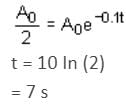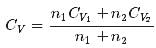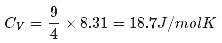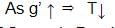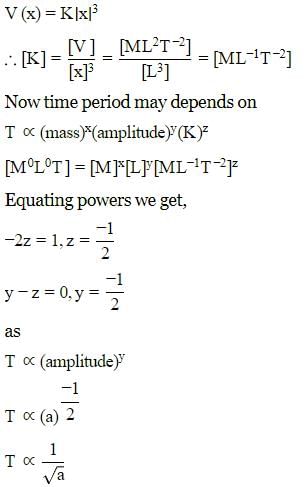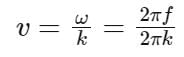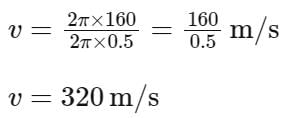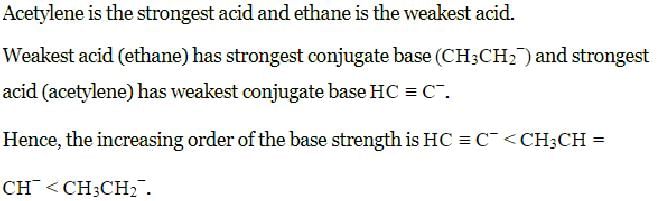JEE Main Part Test - 3 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Mock Tests for JEE Main and Advanced 2025 - JEE Main Part Test - 3
Two bullets A and B are fired horizontally with speed v and 2v respectively.which of the following is true
A 14.5 kg mass, fastened to the end of a steel wire of unstretched length 1.0 m, is whirled in a vertical circle with an angular velocity of 2 rev/s at the bottom of the circle. The cross-sectional area of the wire is 0.065 cm2. Calculate the elongation of the wire when the mass is at the lowest point of its path.
The displacement of a damped harmonic oscillator is given by:
x(t) = e-0.1t cos (10πt + φ). Hence, t is in seconds.
The time taken for its amplitude of vibration to drop to half of its initial value is close to:
1 mole of a monoatomic gas is mixed with 3 moles of a diatomic gas. What is the molecular specific heat of the mixture at constant volume?
The average distance a molecule can travel without colliding is called the
Value of gas constant, R for one mole of a gas is independent of the
According to kinetic theory of gases, 0K is that temperature at which for an ideal gas
Four moles of an ideal diatomic gas is heated at constant volume from 20° C to 30° C. The molar specific heat of the gas at constant pressure (Cp) is 30.3 Jmol-1K-1 and the universal gas constant (R) is 8.3 Jmol-1K-1. The increase in internal energy of the gas is
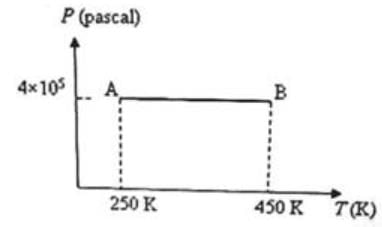
Three moles of an ideal monoatomic gas is initially in the state A shown in the adjoining pressure-temperature graph. It is taken to state B without changing its pressure. If R is the universal gas constant, the work done by the gas in this process is
A second pendulum is mounted in a space shuttle. Its period of oscillations will decrease when rocket is:
Find the amplitude of the S.H.M whose displacement y in cm is given by equation y= 3 sin157t + 4 cos157t, where t is time in seconds.
A particle executes linear simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 2 cm. When the particle is at 1 cm from the mean position, the magnitude of its velocity is equal to that of its acceleration. Then its time period in seconds is:
What is the maximum Kinetic energy and minimum potential energy of a harmonic oscillator with amplitude 0.03m, force constant 4×105 N/m and total mechanical energy of 230 J.
The velocity and acceleration amplitudes of body executing simple harmonic motion is
A particle of mass m is executing oscillation about the origin on X-axis. Its potential energy is V(x)=K∣x∣3. Where K is a positive constant. If the amplitude of oscillation is a, then its time period T is proportional to.
Energy is supplied to the damped oscillatory system at the same rate at which it is dissipating energy, then the amplitude of such oscillations would become constant. Such oscillations are called
In the ideal case of zero damping, the amplitude of simple harmonic motion at resonance is:
The necessary condition for phenomenon of interference to occur is
The equation of wave is given by
Y = 10-2 sin 2π (160t – 0.5x + π/4)
where x and Y are in m and t in s. The speed of the wave is _______ km h-1.
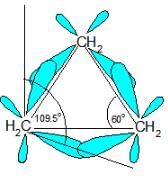
Which of the following correctly ranks the cycloalkanes in order of increasing ring strain per methylene group?
Which of the following cycloalkanes exhibits the greatest molar heat of combustion per —CH2 — group?
Arrange in increasing order of basicity. HC≡C−, CH3CH=CH−, CH3CH2−
What are the hybridization and shapes of the following molecules?
(i) CH3F
(ii) HC ≡ N
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
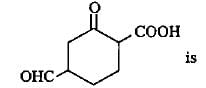
Q. Consider the following compounds.
The correct statement regarding properties of above mentioned compounds is/are
The compound shown below evolve hydrogen gas when refluxed with potassium metal, why?
|
356 docs|142 tests
|