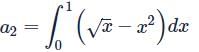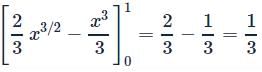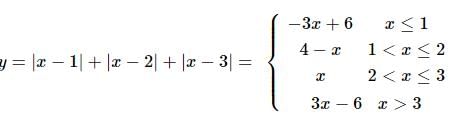JEE Main Mock Test - 11 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Mock Tests for JEE Main and Advanced 2025 - JEE Main Mock Test - 11
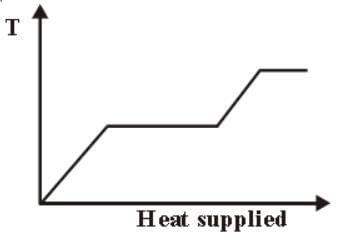
A block of ice at temperature −20∘C is slowly heated and converted to steam at 100∘C. Which of the following diagram is most appropriate?
On six complete rotations, the screw gauge moves by 3 mm on the main scale. If there are 50 divisions on the circular scale the least count of the screw gauge is
Assertion (A) When an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically, its temperature and the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules increase.
Reason (R) The kinetic energy increases because of collisions of molecules with moving parts of wall only.
Reason (R) The kinetic energy increases because of collisions of molecules with moving parts of wall only.
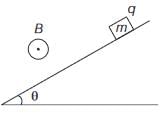
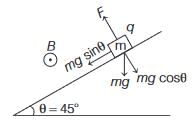
A small block of mass 20 g and charge 4mC is released on a long smooth inclined plane of inclination angle of 45∘, A uniform horizontal magnetic field of 1 T is acting parallel to the surface, as shown in the figure. The time from the start when the block loses contact with the surface of the plane is
The power of biconvex lens is 10 dioptre and the radius of curvature of each surface is 10 cm. Then the refractive index of the material of the lens is :
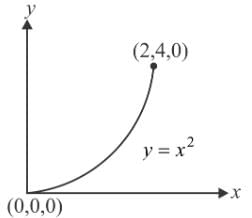
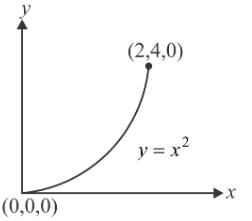
Let 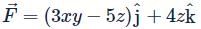 is applied to a particle. The work done by the force when the particle moves from point (0, 0, 0) to point (2, 4, 0) as shown in the figure is
is applied to a particle. The work done by the force when the particle moves from point (0, 0, 0) to point (2, 4, 0) as shown in the figure is
The energy of a photon is equal to the kinetic energy of a proton. The energy of the photon is E. Let λ1 be the de-Broglie wavelength of the proton and λ2 be the wavelength of the photon. The ratio λ1/λ2 is proportional to
Find the Binding energy per nucleon for ₅₀¹²⁰Sn
Mass of proton mp = 1.00783 u,
mass of neutron mn = 1.00867 u,
and mass of tin nucleus mSn = 119.902199 u.
(take 1 u = 931 MeV)
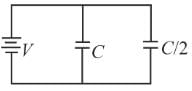
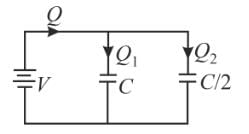
Two condensers, one of capacity C and other of capacity C/2 are connected to a V- volt battery, as shown in the figure. The work done in charging fully both the condensers is
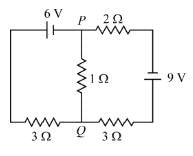
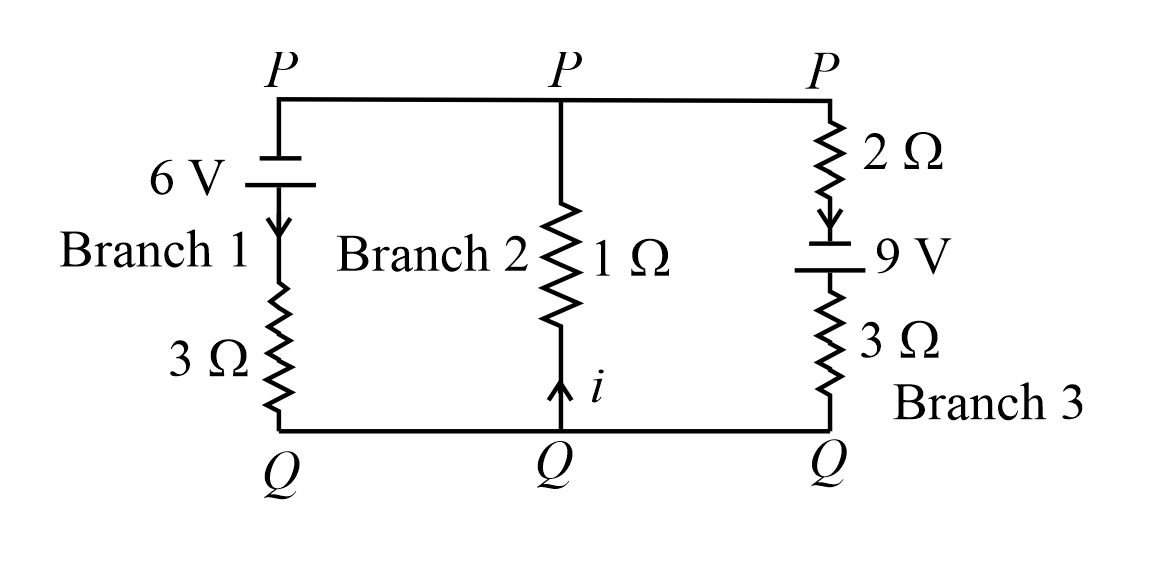
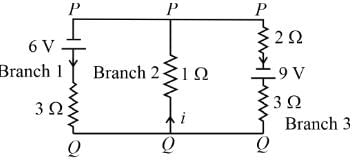
For the circuit given below, if the current in the 1 Ω resistor is x/23 A, what is the value of x? Assume the batteries are ideal.
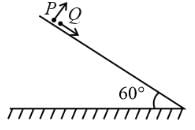
A particle P is projected from a point on the surface of a smooth inclined plane (see figure). Simultaneously another particle Q is released on the smooth inclined plane from the same position. P and Q collide on the inclined plane after t = 4 s. Find the speed of projection in m s−1. (take g = 10 m s−2)
Evaluate the following statements about Group 13 elements:
(A) Atomic radius decreases down the group from B to TI in a regular manner.
(B) Electronegativity decreases gradually down the group from B to TI.
(C) Aluminium can form compounds with a covalency of 6 due to the presence of vacant d-orbitals.
(D) Compounds of boron, like boric acid (H3BO3), exhibit significant pπ−pπ character.
(E) Boron and silicon exhibit similar chemical properties, such as covalent bonding and acidic oxide formation.
Choose the correct combination of statements from the options below:
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points.
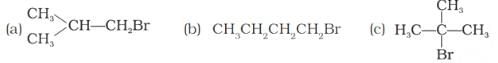
Which of the following reagents gives a yellow precipitate with a hot, faintly acidic solution of Bi³⁺ ions?
The concentration of R in the reaction R→P was measured as a function of time and the following data is obtained:
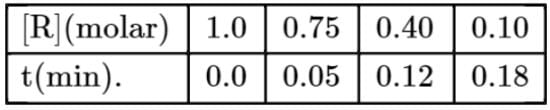
The order of the reaction is
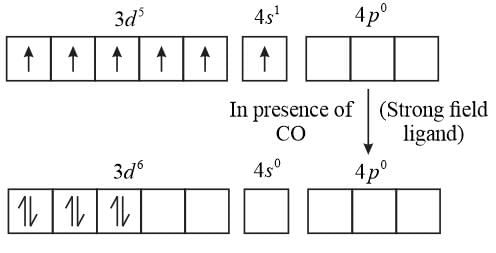
The spin-only magnetic moment value (in Bohr's magneton units) of [Cr(CO)6] is
f:R→R is defined as 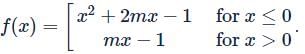
If f(x) is one-one then m must lies in the interval
Number of vectors 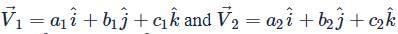 such that
such that 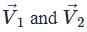 are mutually perpendicular, where a1, b1, c1, a2, b2, c2 ∈ {−2, −1, 1, 2} is equal to
are mutually perpendicular, where a1, b1, c1, a2, b2, c2 ∈ {−2, −1, 1, 2} is equal to
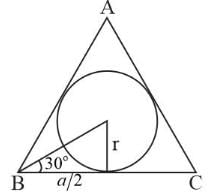
An equilateral triangle’s sides increase at the rate of 2 cm/sec. If the area of its incircle increases at a rate of k cm2/sec (when the length of the side is 6/πcm ), then the value of k is
A vector a̅ = αî + 2ĵ + βk̂ (α, β ∈ ℝ) lies in the plane of the vectors,b̅ = î + ĵ and c̅ = î - ĵ + 4k̂. If a̅ bisects the angle between b̅ and c̅, then
If y = y(x) is the solution of the differential equation 2x² (dy/dx) - 2xy + 3y² = 0 such that y(e) = e³, then y(1) is equal to?
Let A = {(x, y) : y = ex, x ∈ R}, B = {(x, y) : y = e(-x), x ∈ R}. Then
A is a set containing n elements. A subset P of A is chosen. The set A is reconstructed by replacing the elements of P. A subset Q of A is again chosen. Then the number of ways of selecting P and Q such that P∩Q = ∅, is
The number of real values of k for which the lines 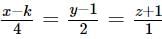 and
and 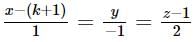 are intersecting is
are intersecting is
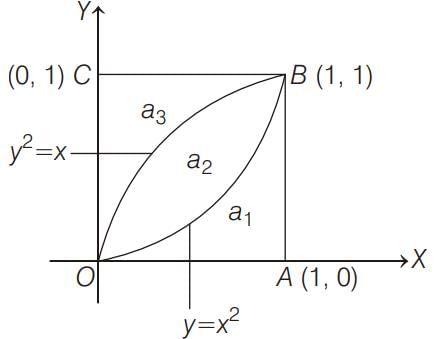
ABC is a unit square where O is the origin and B = (1, 1). The curves y2 = x and x2 = y divide the area of the square into three parts OABO,OBO and OBCO. If a1, a2, a3 are the areas (in sq units) of these parts respectively, then a1 + 2a2 + 3a3 =
The first term of a sequence is 2014. Each succeeding term is the sum of the cubes of the digits of the previous term. Then the 2014th term of the sequence is
Number of solutions of the equation |x − 1| + |x − 2| + |x − 3| = k, k > 2 is
|
356 docs|142 tests
|



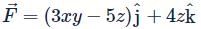
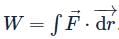
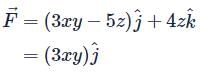
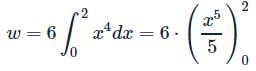
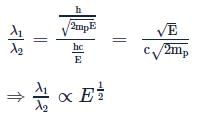
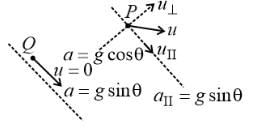
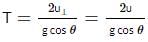
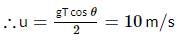
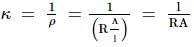
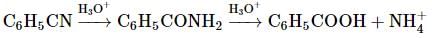
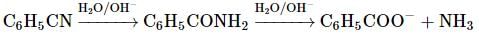
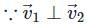
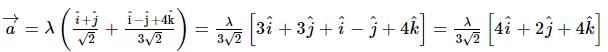
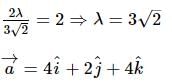
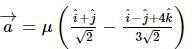
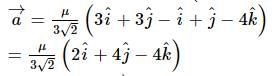
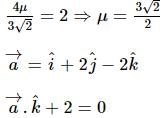
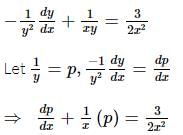
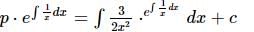
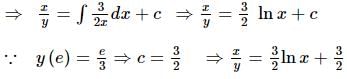 is the particular solution.
is the particular solution.