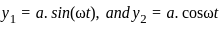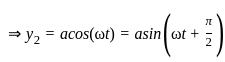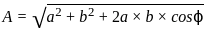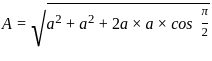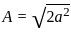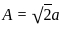MPTET Varg 1 Physics Mock Test - 3 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPTET Varg 1 Physics Mock Test - 3
'जिसके हृदय में ममता नहीं है' इस वाक्यांश के लिए एक शब्द बताइए -
Select the most appropriate article to fill in the blank. If an article is not needed, then select 'no article'.
Can you lend me ______ couple of books?
The following sentence has been divided into parts. One of them may contain an error. Select the part that contains the error from the given options. If you don’t find any error, mark ‘No error’ as your answer.
Every Saturday, / the workers gets / their weekly wages.
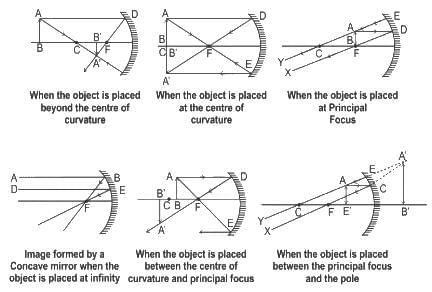
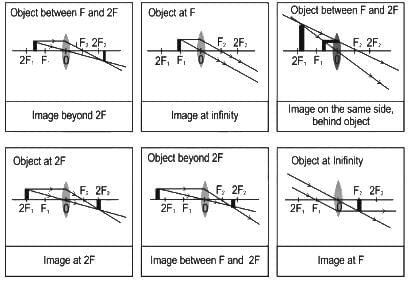
You are provided with a concave mirror, a concave lens, a convex mirror and a convex lens. To obtain an enlarged image of an object you can use either
The self inductance L of a solenoid of length l and area of crosssection A, with a fixed number of turns N increases as
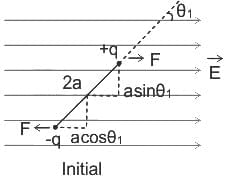
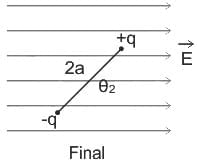
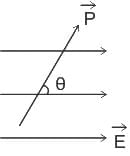
An electric dipole of dipole moment p is placed in a constant external electric field E. The angle between the electric field and dipole moment is θ. The potential energy of the dipole moment is given by (assume potential energy to be zero when electric field and dipole moment make an angle π/2)
A particle of mass 5 m at rest suddenly breaks on its own into three fragments. Two fragments of mass m each move along a mutually perpendicular direction with speed v each. The energy released during the process is,
Binding energy per nucleon of 235U and 116Pd is 7.2 MeV and 8.2 MeV respectively. Calculate the energy released (Q) in the reaction given below. (Energy of a g ray = 5.2 MeV)
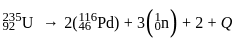
In a LCR circuit capacitance is changed from C to 5C for the resonant frequency to remain unchanged, the inductance should be changed from L to value:
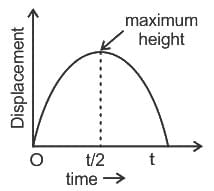
Which one of the following displacement (s) - time (t) graphs correctly represent the motion of a body thrown vertically up and falling back to the point of projection?
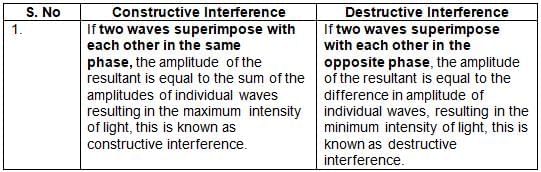
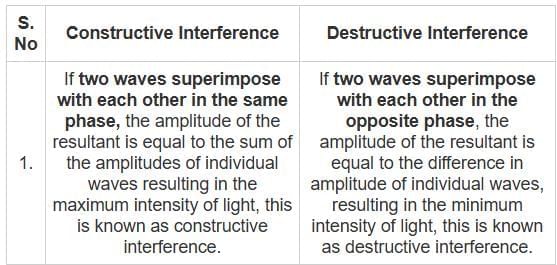
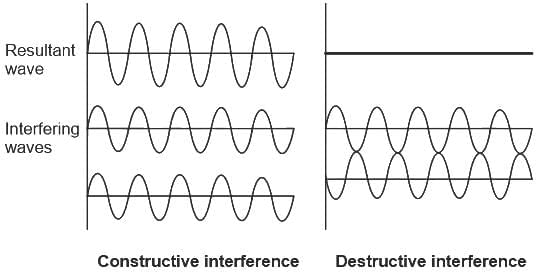
For the destructive interference of the two similar waves, the phase difference between the waves must be:
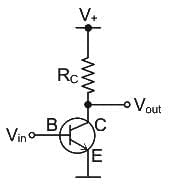
In a CE amplifier, the input ac signal to be amplified is applied across
A black body is at a temperature of 500 K. It emits energy at a rate which is proportional to
A body such as a wheel or primarily a circular solid body which is moving over a horizontal surface undergoes-
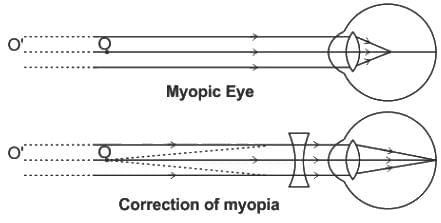
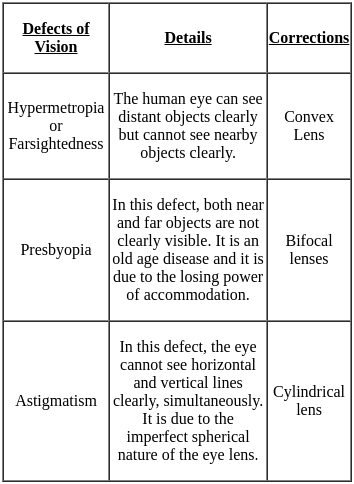
Which type of lens is required for correcting the vision of a person with myopia?
The force acting on the bullet when it moves through the air toward a target is:
The position of a particle is given by x = -2t2 + 4t. How much time the particle will take to come in rest?
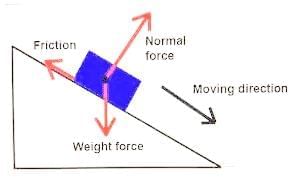
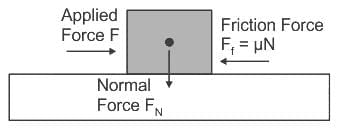
A block of 100 N weight is placed on the surface. The friction force acting in the opposite direction is 28 N. Calculate the coefficient of friction.
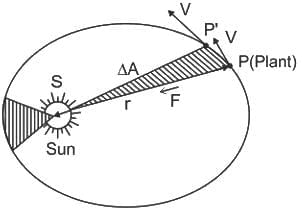
Two planets A and B are moving around the sun in the elliptical orbit. If the ratio of the length of the semimajor axis of planet A to planet B is 4 : 1, then find the ratio of the time-period of planet A to time-period of planet B.
A convex lens is made of a material having refractive index 1.2. Both the surfaces of the lens are convex. If it is dipped into water (μ = 1.33), it will behave like:
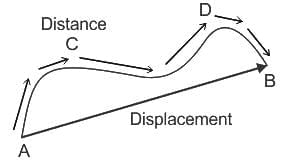
If a body after travelling some distance comes back to its starting point then-
Two long wires A and B are placed parallel to each other. If the ratio of current in the wire A to wire B is 1 : 2, then the ratio of the force per unit length on wire A to wire B is:
Two waves are represented by y1 = a∙sin (ωt), and y2 = a∙cos (ωt). If both the waves are superimposed then the resultant amplitude will be:
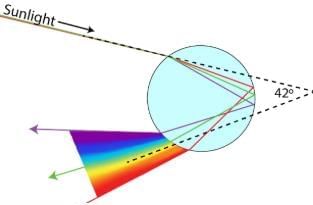
The two necessary conditions for observing a rain bow in the sky are:




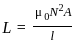
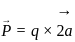
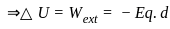
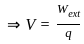
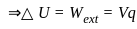
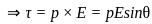
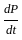
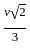
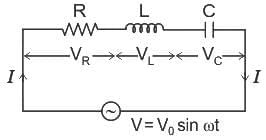
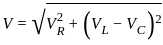

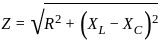
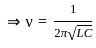
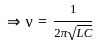
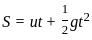
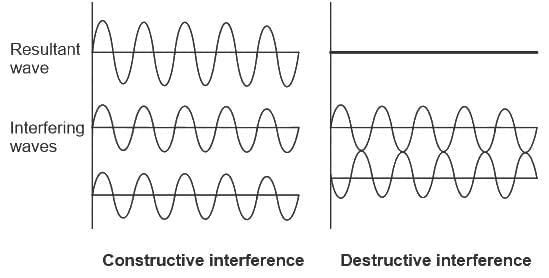
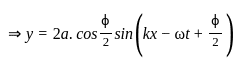
 .
.
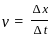
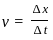
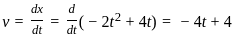
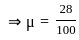
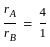
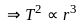 -----(1)
-----(1)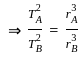
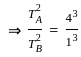
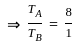
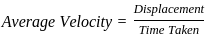

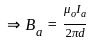
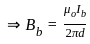
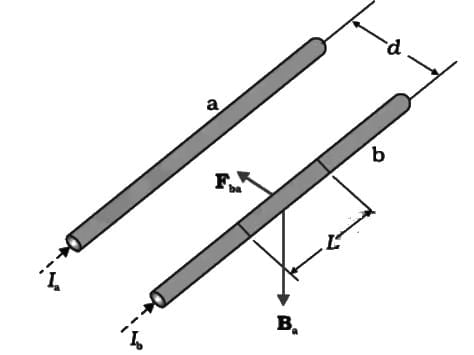
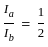
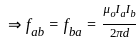 -----(1)
-----(1)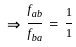
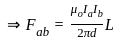
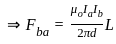
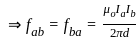
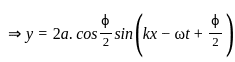
 .
.