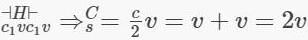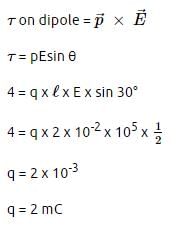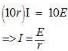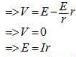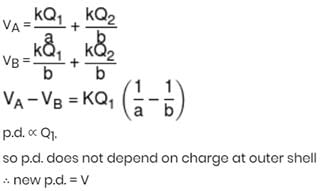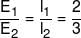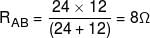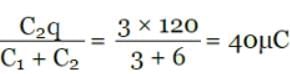JEE Main Physics Test- 4 - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Mock Tests for JEE Main and Advanced 2025 - JEE Main Physics Test- 4
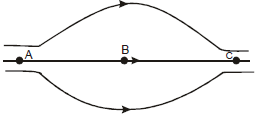
Figure shows some of the electric field lines corresponding to an electric field. The figure suggests that
When the separation between two charges is increased, the electric potential energy of the charges
An electric dipole is placed in a uniform electric field. The net electric force on the dipole
A charge q is placed at the centre of the open end of a cylindrical vessel in figure. The flux of the electric field through the surface of the vessel is
Two capacitors each having capacitance C and breakdown voltage V are joined in series. The capacitance and the breakdown voltage of the combination will be
A dielectric slab is inserted between the plates of an isolated capacitor. The force between the plates will
Two metal spheres of capacitances C1 & C2 carry some charges. They are put in contact and then separated. The final charges Q1 and Q2 on them will satisfy
Two resistances R and 2R are connected in parallel in an electric circuit. The thermal energy developed in R and 2 R are in the ratio
The equivalent capacitance between the points A and B of five identical capacitors each of capacity C, will be
The electric field intensity at a point situated 4 meters from a point charge is 200 N/C. If the distance is reduced to 2 meters, the field intensity will be
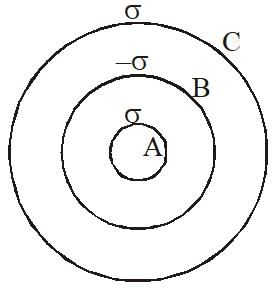
Three concentric metal shells A, B and C of respective radii a, b and c (a < b < c) have surface charge densities +σ,−σ and +σ respectively. The potential of shell B is :-
If an electron is brought towards an another electron, the electric potential energy of the system
An electric dipole is placed at an angle of 30° with an electric field intensity 2 × 105 N/C. It experiences a torque equal to 4 N m. The charge on the dipole, if the dipole length is 2 cm, is
Shown in the figure is a distribution of charges. The flux of electric field due to these charges through the surface S is
Ten identical cells each of emf E and internal resistance r are connected in series to form a closed circuit. An ideal voltmeter connected across the three cells will read
A dipole consists of two particles one with charge +1µC and mass 1kg and the other with charge –1µC and mass 2kg separated by a distance of 3m. for small oscillations about its equilibrium position, the angular frequency, when placed in a uniform electric field of 20kV/m is :-
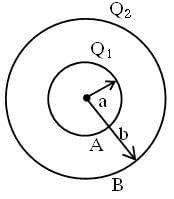
A solid conducting sphere having a charge Q is surrounded by an uncharged concentric conducting hollow spherical shell. Let the potential difference between the surface of the solid sphere and that of the outer surface of the hollow shell be V. If the shell is now given a charge –3Q, the new potential difference between the same two surface is xV, then x is :-
A potentiometer is used for the comparison of e.m.f. of two cells E1 and E2. For cell E1 the no deflection point is obtained at 20 cm and for E2 the no deflection point is obtained at 30 cm. The ratio of their e.m.f.’s is N/3 then N is:
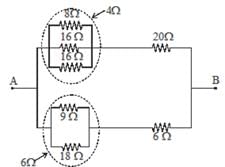
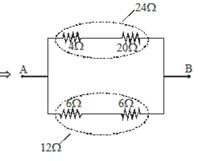
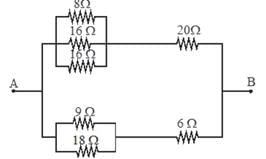
The equivalent resistance of the arrangement of resistances shown in adjoining figure between the points A and B is N × 4 ohm then N is:
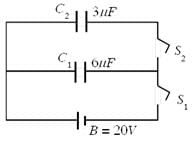
In the circuit shown here C1 = 6μ F, C2 = 3μ F and battery B = 20V. The switch s1 is first closed. It is then opened and afterwards s2 is closed. What is the charge finally on C2.
|
356 docs|142 tests
|


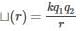
 decrases. if q1 and q2 are of opposite
decrases. if q1 and q2 are of opposite  increases.
increases. may increase or decrease.
may increase or decrease.