MPTET Varg 1 Physics Mock Test - 2 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPTET Varg 1 Physics Mock Test - 2
निम्नलिखित में से कौन-सा शब्द 'पति' का पर्यायवाची है?
'उत्तराधिकार में प्राप्त सम्पत्ति' - इन अनेक शब्दों के लिए एक शब्द है-
“अनुग्रह - अनुकंपा, आधि - व्याधि” इन समोच्चारित शब्दों के क्रमशः सही अर्थ वाली पंक्ति को चुनें?
Choose the most appropriate antonym of the underlined word given in the sentence below:
There was jubilation in the crowd as the winning goal was scored.
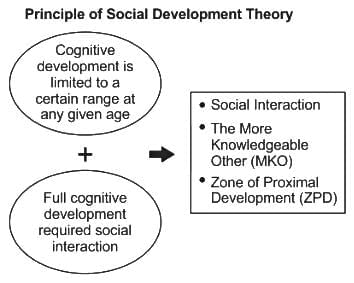
Which of the following statements describe Piaget and Vygotsky's views on language and thoughts correctly?
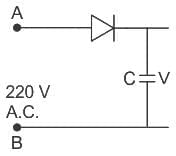
A 220 V A.C. supply is connected between points A and B as shown in the figure. What will be the potential difference V across the capacitor?
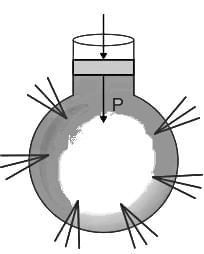
The pressure excreted by the liquid at the bottom of a vessel depends on:
Which among the following statements is true about Huygen's principle
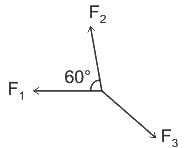
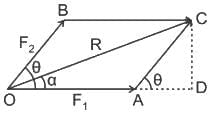
The magnitude of resultant forces F1 and F2 is
A wire of young modulus Y has length L and area A. Find the minimum force required to increase the length of wire by 'l'.
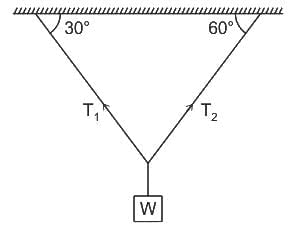
While teaching in a class Mayank ask a question on the equilibrium of particle as shown in the figure and ask the student to find the weight of a body, if T2 = 100 N. Shreya gives the correct answer. So, what is the answer given by Shreya?
Which of the following processes are thermodynamically reversible?
For a projectile, the maximum height reached H and the time of flight T are related as H = nT2. The value of n is (Take g = 10 m/s2)
If the net external torque on a rotating object is zero, Which of the following quantity will be constant?
Which of the following is not a unit of electric field?
If an electron is moving in a magnetic field, then for which of the following condition the magnetic force is maximum?
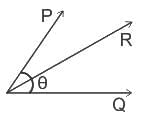
Two coplanar concurrent forces of magnitude 3 kN and 4 kN makes an angle 60° with each other, then the magnitude of resultant is:
Match List I with List II
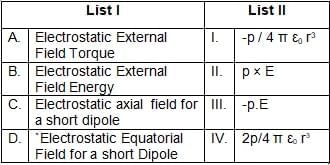
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The magnitude of the magnetic field at a far distance along the axis of the solenoid is B. If the current in the solenoid is doubled then the magnetic field at that point will become:



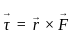
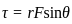
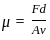 , where, F= force, d= distance between the layers, A= cross-sectional area, v= velocity
, where, F= force, d= distance between the layers, A= cross-sectional area, v= velocity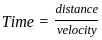
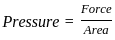
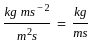 . . . . . . . . .(1)
. . . . . . . . .(1)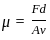
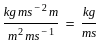 . . . . . . . . (2)
. . . . . . . . (2)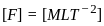
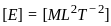
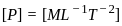
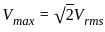
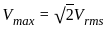
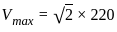

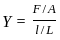
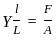
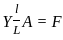
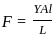
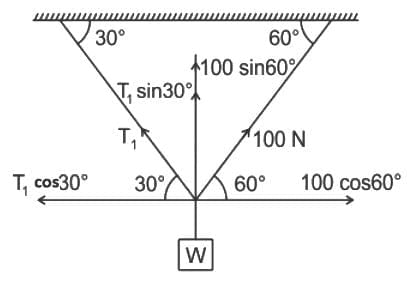
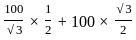 = W
= W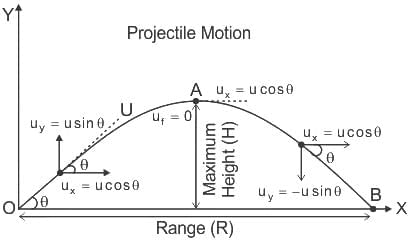
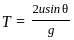
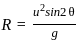
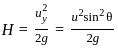
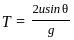
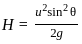
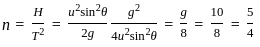
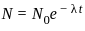
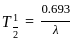
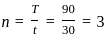
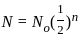
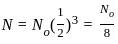
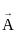 and
and 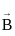 , the resultant will be:
, the resultant will be: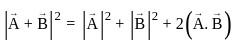
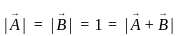
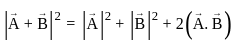
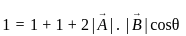
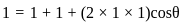
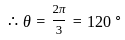
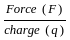
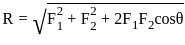
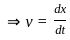
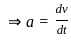
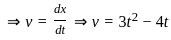
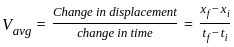
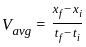
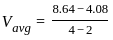
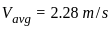
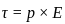
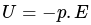
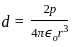
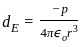
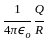
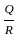
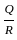
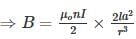
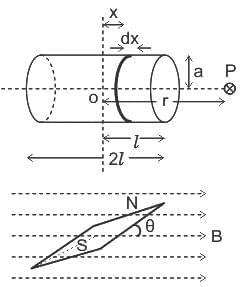
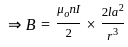 -----(1)
-----(1)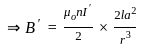
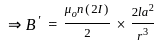
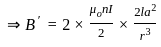 -----(2)
-----(2)















