Kerala SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 1 (Geography) - KTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Kerala SET Mock Test Series 2025 - Kerala SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 1 (Geography)
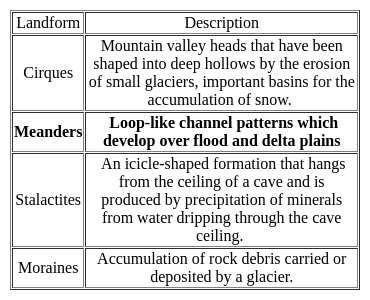
________ are loop-like channel patterns which develop over flood and delta plains.
The theory of plate tectonics proposes that the earth’s lithosphere is divided into ______ major and some minor plates.
Consider the following pairs:
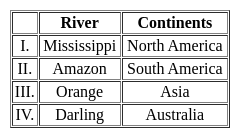
How many of the above mentioned pairs are correctly matched?
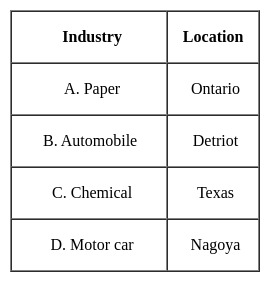
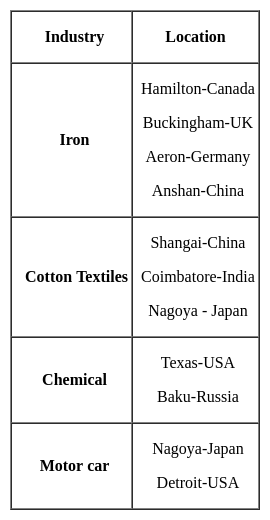
What kind of products were exported by Canada during the 19th century?
a. GIS is an institutional entity, reflecting an organisational structure that integrates technology with a database, expertise and continuing financial support over time.
b. GIS is an internally referenced, automated, spatial information system.
c. GIS is any manual or computer-based set of procedures used to store and manipulate geographically referenced data.
d. GIS can present the results of information analyses using multimedia technologies
Which of the following statements above is /are correct?
i. The type of society has strong influence over the environment .
ii. Human characteristics have impact on the environment.
iii. Education is a key factor on people’s view of life.
iv. Ecosystem services are important for human well-being.
Choose the correct option from below:
Arrange the following continents in descending order of size:
South America, Africa, Antarctica, Europe, North America
Choose the correct option.
Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct answer using the code given below.
Assertion (A) :
Reason (R) : Prices and demand of real increases as distance towards CBD reduces.
i. Goods have high demand with low prices.
ii. The demand curve rotated round the production point to give shape.
iii. As the competition increases, the market areas becomes hexagonal.
a) The Geographical Pivot of History was written by Sir Halford Mackinder in the year 1904
b) According to Spykman, aerial mobility is the new type of geopolitical structure.
Which of the following options are correct?
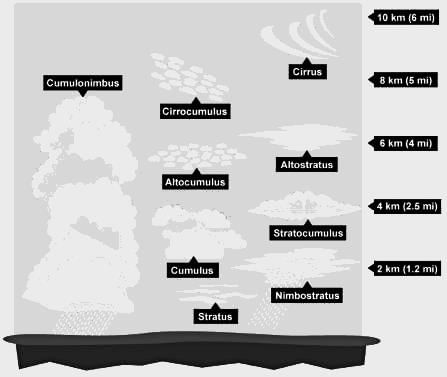
Which of the following is true about Tropical Rain forest?
(A) These forest are called evergreen forests.
(B) The trees in these forests shed their leaves at different times of the year.
(C) Sal, Teak and Shisham are important trees of these forests.
(D) These forests are called monsoon forests.
Choose the correct option
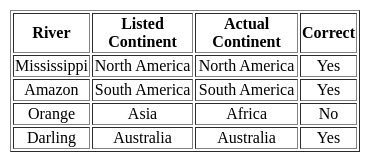
Which one of the following pairs is not correctly matched?
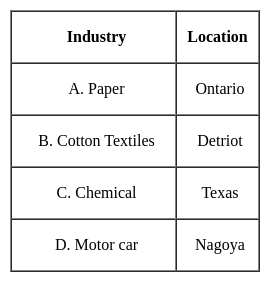
Consider the following statements regarding the Remote Sensing Survey:
1) Information transfer is accomplished by the use of electromagnetic radiation
2) Remote Sensing from space is done by satellites
3) Remote Sensing has no application in Earthquake prediction
Which of the above statements are correct?
A medical geographer researching the spatial distribution of asthma among children 12–17 years of age in a major U.S. city hypothesizes that there is a link between poverty and the prevalence of the disease. Which of the following research strategies would best enable the geographer to explore that hypothesis?
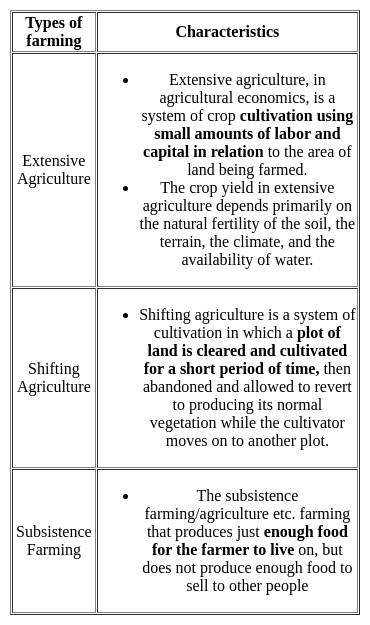
A type of farming in which higher doses of modern inputs are used to obtain higher productivity is known as
(a) The satellite towns are a part of the main city’s municipal corporation.
(b) The satellite towns develop beyond city’s green belt.
(c) The satellite towns are totally dependent upon the main city area.
(d) The satellite towns are separated from the main city physically by a geographical barrier like river.
Code:
A potential downside of medical tourism can be:
Which one of the following is the junction point of the Eastern Ghats and Western Ghats?