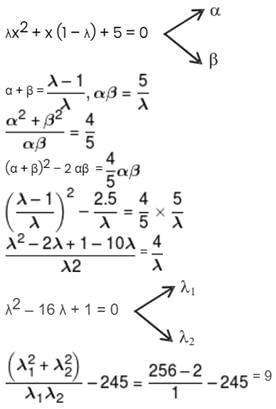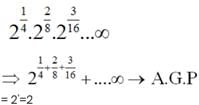JEE Main Maths Test- 3 - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Mock Tests for JEE Main and Advanced 2025 - JEE Main Maths Test- 3
The number of straight lines that can be drawn out of 10 points of which 7 are collinear is
If the correlation coefficient between two variables is 1, then the two least square lines of regression are
If the solution of quadratic equation x2-11x+22 are x=3 and x=6, then the base of the number is
In ΔABC, ∠B = 90o and b a = 4. The area of the triangle is the maximum when ∠C is
Let E be the ellipse and C be the circle x2 y2 = 4. Let P and Q be the point (1,2) and (2,1) respectively. Then
The third term of a G.P. is 4. The products of the first five term is
If cos-1 x/2 + cos -1 y/3 = θ Then 9x2 - 12xy cos θ + 4y2 is
If A1, A2 be two A.M’s and G1, G2 be two G..M.’s between a and b, then ( A1, A2 )/G1,G2 is equal to
A tree is broken by wind, its upper part touches the ground at a point 10 meters from the foot of the tree and makes an angle of 60º with the ground the entire lenght of the tree of
The locus of the mid-point of the chords of a circle x2 + y2 =4, which subtended a right angle at the centre is
If α and β are roots of eq. λ(x2–x) + x + 5 = 0
If λ1, λ2 are two values of λ for which  then
then 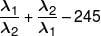
If graph of x2 + bx + d is following.
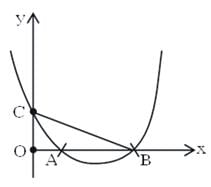
ΔOBC is right angled isosceles triangle and A is mid point of OB then d =
Sum of non real roots of eq.
(x2 + x – 2) · (x2 + x – 3) = 12 is …..
If ƒ(x) = |x – 3| + |x – 16| + |22 – x|, ∀ x ∈ R increases in (a,∞), then a/4 is equal to
|
356 docs|142 tests
|