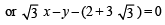JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Straight Lines and Pair of Straight Lines - JEE MCQ
23 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Straight Lines and Pair of Straight Lines
The points (–a, – b), (0, 0), (a, b) and (a2, ab) are : (1979)
Th e poin t (4, 1) under goes th e following t hr ee transformations successively. (1980)
(i) Reflection about the line y = x.
(ii) Translation through a distance 2 units along the positive direction of x-axis.
(iii) Rotation through an angle p/4 about the origin in the counter clockwise direction.
Then the final position of the point is given by the coordinates.
(i) Reflection about the line y = x.
(ii) Translation through a distance 2 units along the positive direction of x-axis.
(iii) Rotation through an angle p/4 about the origin in the counter clockwise direction.
Then the final position of the point is given by the coordinates.
The straight lines x + y = 0, 3x + y – 4 = 0, x + 3y – 4 = 0 form a triangle which is (1983 - 1 Mark)
If P = (1, 0), Q = (–1, 0) and R = (2, 0) are three given points, then locus of the point S satisfying the relation SQ2 + SR2 = 2SP2, is (1988 - 2 Marks)
Line L has intercepts a and b on the coordinate axes. When the axes are rotated through a given angle, keeping the origin fixed, the same line L has intercepts p and q, then (1990 - 2 Marks)
If the sum of the distances of a point from two perpendicular lines in a plane is 1, then its locus is (1992 - 2 Marks)
The locus of a variable point whose distance from (–2, 0) is 2/3 times its distance from the line x = -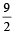 is (1994)
is (1994)
The equation s to a pair of opposite sides of parallelogram are x2 – 5x + 6 = 0 and y2 – 6y + 5 = 0, the equations to its diagonals are (1994)
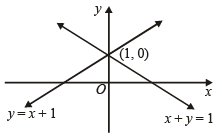
The orthocentre of the triangle formed by the lines xy = 0 and x + y = 1 is (1995S)
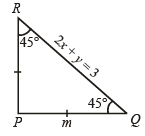
Let PQR be a right angled isosceles triangle, right angled at P (2, 1). If the equation of the line QR is 2x + y = 3, then the equation representing the pair of lines PQ and PR is (1999 - 2 Marks)
If x1, x2, x3 as well as y1, y2, y3, are in G.P. with the same common ratio, then the points (x1, y1), (x2, y2) and (x3, y3). (1999 - 2 Marks)
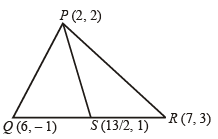
Let PS be the median of the triangle with vertices P(2, 2), Q(6, –1) and R(7, 3). The equation of the line passing through (1,–1) and parallel to PS is (2000S)
The incentre of the triangle with vertices (1, √3 ), (0, 0) and (2, 0) is (2000S)
The number of integer values of m, for which the x-coordinate of the point of intersection of the lines 3x + 4y = 9 and y = mx + 1 is also an integer, is (2001S)
Area of the parallelogram formed by the lines y = mx, y = mx + 1, y = nx and y = nx + 1 equals (2001S)
Let 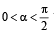 be fixed angle. If P = (cos q, sin q) and Q = (cos(a - q), sin(a - q)) , then Q is obtained from P by (2002S)
be fixed angle. If P = (cos q, sin q) and Q = (cos(a - q), sin(a - q)) , then Q is obtained from P by (2002S)
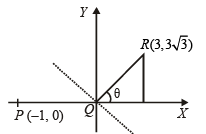
Let P = (-1, 0), Q = (0, 0) and R = (3, 3√3 ) be three points.
Then the equation of the bisector of the angle PQR is (2002S)
A straight line through the origin O meets the parallel lines 4x + 2y = 9 and 2x + y + 6 = 0 at points P and Q respectively.Then the point O divides the segemnt PQ in the ratio (2002S)
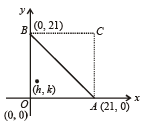
The number of intergral points (integral point means both the coordinates should be integer) exactly in the interior of the triangle with vertices (0,0), (0,21) and (21,0), is (2003S)
Orthocentre of triangle with vertices (0, 0), (3, 4) and (4, 0) is (2003S)
Area of the triangle formed by th e lin e x + y = 3 an d an gle bisectors of the pair of straight lines x2 – y2 + 2y = 1 is (2004S)
Let O(0, 0), P(3, 4), Q(6, 0) be the vertices of the triangles OPQ. The point R inside the triangle OPQ is such that the triangles OPR, PQR, OQR are of equal area. The coordinates of R are (2007 -3 marks)
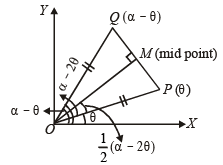
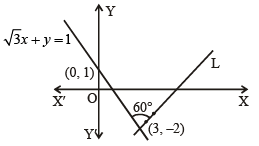
A straight line L through the point (3, –2) is inclined at an angle 60° to the line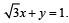 If L also intersects the x-axis, then the equation of L is (2011)
If L also intersects the x-axis, then the equation of L is (2011)


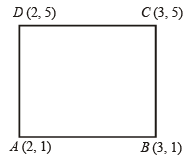
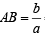 Slope of BC = slope of BD
Slope of BC = slope of BD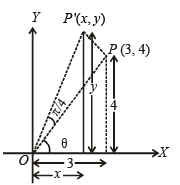
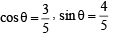
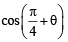
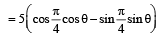
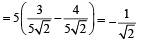
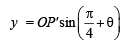
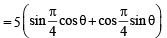
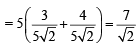
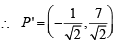

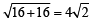
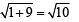
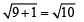 ∴ Δ is isosceles.
∴ Δ is isosceles.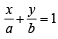 .....… (1)
.....… (1) .....… (2)
.....… (2)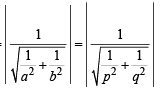
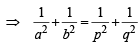
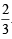 PM where PM is the perpendicular distance of point P from given line x = – 9/2
PM where PM is the perpendicular distance of point P from given line x = – 9/2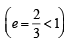
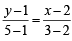 or y = 4x – 7
or y = 4x – 7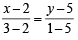 or 4x + y = 13
or 4x + y = 13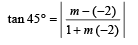
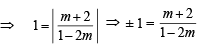
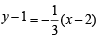
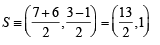
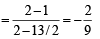
 or 2x + 9y + 7 = 0
or 2x + 9y + 7 = 0
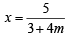
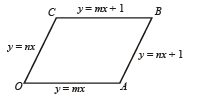
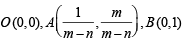
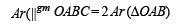
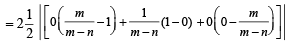
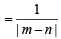
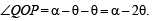
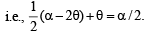
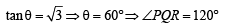
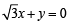

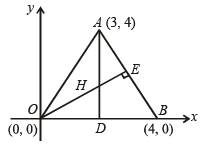
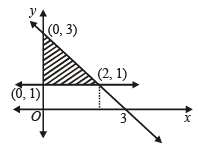
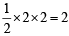 sq. units.
sq. units.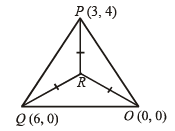
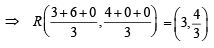
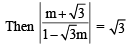
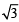 (x – 3)
(x – 3)