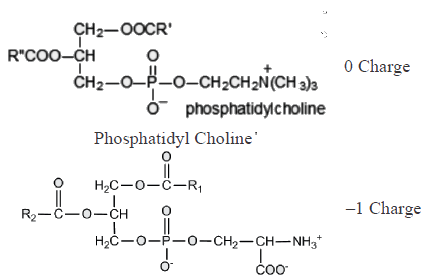Lipids MCQ - Biotechnology Engineering (BT) MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test - Lipids MCQ
Which organ is depended most on the free fatty acids for its regular functioning and energy requirements?
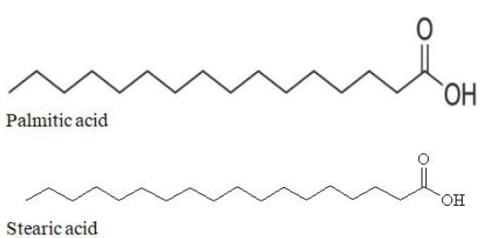
Fatty acids are the long chain carboxylic acids, and their long chain is several carbon atoms long making them amphipathic molecules, some fatty acids contain double bonds and are called unsaturated fatty acids while others that do not contain any double bond in carbon chain are called saturated fatty acids. Pick up the correct option that contains all saturated fatty acids
Platelet activation factor found in heart is one of fastest acting biomolecule, with extremely fast rate kinetics. Biochemically PAF is
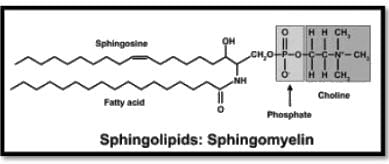
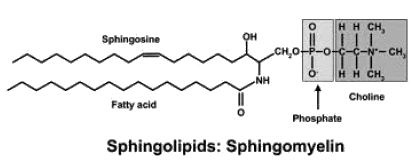
Gangliosides having one, two and three neuraminic acid residues respectively will be names as
‘Drying oil’, oxidized spontaneously by atmospheric oxygen at ordinary temperature and forms a hard water proof material is
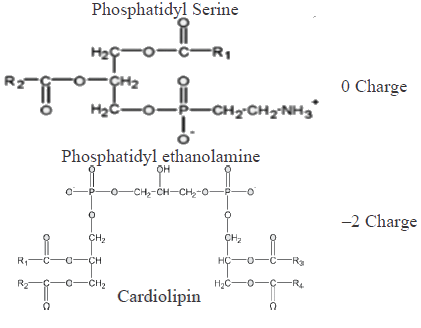
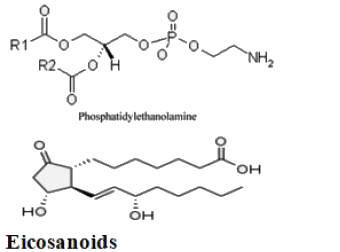
Which of the following combinations represent the correct set of charge on different phospholipids [PC: phosphotidylcholine; PS: Phosphotidylserine, PE: Phosphotidylethanolamine, CL: cardiolipin]
Which of the following types of lipid is present abundantly in the membrane of a cell
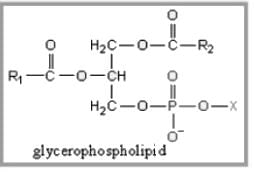
Which one of the following lipids will NOT form a biological membrane?
In Phosphoinositol signalling pathway- Extracellular signals promote activation of phospholipase C, which cleaves the phospholipid phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bisphosphate (PIP2)into two components, what are these two components?
On an average, in an adult human of 70 kg, around 10 kg is fat reserve. It is given that the calorific value of fat is 9 kcal/g and that of glucose is 4 kcal/g. The approximate weight (in kg) of the same human being, if he would have had no fat but stored glucose to generate equivalent energy will be_________ (answer upto one decimal place)
The number of possible stereoisomers of cholesterol are_______. (Answer in integer). (Based on the number of asymmetric carbon atoms present in cholesterol).
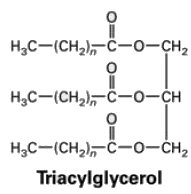
A 250 mg sample of pure oil requires 47.5 mg of KOH for complete saponification. The average MW of the triglycerides in the olive oil is________. (Answer in integer)
The olive oil was reacted with iodine. The average MW of triglycerides present in the olive oil is 884 g. Exactly 578 mg of I2 were absorbed by 680 mg of the oil. On an average, the number of double bonds that are present in a molecule of triglyceride are _______ (Answer in integer)