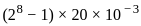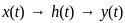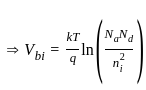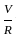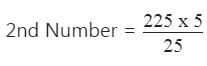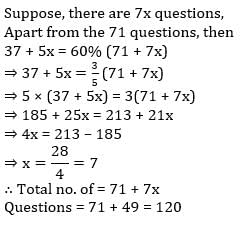MPPGCL JE Electronics Mock Test - 4 - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPPGCL JE Electronics Mock Test - 4
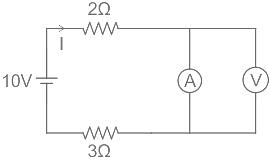
Find the value of current density for a compensated p-type material having the mobility of 500 cm2/V-sec and intensity of Electric field as 5 V. The carrier concentrations are Na = 1016/cm3 and Nd = 5 × 1015/cm3.
Consider the following statements regarding Programming Logic Controller (PLC):
1. It was developed to replace the microprocessor.
2. Wiring between devices and relay contacts are done in its program.
3. Its I/O interface section connects it to external field devices.
4. It requires extensive wiring in the application.
Which of the above statements are correct?
For a (7, 4) cyclic code, the generator polynomial g(x) = 1 + x + x3.
Find the data word for the codeword 0110100
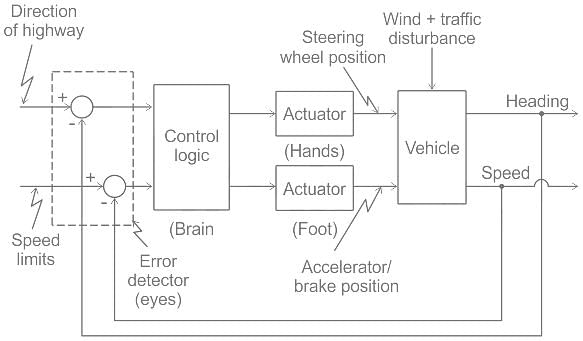
The control system illustrated in the figure is an example of a/an:
Protocols in which the sender sends one frame and then waits for an acknowledgement before proceeding for next frame are called as ________.
In a NPN transistor, if the base current is 100 μA and the current gain, β = 200, the collector current will be:
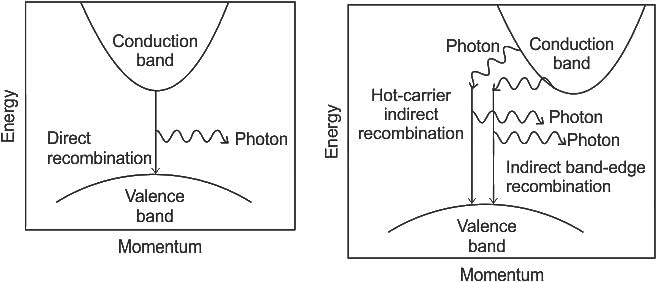
In frequency modulation, if the frequency of the modulating voltage is doubled, the frequency deviation
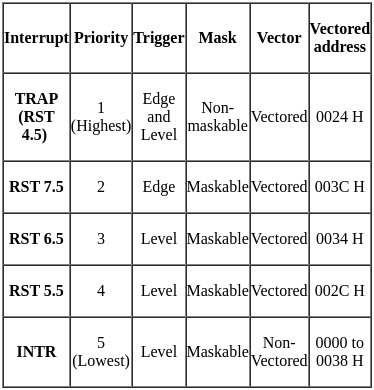
What is the restart address of TRAP interrupt in 8085 microprocessor?
In the circuit shown below, the reading of the ideal ammeter and voltmeter, respectively, will be:
Which of the following statements is NOT true:
The most suitable material for manufacturing of LED is:
The minimum change in the measured variable which produces an effective response of the instrument is known as
LCM of two numbers is 225 and their HCF is 5. If one number is 25, the other number will be?
What is the area of the largest square that can be made in a rectangle with 10 meters length and 4 meters width?
Suresh solved 60% of the question in an examination correctly. If out of 71 Questions solved by Suresh, 37 questions are correct and out of remaining every 7 questions, 5 questions have been solved by Suresh correctly. Then find the total number of questions asked in the examination?
Directions: Each of the following consists of a question and two statements numbered I and II given below it. You have to decide whether the data provided in the statements are sufficient to answer the question:
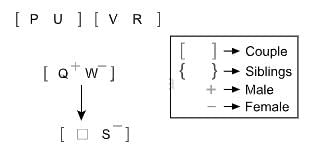
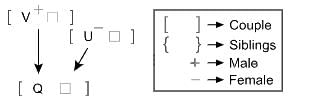
Nine persons P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, and X belongs to a family of three generation where only married couples have children.
How is X related to S?
I. P is married to U. V is married to R. Q is the husband of W. S is the daughter-in-law of W.
II. V is the father of Q. U is the mother-in-law of Q. T is the sibling of X. T is unmarried.
Without stoppage, a train travels a certain distance with an average speed of 60 km/h, and withstoppage, it covers the same distance with an average speed of 40 km/h. On an average, howmany minutes per hour does the train stop during the journey?
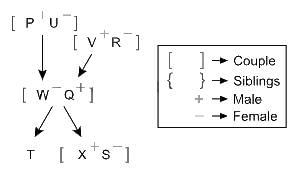
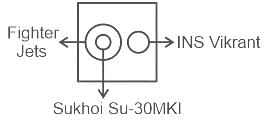
Identify the diagram that best represents the relationship among classes given below:
Fighter Jets, Sukhoi Su-30MKI, INS Vikrant
In the number 76534218, each digit is replaced by the next digit i.e., '1' is replaced by '2', '2' is replaced by '3' and so on and then the digits are arranged in ascending order from left to right, which digit will be fifth from the left end?


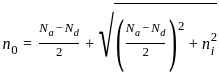

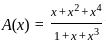
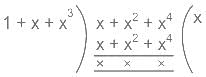
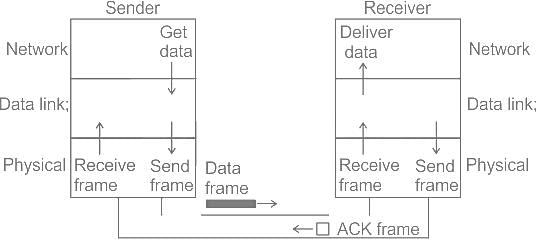
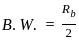 ; where Rb = Bit rate, given by;
; where Rb = Bit rate, given by;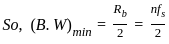
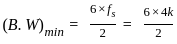
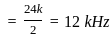
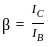
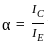
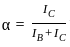
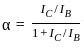
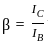
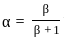 'or'
'or'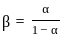
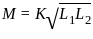
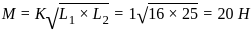
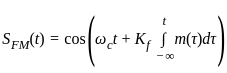
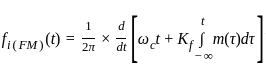
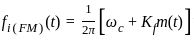
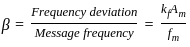
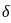 is:
is: 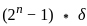 where n is the number of bits
where n is the number of bits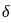 = 20 mV
= 20 mV