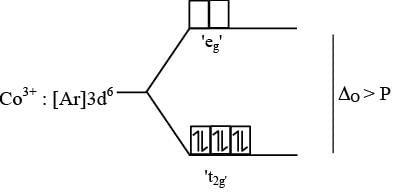
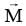 is magnetic moment
is magnetic moment 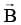 is magnetic field
is magnetic field 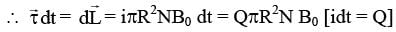
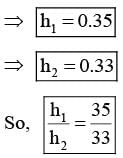
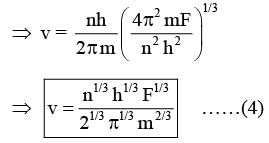
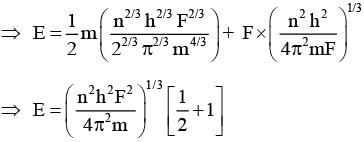
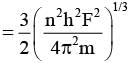
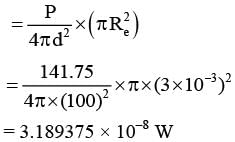
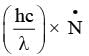
 Number of photons entering into eye per second
Number of photons entering into eye per second 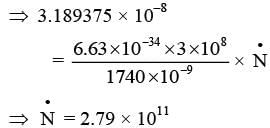
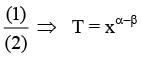
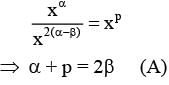
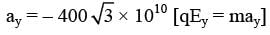
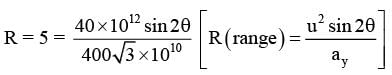
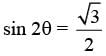
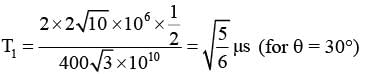
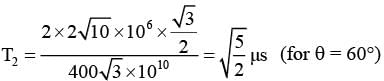
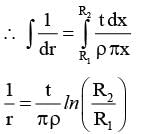
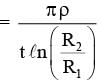
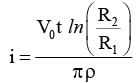 (A)
(A)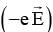 will be inward direction in order to provide centripetal acceleration. Therefore electric field will be radially outward
will be inward direction in order to provide centripetal acceleration. Therefore electric field will be radially outward 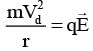
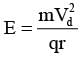 (I = neAVd ⇒ Vd ∝ i)
(I = neAVd ⇒ Vd ∝ i)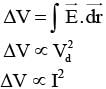
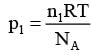
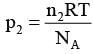
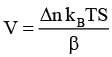
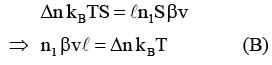
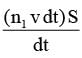
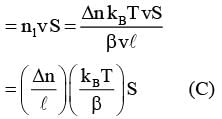







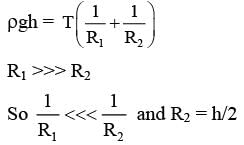
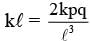
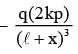
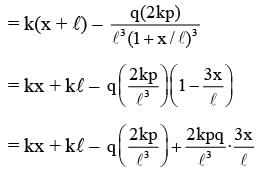
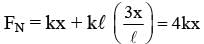
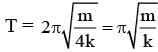
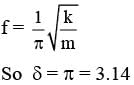
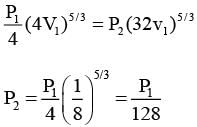
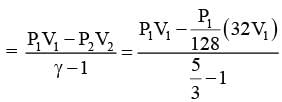
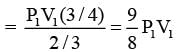
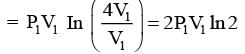
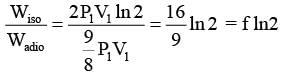
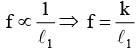 ...(1)
...(1)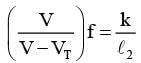 {VT Speed of tuning fork, l2 → new length of pipe} ...(2)
{VT Speed of tuning fork, l2 → new length of pipe} ...(2)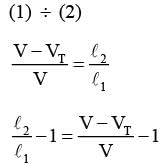
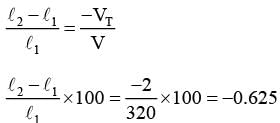
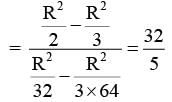


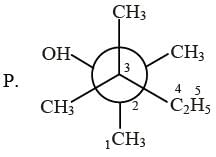 2, 3, 3-trimethyl pentan-2-ol
2, 3, 3-trimethyl pentan-2-ol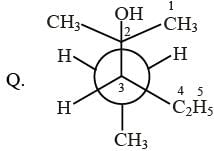 3-ethyl-2-methyl pentan-2-ol
3-ethyl-2-methyl pentan-2-ol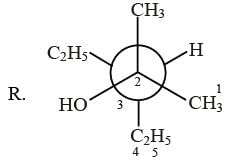 3-ethyl-2-methyl pentan-2-ol
3-ethyl-2-methyl pentan-2-ol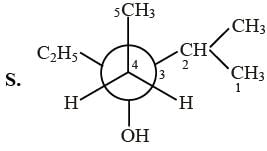 3-ethyl-2-methyl pentan-3-ol
3-ethyl-2-methyl pentan-3-ol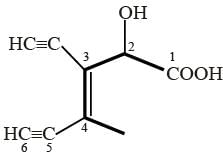
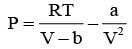
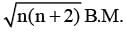
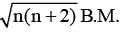
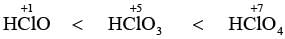
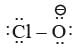 Linear shape
Linear shape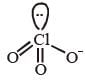 Trigonal pyramidal shape
Trigonal pyramidal shape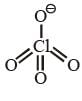 Perfect tetrahedral shape due to resonance
Perfect tetrahedral shape due to resonance