OPSC OAS Prelims Paper 1 Mock Test - 1 - OPSC OCS (Odisha) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - OPSC OAS Prelims Paper 1 Mock Test - 1
Consider the following events:
- Abolition of sati
- Passing of the Widow Remarriage Act
- Beginning of the 1857 revolt
- Queen’s Proclamation
The correct chronological order of these events is:
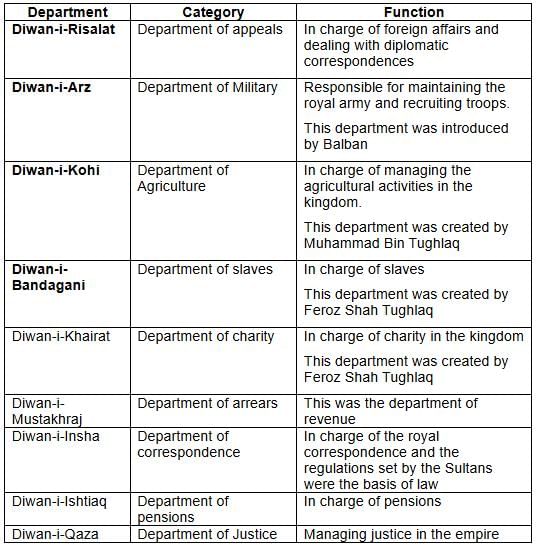
In the context of Indian history, the principle of 'Dual government' refers to
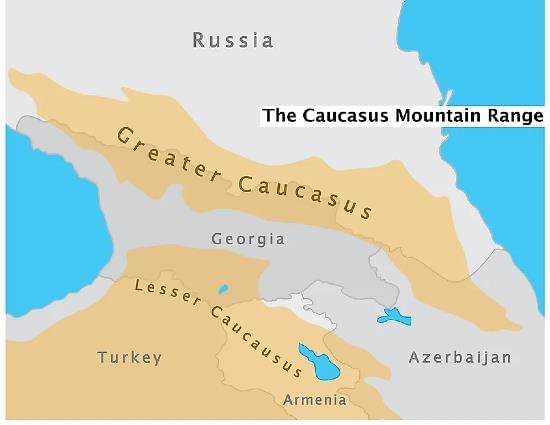
Consider the following pairs:
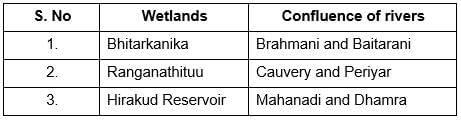
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?

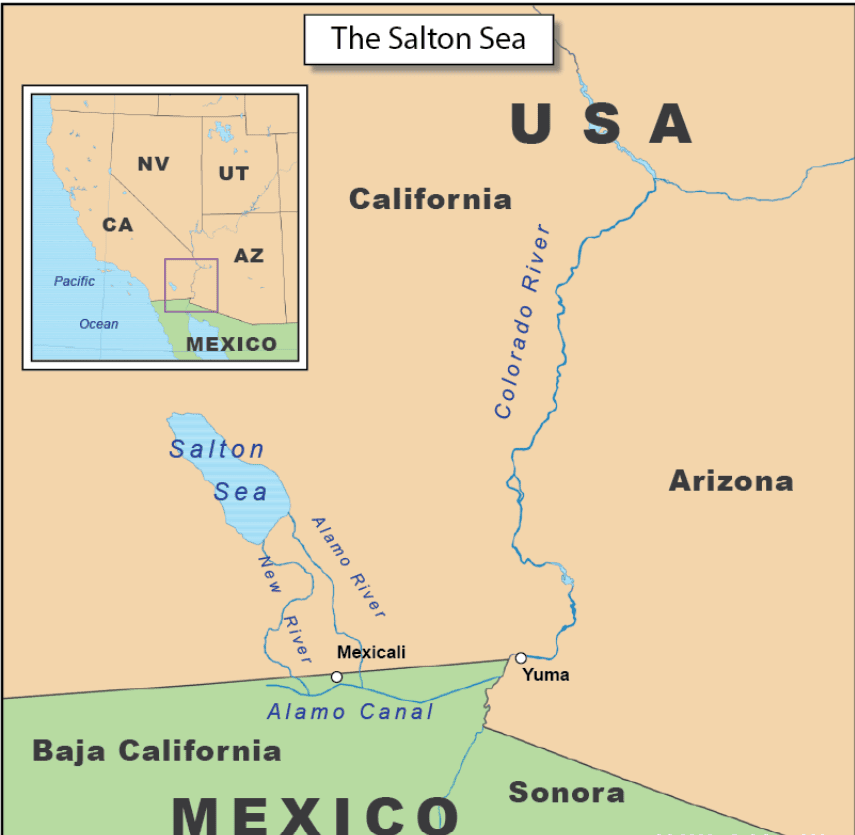
The Salton Sea a landlocked sea, was recently in the news due to the discovery of a lithium reserve, it is located in
Which one of the following activities of the Reserve Bank of India is considered to be part of 'sterilization'?
Which of the following is not a method adopted by RBI to maintain the liquidity of economy?
Consider the following pairs:
How many pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
Which one of the following statements is correct regarding the Wolbachia method recently in news?
Consider the following pairs:
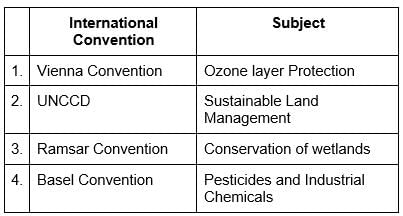
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
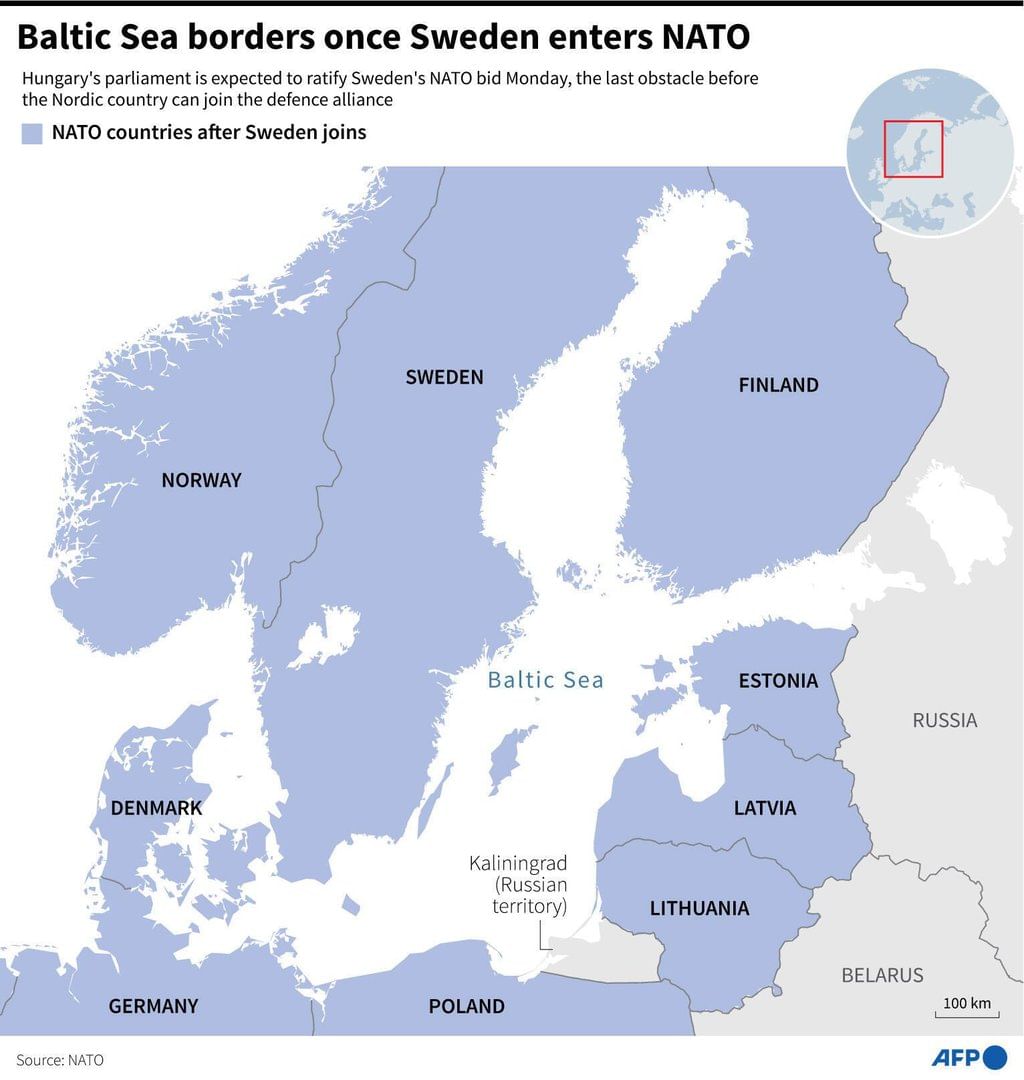
The term NATO lake often seen in the news, is associated with:
With reference to Lok Adalats, which of the following statements is incorrect?
Bead industries were found in which among the following sites of Indus valley civilization:
- Lothal
- Banawali
- Chanhudaro
- Dholavira
- Alamgirpur
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
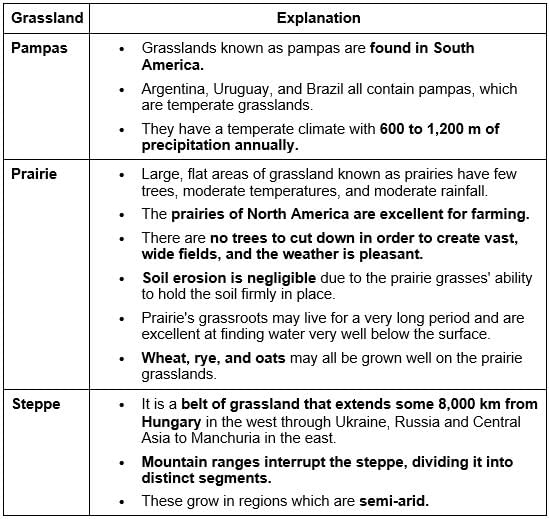
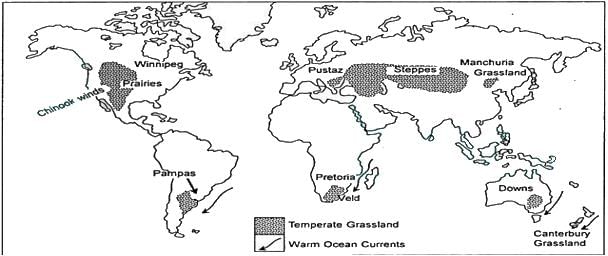
A type of savanna grassland that lies between 24o-35o south. This is rich in plant species and is more diverse than forest ecosystems. The climate here is subtropical humid and the rainfall is distributed throughout the year.
Which among the following vegetation types is described in the above paragraph?
Who appoints the Chairman and members of the State Public Service Commission?
In the Government of India Act 1919, the functions of Provincial Government were divided into "Reserved" and "Transferred" subjects. Which of the following were treated as "Reserved" subjects?
- Administration of Justice
- Local Self-Government
- Land Revenue
- Police
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Red colour lights are used for emergency purposes because
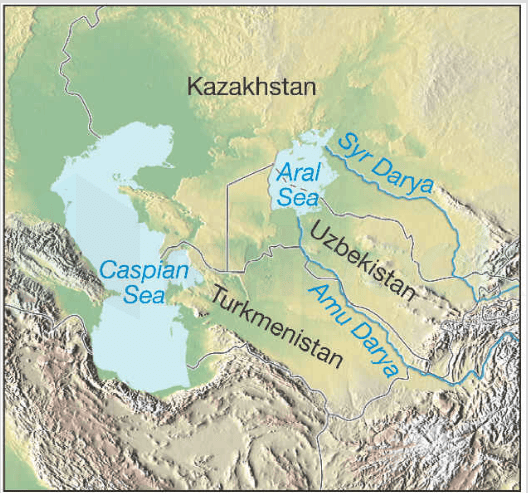
Aral Sea is located between which two countries:
Which one of the following protected areas is well-known to be a natural habitat for Golden Langurs, an endangered primate species?
Consider the following functions
- Urban planning including town planning.
- Regulation of land use and construction of buildings.
- Planning for economic and social development.
- Roads and bridges.
The Twelfth Schedule of the Constitution lists the various Functions of Municipalities. Which of the above functions are included in the schedule?
In which of the following matters, the powers, and status of the Legislative council are broadly equal to that of the Legislative assembly?
- Approval of ordinances issued by the governor.
- With respect to the ratification of a constitutional amendment bill.
- Selection of ministers including the chief minister.
- With respect to the passing of a no-confidence motion to remove the council of ministers.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Average temperature of warm dry summer months ranges between 27ºC and 32ºC. Most of their annual rainfall occurs through cyclonic and orographic types of rain. Trees are normally deciduous. The forest is open and less luxuriant. Most of the forests yield valuable timber like teak. Other kinds of timber are sal, acacia and eucalyptus. This is the most likely description of?
With reference to the Gandhara School of Art, consider the following statements:
- It was a combination of Hellenistic, West Asiatic, and native elements.
- This style of art was closely associated with Hinayana Buddhism and hence the main theme of this art was Lord Buddha and Bodhisattvas.
- Early Gandhara School used bluish-grey sandstone while the later period saw the use of mud and stucco.
- It mostly flourished in the areas of Pakistan and present North-Western India.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
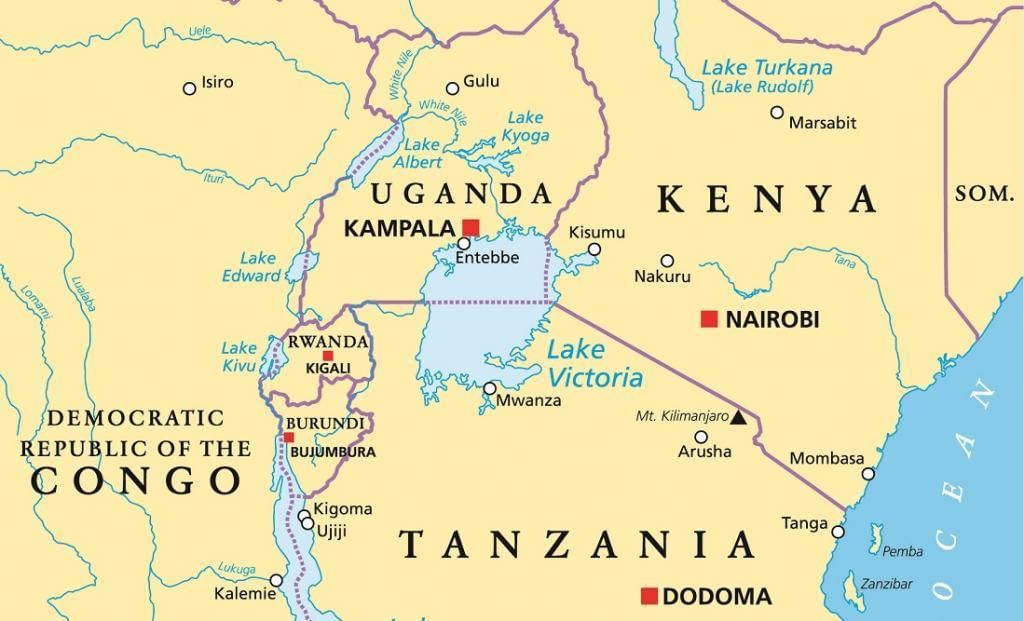
Consider the following countries:
- Sudan
- Tanzania
- Uganda
- Kenya
How many of the above countries share a land border with Lake Victoria?
'Extended Fund Facility' relates to the lending provisions by which one of the following?
Who among the following is prescribed to declare 'Scheduled areas' in India?
Consider the following statements with respect to the powers and functions of the Chief Minister of a state:
- The governor appoints only those persons as ministers who are recommended by the Chief Minister.
- He can bring about the collapse of the council of ministers by resigning from office.
- He can recommend the dissolution of the legislative assembly to the governor at any time.
- He is a member of the Inter-State Council and the Governing Council of NITI Aayog.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which of the following statement/s is/are correct about Moderate Nationalism?
- They adopted peaceful and constitutional means to achieve their demands.
- They were not loyal to the British.
- The Moderates used petitions, resolutions, meetings, leaflets and pamphlets, memorandum and delegations to present their demands.
- Some Moderates like Ranade and Gokhale favoured social reforms.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Consider the following organizations/bodies in India :
- The National Commission for Backward Classes
- The National Human Rights Commission
- The National Law Commission
- The National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
How many of the above are constitutional bodies?
Consider the following pairs:
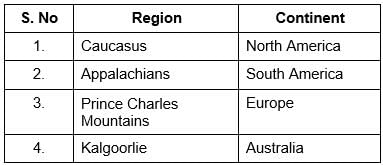
How many pairs given above are incorrectly matched?
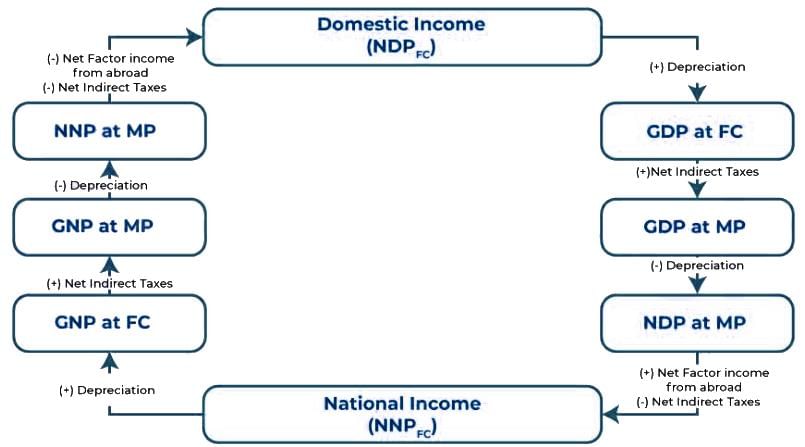
Which of the following is correct regarding Net Factor Income from Abroad (NFIA)?