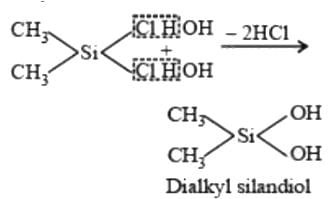
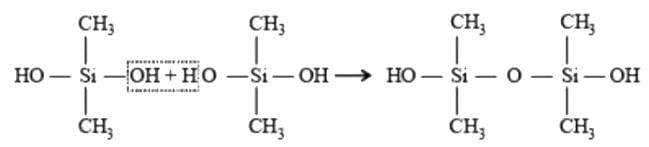
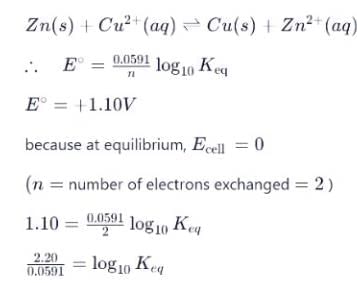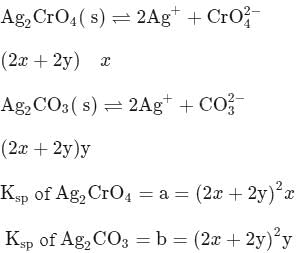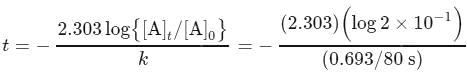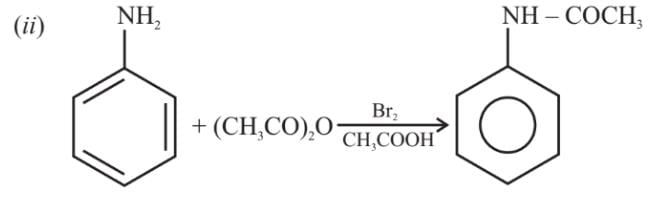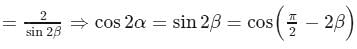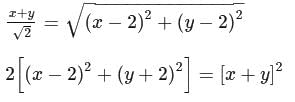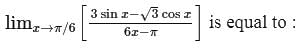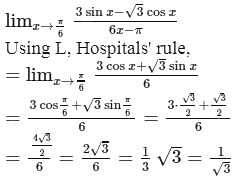JEE Main Mock Test - 2 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Mock Tests for JEE Main and Advanced 2025 - JEE Main Mock Test - 2
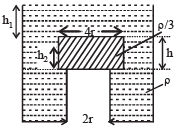
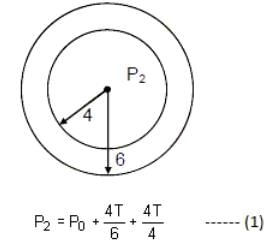
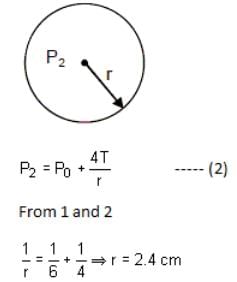
A small soap bubble of radius 4 cm is trapped inside another bubble of radius 6 cm without any contact. Let P2 be the pressure inside the inner bubble and P0 be the pressure outside the outer bubble. Radius of another bubble with pressure difference P2 - P0 between its inside and outside would be
A planet of mass M is revolving around sun in an elliptical orbit. If dA is the area swept in a time dt, angular momentum can be expressed as
A spherical hole is made in a solid sphere of radius R. The mass of the original sphere was M.The gravitational field at the centre of the hole due to the remaining mass is
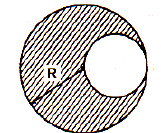
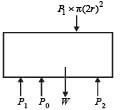
A cylindrical tank has a hole of diameter 2r in its bottom. The hole is covered wooden cylindrical block of diameter 4r, height h and density ρ/3.
Situation I : Initially, the tank is filled with water of density ρ to a height such that the height of water above the top of the block is h1 (measured from the top of the block).
Situation II : The water is removed from the tank to a height h2 (measured from the bottom of the block), as shown in the figure.
The height h2 is smaller than h (height of the block) and thus the block is exposed to the atmosphere.
Q. Find the minimum value of height h1 (in situation 1), for which the block just starts to move up?
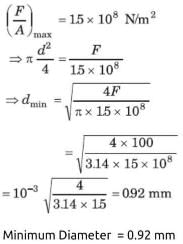
If the elastic limit of copper is 1.5 × 108 N/ m2, determine the minimum diameter a copper wire can have under a load of 10.0 kg if its elastic limit is not to be exceeded.
At what temperature is the r.m.s velocity of a hydrogen molecule equal to that of an oxygen molecule at 47°C?
Heat generated through a resistive wire will increase _______ times in unit time, if current in the wire becomes twice.
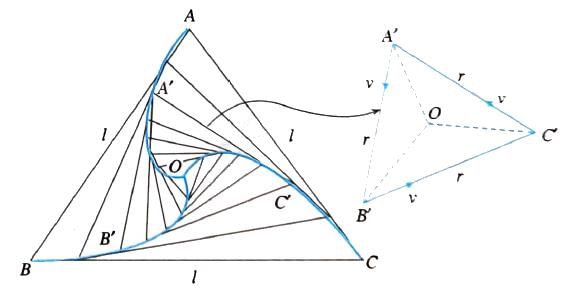
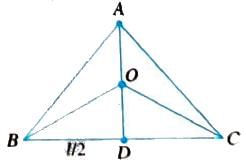
Three particles A, B and C are situated at the vertices of an equilateral triangle of side l at t = 0. The particle A heads towards B, B towards C, C towards A with constant speeds v. Find the time of their meeting.
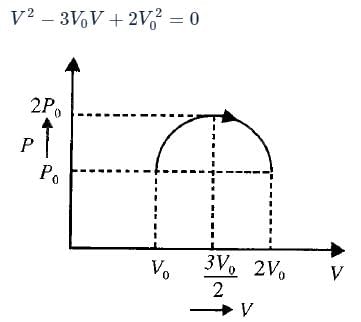
The P−V equation for a process of an ideal gas is given as
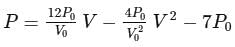
The graphical representation of the above process is shown as
The superposition takes place between two waves of frequency f and amplitude a. The maximum intensity Imax = constant × ____
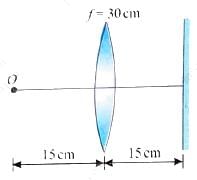
An object O is kept in front of a converging lens of focal length 30 cm behind which there is a plane mirror at 15 cm from the lens. Choose the correct statements.
A TV tower has a height of 50 m. The maximum distance up to which TV transmission can be received is approximately equal to (radius of earth = 6.4 × 106 m)
Which statement(s) is/are true?
(i) Kirchhoff's law is equally applicable to both AC and DC.
(ii) Semiconductors have a positive temperature coefficient of resistance.
(iii) Meter bridge has a greater sensitivity when the resistances of all the four arms of the bridge are of the same order.
(iv) The emf of a cell depends upon the size and area of electrodes.
For the following electrochemical cell reaction at 298 K:
Zn(s) + Cu²⁺(aq) ⇌ Cu(s) + Zn²⁺(aq),
Given that the standard cell potential (E° cell) is +1.10 V.
We know that the relationship between Kc and Kp is Kp = Kc (RT)Δn
What would be the value of Δn for the reaction NH4Cl (s) ⇔ NH3 (g) + HCl (g)
Ag2CrO4 and Ag2CO3 are simultaneously dissolved in water. The solubility of Ag2CrO4& Ag2CO3 are 'x′ and 'y′mol/l respectively. If the Ksp of Ag2CrO4 is 'a′ and that of Ag2CO3 is 'b', then which of the following is correct?
The half-life for the thermal decomposition of acetone is 80 s and is independent of initial concentration of acetone. The time required for the reaction to go to 80% composition is (Given: log2 = 0.30)
Given below are two statements :
Statement I: A unit formed by the attachment of a base to 1′ position of sugar is known as nucleoside
Statement II: When nucleoside is linked to phosphorous acid at 5′-position of sugar moiety, we get nucleotide.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
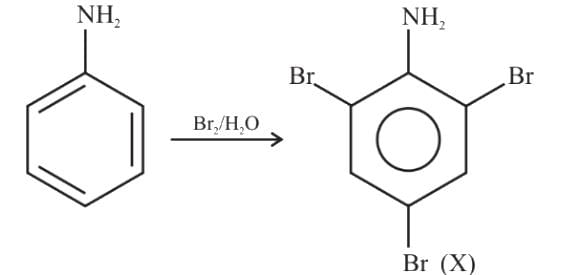
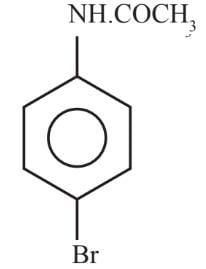
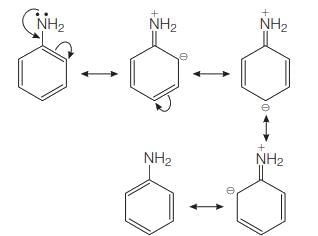
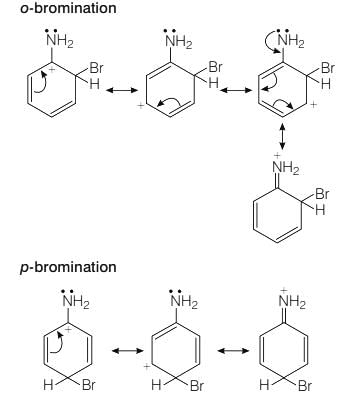
Assertion (A) −NH2 group of aniline is ortho, para directing in electrophilic substitutions.
Reason (R) −NH2 group stabilises the arenium ion formed by the ortho, para attack of the electrophile.
The correct answer is
For the reaction at 298 K: 2A +B → C
ΔH = 400 J mol−1; ΔS = 0.2 JK−1mol−1
Determine the temperature at which the reaction would be spontaneous.
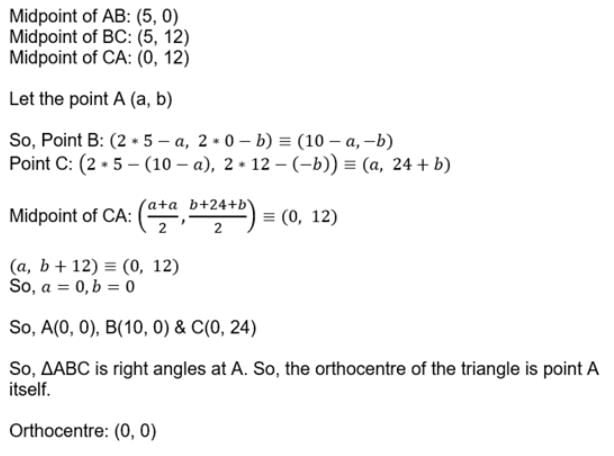
The mid points of the sides of a triangle are (5, 0), (5, 12) and (0, 12), then orthocentre of this triangle is
If 2 sec 2α = tan β + cot β, then one of the values of α + β is
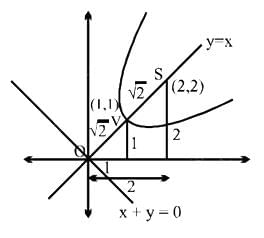
The axis of a parabola lie along the line y = x and the distance of its vertex from origin is √2 and that of focus is 2√2. If both focus and vertex lie in the first quadrant, then the equation of the parabola will be
|
356 docs|142 tests
|



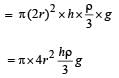
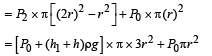
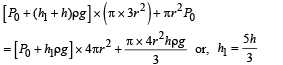
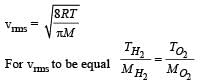
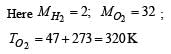
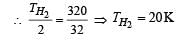
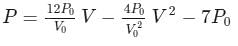
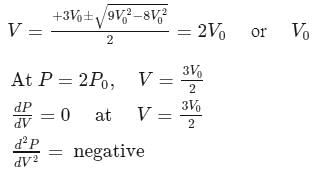
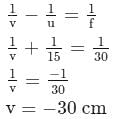
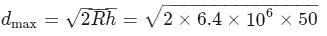 = 25.3 km
= 25.3 km