Newton's Law Of Motion NAT Level - 2 - Physics MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Topic wise Tests for IIT JAM Physics - Newton's Law Of Motion NAT Level - 2
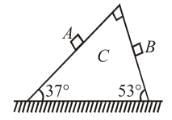
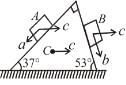
In the figure shown blocks A and B are kept on a wedge C. A, B and C each have mass m. All surfaces are smooth. Find the acceleration of C.

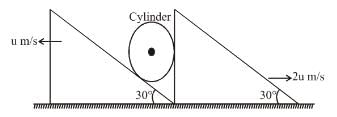
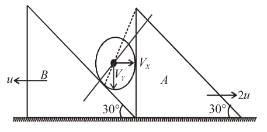
System is shown in the figure. Assume that cylinder remains in contact with the two wedges. if u = 1.52, The velocity of cylinder (in m/s) is :

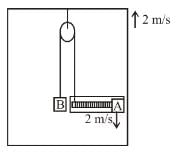
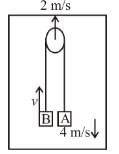
In the figure shown the velocity of lift is 2m/s while string is winding on the motor shaft with velocity 2m/s block A is moving downwards with a velocity of 2m/s, then find out the velocity of block B (in m/s).

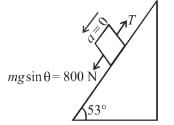
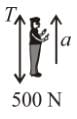
In the arrangement shown, by what acceleration (in m/s2) the boy must go up so that 100kg block remains stationary on the wedge. The wedge is fixed and friction is absent everywhere. (Take g = 10 m/s2)

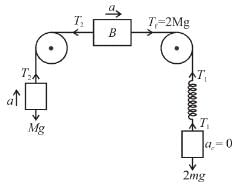
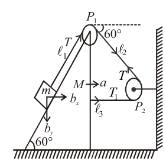
In the figures shown P1 and P2 are massless pulleys. P1 is fixed and P2 can move. Masses of A, B and C are 9m/64, 2m and m respectively. All contacts are smooth and the string is massless 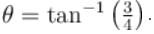 Find the acceleration of block C in m/s2.
Find the acceleration of block C in m/s2.
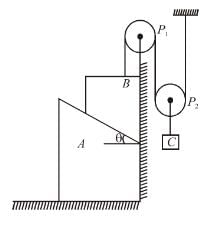
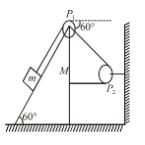
In the arrangement shown in the Figure, a block of mass m = 2 kg lies on a wedge on mass M = 8 kg. The initial acceleration of the wedge (if the surfaces are smooth) given by 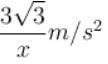 then x is.
then x is.
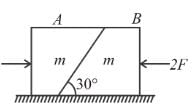
Two block A and B each of mass m are placed on a smooth horizontal surface. Two horizontal force F and 2F are applied on both the blocks A and B respectively as shown in figure. The block A does not slide on block B. Then the normal reaction acting between the two blocks is nF : find the value of n.
In the figure shown, the pulleys and strings are massless. The acceleration (in m/s2) of the block of mass 4m just after the system is released from rest is ...........
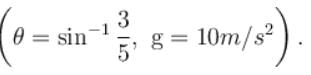
Inside a horizontally moving box, an experimenter finds that the when an object is placed on a smooth horizontal table and is released, it moves with an acceleration of 10 m/s2. In this box if 1 kg body is suspended with a light string, the tension (in N) in the string in equilibrium position. (w.r.t.) experimenter will be (Take g = 10 m/s2)
In the figure shown all the contacts are smooth. Strings and spring and light. Initially A is held by someone and B and C are at rest and in equilibrium also. Find out the acceleration of block C in m/s2 just after the block A is released. Masses of A, B and C are M, M and 2M respectively.
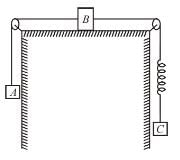


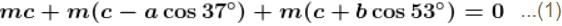
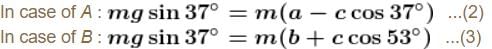
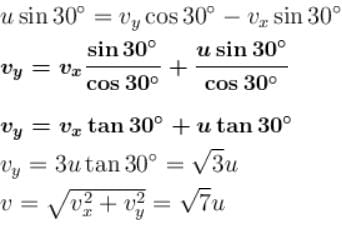

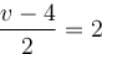
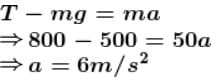
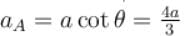 towards left.
towards left.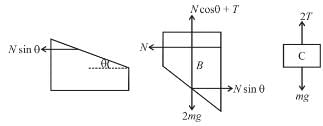

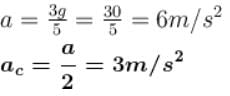
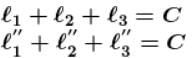

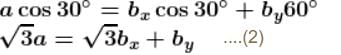
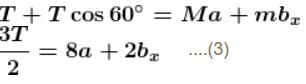
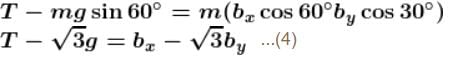
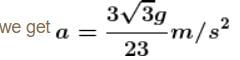
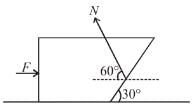
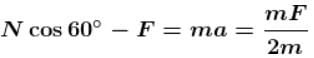
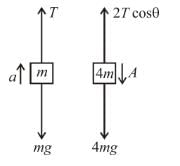

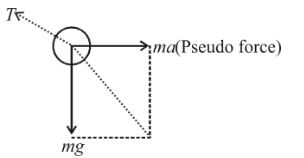
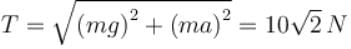
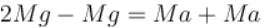 ⇒ a = g/2
⇒ a = g/2