MPTET Varg 1 Chemistry Mock Test - 1 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPTET Varg 1 Chemistry Mock Test - 1
Learning and knowledge are the greatest assets of a man.
इस वाक्य का हिंदी रूपांतरण है?
इस वाक्य का हिंदी रूपांतरण है?
I am given this responsibility.
वाक्य का हिन्दी अनुवाद होगा-
वाक्य का हिन्दी अनुवाद होगा-
Direction: Choose the word which is most nearly SIMILAR in meaning as the word printed in underline.
She suddenly felt old and weary.
She suddenly felt old and weary.
Select the most appropriate synonym of the underlined word.
He was a benevolent old man and wouldn't hurt a fly
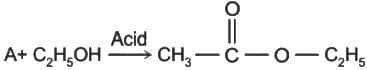
Mixture of 1°, 2°, and 3° amines can be separated by
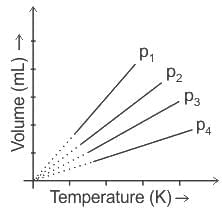
A plot of volume (V) versus temperature (T) for a gas at constant pressure is a straight line passing through the origin. The plots at different values of pressure are shown in Fig given below. Which of the following orders of pressure is correct for this gas?
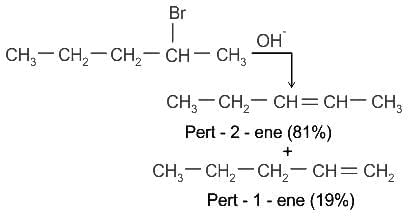
The major product formed in the dehydrohalogenation reaction of 2-Bromo pentane is Pent-2-ene. This product formation is based on?
The number of electrons involved in the process of 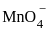 getting reduced to Mn2+ in acidic medium is:
getting reduced to Mn2+ in acidic medium is:
Given below are two statements
Statement I: The possibility of molecularity being three is very rare.
Statement II: The probability of more than three molecules colliding simultaneously is very small.
In the light of the above statement, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
Which is the correct increasing order of boiling points of the following compounds
1-bromoethane, 1-bromopropane, 1-bromobutane, Bromobenzene
In the Nucleophilic substitution reactions of Alkyl halides, which one of the following Nucleophiles cannot act as an Ambident Nucleophile?
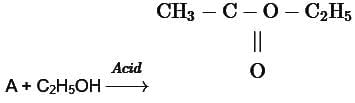
R - OH + HX → R - X + H2O In the above reaction, the reactivity of different alcohols is
Which of the following oxo-acids of sulphur has peroxide linkage ?
The correct option for free expansion of an ideal gas under adiabatic condition is :
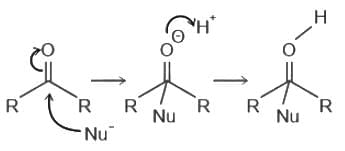
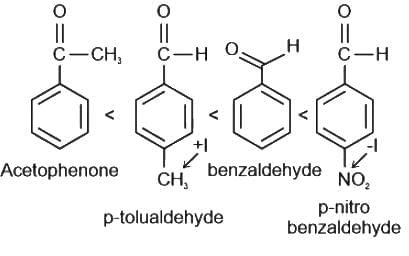
Increasing order of reactivity towards nucleophilic addition is:



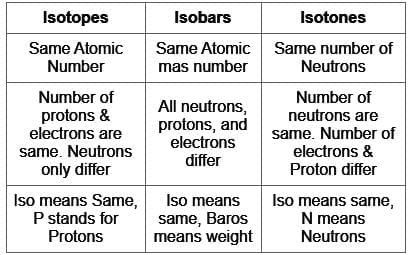
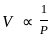
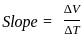
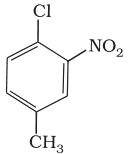
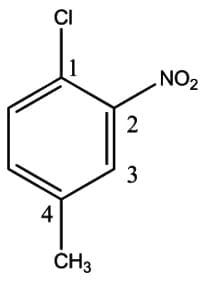
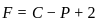
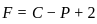
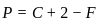
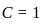
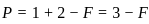
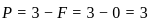

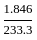
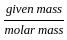
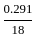
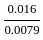
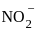 ,
,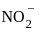 has two attacking centres i.e.. O and N.
has two attacking centres i.e.. O and N.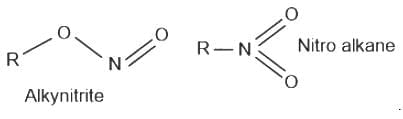 .
.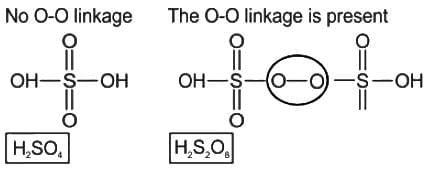
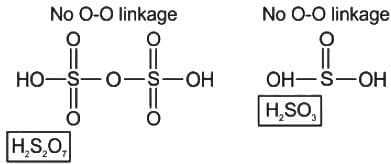
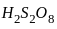 is having -O-O- linkage.
is having -O-O- linkage.
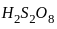 .
.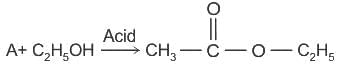
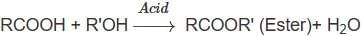

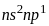 ) show +3 and +1 oxidation states in their compounds. The stability order of these oxidation states will be as,
) show +3 and +1 oxidation states in their compounds. The stability order of these oxidation states will be as,