OSSTET Science (CBZ) Mock Test - 3 - OTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - OSSTET Science (CBZ) Mock Test - 3
‘‘ତାରା ପୁଞ୍ଜେ ଯଥା ଶୋଭେ ହରିତାଳୀ,
ପୁଳିନ ତେସନ ଶୁଭ୍ର - ଶକ୍ତିଶାଳୀ ।’’ - ଏଥୁରେ କେଉଁ ଅଳଙ୍କାର ରହିଛି ?
‘ପାଲିଙ୍କି ଉପରେ ପାଟଛତା’ ରୂଢ଼ିଟି କେଉଁ ଅର୍ଥରେ ପ୍ରଚଳିତ ?
ପ୍ରତି ନୂତନ ଯୁଗ ମଣିଷପାଇଁ ନୂଆ ସତ୍ୟ, ଜୀବନର ନୂଆ ରୂପ ନୂଆ ଅର୍ଥ, ନୂଆ ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣାର ସମ୍ବାବନା ନେଇ ଆସେ । ମଣିଷକୁ ଚ୍ୟାଲେଞ୍ଜ କରି ଆସେ । ତା'ର ଆହ୍ଵାନକୁ କର୍ଣ୍ଣପାତ ନ କରି ଆମେ ଅତୀତର ଜୀବନ୍ୟାସପାଇଁ ତନ୍ତ୍ରସାଧନା କରୁଛୁ । ପ୍ରତି ନୂତନ ଯୂଗରେ ମଣିଷ ଅନେକ ରାଜ୍ୟ ହରାଏ, ପୁଣି ଅନେକ ନୂଆ ରାଜ୍ୟ ଜିଣିନିଏ । ମାତ୍ର ଯେଉଁ ସ୍ତମ୍ବମାନଙ୍କ ଉପରେ ଆଧୁନିକ ସମାଜ ପ୍ରତିଷ୍ଠିତ ଯେଉଁ ସେନାପତିଙ୍କ ସାହାଯ୍ୟରେ ଆମେ ନୂତନ ରାଜ୍ୟ ଜିଣନ୍ତୁ, ସେମାନଙ୍କୁ ଆମେ କେଉଁ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିରେ ଦେଖୁ ? ଗୋଟିଏ ଗଣତାନ୍ତିକ ସମାଜରେ ସାହିତ୍ୟର ସାମାଜିକ ଦାୟିତ୍ୱ ଅନସ୍ୱୀକାର୍ଯ୍ୟ । ପାଠ୍ୟ-ପୂସ୍ତକ ଜାତୀୟକରଣ ପରେ ପ୍ରାଇଜ୍ ସିଲାବସ୍ରୁ ବାହାରି ପଦାକୁ ଆସି ପାରି ନ ଥିବା ଆମ ସାହିତ୍ୟ ମଲାଣି କି ବଞ୍ଚିଛି ତଦନ୍ତ କରିବାପାଇଁ ଏକ କମିଶନ ବସିବା ଦରକାର ପଡୁଛି। ପ୍ରକୃତିର ଅତ୍ୟାଚାରରୁ ଲୋକଙ୍କୁ ରକ୍ଷା କରିବାର ବିଜ୍ଞାନ ଅଭ୍ୟୁଦୟର ଗୋଟିଏ କାରଣ। ବିଜ୍ଞାନର ଅଭ୍ୟୁଦୟ ଓ ଗଣତନ୍ତ ବିକାଶ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧଯୁକ୍ତ ବୋଲି ପ୍ରମାଣ କରିବା ହୁଏତ କଷ୍ଟକର । ବିଜ୍ଞାନ ପ୍ରତି ଆମର ଦୃଷ୍ଟିକୋଣ ହେଲା ଗୋଟିଏ ଅଚ୍ଛଦ ପରି ବିଜ୍ଞାନ ଆମପାଇଁ ମୂଲଲାଗୁ । ଦେଶ ଦରିଦ୍ର ହେଲା, ଲୋକସଂଖ୍ୟାଗୁଡ଼ାଏ ବଢ଼ିଲା ବୋଲି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ ବଢ଼ାଇବାକୁ ଏ ଅଣଆଧ୍ୟାତ୍ମିକ ବିଜ୍ଞାନର ସାହାଯ୍ୟ ନେବାକୁ ପଡ଼ିଲା ସିନା ! ବିଜ୍ଞାନ ଆମର ସାମାଜିକ ଜୀବନକୁ କଳୁଷିତ କରୁଛି, ସଂସ୍କୃତି ନଷ୍ଟ କରୁଛି। ତଥାପି ତାକୁ ସେତେବେଳେ ଛାଡ଼ି ହେଉନି, ଆମର ଆଶା ଧର୍ମକର୍ମ ଟିକିଏ ବଢ଼େଇଦେଲେ, ବିଜ୍ଞାନ ଦ୍ୱାରା ଘଟୁଥିବା କ୍ଷତିପରୂରଣ ହୋଇଯିବ । କାହାକୁ ଆମର ତନ୍ତ୍ରସାଧନା ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଇଛି ?
Select the correct passive form of the given sentence.
You can see several neem trees along the road to Connaught place.
The word 'acquire' as used in the passage means
The principal quantum number of an atom indicates:
Which of the following elements has the highest electronegativity?
The flower colour in the dog flower (snapdragon or Antirrhinum sp.) is an example of
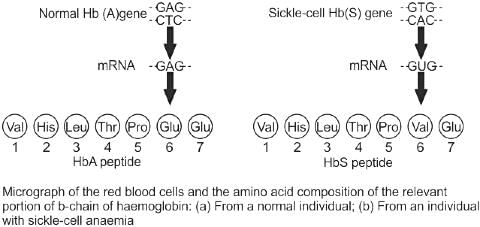
Point mutation causes substitution of one amino acid with another. Which of the following substitution causes sickle-cell anaemia?
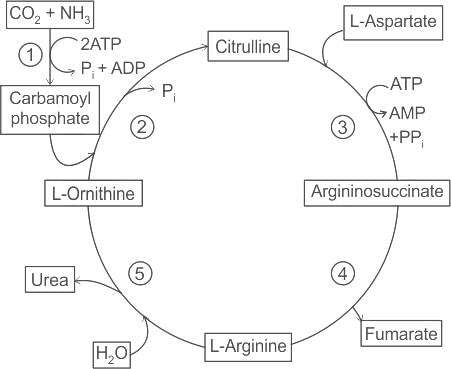
Ornithine cycle is concerned with the biosynthesis of:
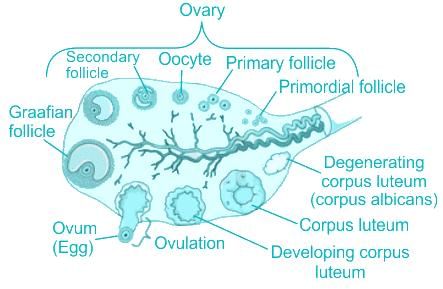
The fluid-filled space within the human Graafian follicle is called
Who is author of "Animal Learning" published in 1898 ?
In which of the following grading methods grades are provided on the basis of the relative position (ranks) of the students in their class or group?



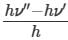 = v where
= v where