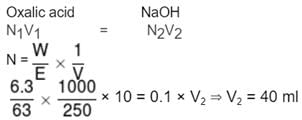JEE Main Chemistry Test- 2 - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Mock Tests for JEE Main and Advanced 2025 - JEE Main Chemistry Test- 2
Which of the following alkenes will react fastest with 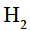 under catalytic hydrogenation conditions
under catalytic hydrogenation conditions
The heat of hydrogenation of 1-hexene is 126 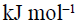 . When a second double bond is introduced in the molecule, the heat of hydrogenation of the resulting compound is 230
. When a second double bond is introduced in the molecule, the heat of hydrogenation of the resulting compound is 230 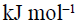 . The resulting compound (diene) is
. The resulting compound (diene) is
The enthalpy of fusion of water is 1.435 kcal/mol. The molar entropy change for the melting of ice at 0°C is
The Kp for the decomposition of SO2Cl2 (if its degree of dissociation under one atomic pressure is 90%) is
In a reversible chemical reaction at equilibrium, if the concentration of any one of the reactants is doubled, then the equilibrium constant will
Enthalpy of neutralization of H3PO3 acid is –106.68 KJ/mole using NaOH. If enthalpy of neutralization of HCl by NaOH is –55.84 KJ/mole. Calculate ΔHionisation of H3PO3 into its ions. (in KJ)
An aqueous solution of 6.3 g of oxalic acid dihydrate is made upto 250 mL. The volume of0.1 N NaOH required to completely neutralise 10 mL of this solution is :
100 mL of 0.6 M acetic acid is shaken with 2 g activated carbon. The final concentration of the solution after adsorption is 0.5 M. What is the amount of acetic acid adsorbed per gram of carbon.
Which of the following is the most stable carbocation?
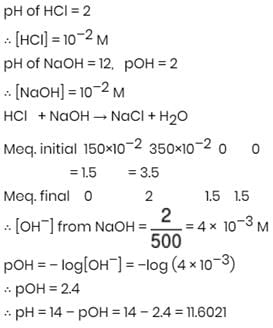
What will be the resultant pH when 150 mL of an aqueous solution of HCl (pH = 2.0) is mixed with 350 mL of an aqueous solution of NaOH (pH = 12.0)?
How many grams of NH4Cl should be dissolved per litre of solution to have a pH of 5.13 ? Kb for NH3 is 1.8 × 10–5.
The oxidation state of chromium in potassium dichromate (K₂Cr₂O₇) is:
|
356 docs|142 tests
|