Kerala SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 3 (History) - KTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Kerala SET Mock Test Series 2025 - Kerala SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 3 (History)
Who among the following is not related with the Philosophy of Vedanta?
Among the followings the author of the text ‘Khanda Khaddhak’ is-
Stupas have a great significance in Buddhist architecture. In this reference, consider the following statements about the Bharhut stupa:
- It was initially built by Ashoka and was later improvised by the Sungas.
- Its railing contains numerous birth stories of the Buddha’s previous lives or Jataka stories.
- It represents the aniconic phase of Buddhist art.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
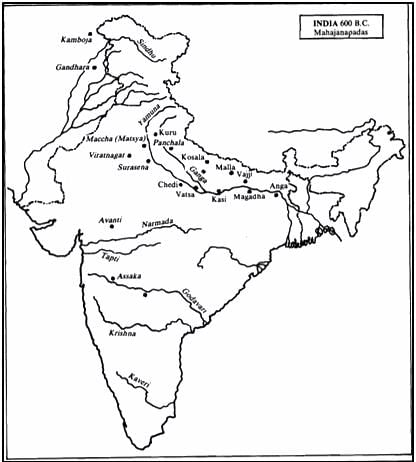
In the context of pre-Mauryan history, consider the following statements:
1. The Mahajanapada period is referred to as the first urbanisation.
2. During this period, the political centre shifted from Indo-Gangetic plains to lower Ganga valley.
3. The 16 mahajanapadas find reference only in Buddhist scriptures.
4. Among the mahajanapadas, rajyas were monarchies and ganas were republics.
Which of the above statements is/are not correct?
With reference to the Pali texts, consider the following statements.
1) The Pali texts speak of two types of villages.
2) The first category included the typical village inhabited by various castes and communities.
3) The second category included the suburban villages which were in the nature of craft villages.
Choose the correct statement
Which among the following is NOT a correct statement in context with the Gupta Era?
In 1950, the four-fold classification of the state put the erstwhile princely states with the legislature in which part?
Logographers, the predecessors of Greek historians, are MOST distinguished from Herodotus, the "Father of History," by their:
Consider the following statements, with reference to the Pali texts.
1) The peasants had to pay one sixth of their produce.
2) Taxes were collected through an intermediate landlord between the peasant and the State.
Choose the correct statement.
Consider the following pairs about Mughal Administration

Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
Who among the following Generals has also been called “Heaven Born General”?
Which act provided some share to Indians in the administration of their county?
Choose the incorrect pair.
1) Epigraphy:- study of the old writings used in the inscriptions.
2) Palaeography:- study of inscriptions.
3) Numismatics:- study of coins
The book 'India's Struggle for Independence' was authored by-
The ‘Saptanga Theory of State’ (Theory of Seven Limbs of the State) was propounded by :
Which of the following coastal regions was the main trading point of the Portuguese?
Which of the following assertions best describes the ideology and methods of the Assertive Nationalists within the Indian freedom movement?
Which of the following Pandya king take help from Sri Lankan king Kassapa-V against Cholas in the battle of Velur.
Consider the following statements about colonialism in India.
Statement (I): Each social class and group felt the effects of colonialism equally.
Statement (II): The notion of freedom was not always the same for each class and group.
Which of the following statements given below is/are correct?
With reference to Pallava dynasty, consider the following pairs:
- Seven Ratha Temple: Built by Rajasimha in eight century
- Kailashnath Temple: Built by Narasimhavarman in seventh century
Which of the pairs given above is/are incorrect?
Who developed Jij Muhammad-shahi in 18th century India?
What was the immediate reason for the Second Carnatic War?