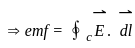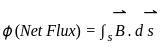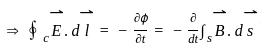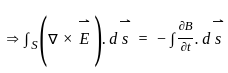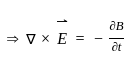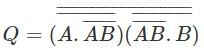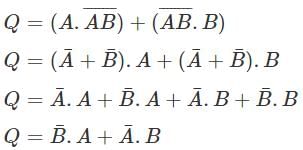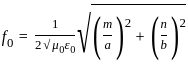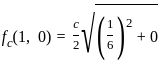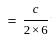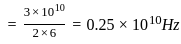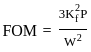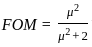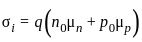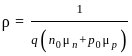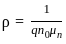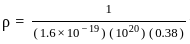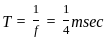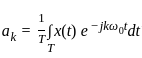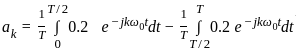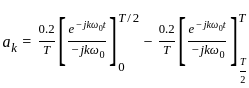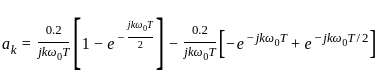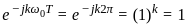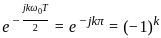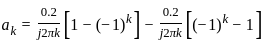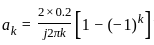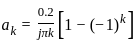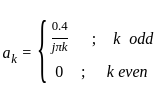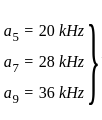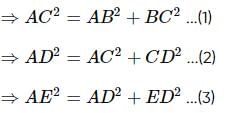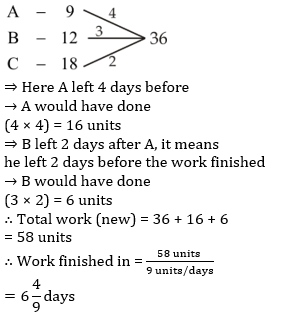MPPGCL JE Electronics Mock Test - 2 - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPPGCL JE Electronics Mock Test - 2
What will be the minimum numbers of tap require to realize a FIR filter having fpass = 10 kHz and fstop = 15 kHz, 0.1 dB pass band ripple and 60 dB attenuation in stop band. The sampling frequency is 200 kHz.
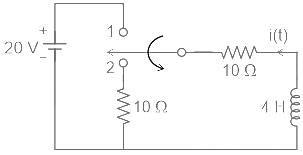
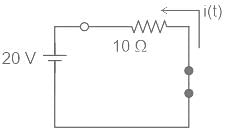
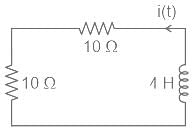
For the circuit shown in figure, find current i(t) after the switch moves from position '1' to position '2' -
 q
q
 q
qThe bit stream 01001 is differentially encoded using ‘delay and EXNOR’ scheme for DPSK transmission. Assuming reference bit as 1 and assigning ‘0’ and ‘π’ for 1s is and 0s respectively, in the encoded sequence, the transmitted phase sequence is:
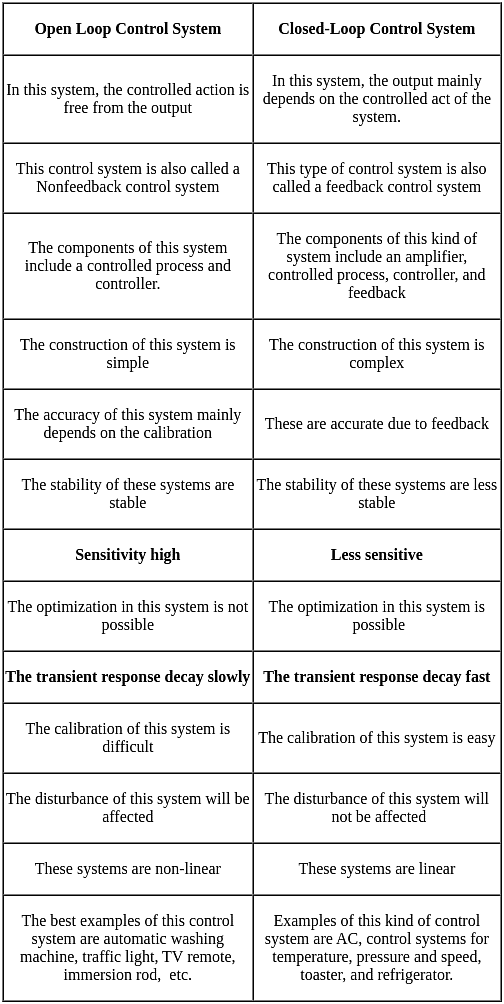
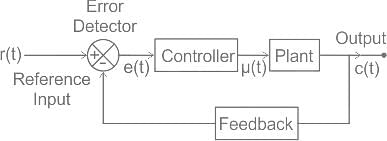
An automatic control system in which the output is a variable is called a/an-
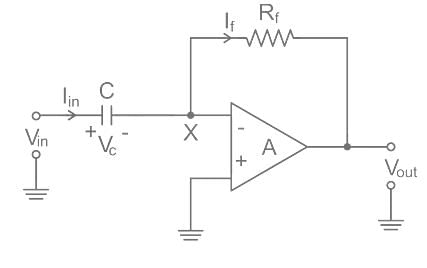
Which of the following statements about the Op-Amp differentiator circuit is INCORRECT?
A DSB-SC signal is generated using the carrier cos(ωet+θ) and modulating signal x(t). The envelope of the DSB-SC signal is
On which of the following factors does the ray's brightness of a CRO depend?
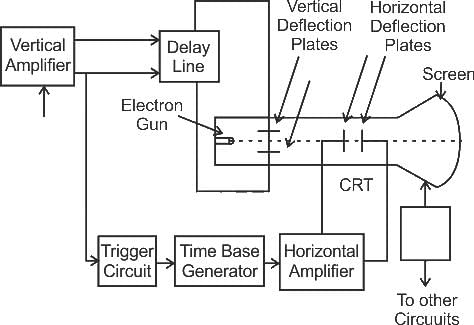
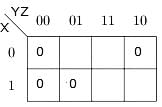
A boolean function is given as F(x, y, z) = ∑(1, 3, 6, 7). What is its equivalent canonical form?
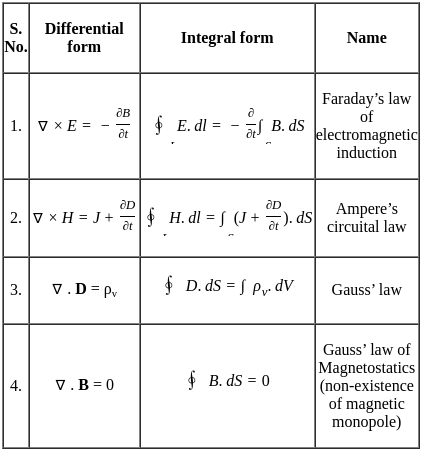
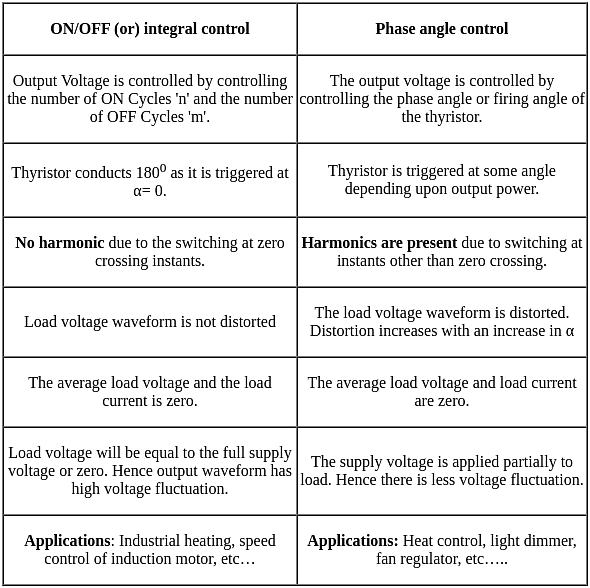
Consider the following statements regarding the advantages of closed loop negative feedback control systems over open loop systems:
1. The overall reliability of the closed loop systems is more than that of open loop system.
2. The transient response in the closed loop system decays more quickly than in open loop system.
3. In an open loop system, closing of the loop increases the overall gain of the system.
4. In the closed loop system, the effect of variation of component parameters on its performance is reduced.
Of these statements are correct.
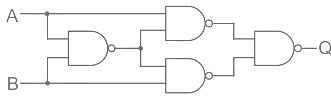
Which of the following will be the value of Q
Consider a rectangular waveguide with dimensions a = 6 cm and b = 3 cm. operating in the dominant mode (TE10).
If three signals (1 GHz, 2 GHz, 3 GHz) are available for propagation, which of the following options is correct?If the transmission bandwidth is doubled in FM, then the figure of merit (FOM) is
In the following, pick out the linear systems
(i) d2y(t)/dt2 + 9a1dy(t)/dt + a2y(t) = u(t)
(ii) y(t)dy(t)/dt + a1y(t) = a2 u(t)
(iii) 2d2y(t)/dt2 + tdy(t)/dt + t2y(t) = 5
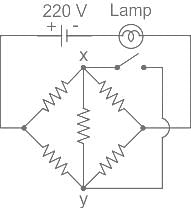
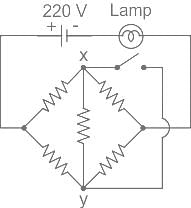
For the circuit shown, if the resistance of each resistor is 100 ohm, the potential at X is ________.
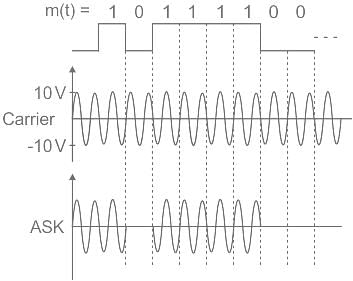
In ______ a Carrier is transmitted for a 1-bit, and nothing is transmitted for 0-bit, this is analogous to flashing light communication.
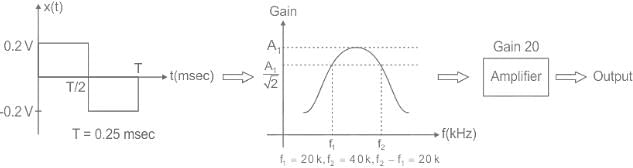
A 4 kHz square wave of duty cycle 50% and p-p (0.2V to +0.2V) is applied as input to 20 kHz narrow bandpass filter which is followed by an amplifier of voltage gain 20. Find out the frequency components present in the output. Given that cut off frequencies of a narrow bandpass filter is 20 kHz and 40 kHz.
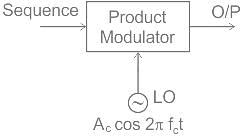
In which modulation technique does the phase of the carrier signal is changed by varying the sine and cosine inputs at a particular time.
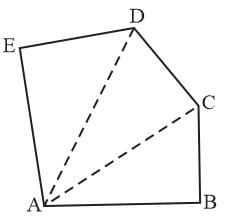
In a polygon ABCDE, BC is perpendicular to AB, CD to AC and DE to AD, then AB2 + BC2 + CD2 + DE2 is
A, B and C can complete a piece of work in 9, 12 and 18 days respectively. They started working together, but A left the work before 4 days of its completion. B also left the work 2 days after A left. In how many days was the work completed?
'Forest' is related to 'Vivarium' in the same way as 'sea' is related to:
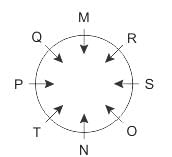
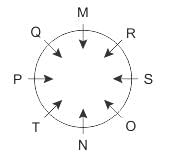
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions besides.
M, N, O, P, Q, R, S and T are sitting around a circular table and all are facing the centre of the table. M is sitting fourth to the right of N. P is sitting second to the left of N. Q is sitting third to the right of S. T is sitting second to the left of O. S is not sitting beside P. O is not sitting beside M.
Q. Who among the following sits exactly opposite to Q?


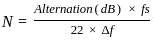
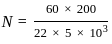

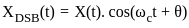
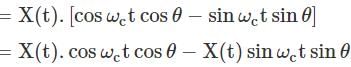
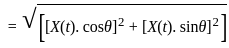
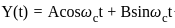
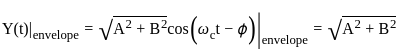
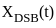
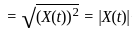 .
.
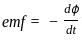 ----(1)
----(1)