Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Tests > Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 - Class 7 MCQ
Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 - Class 7 MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2
Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 for Class 7 2025 is part of Class 7 preparation. The Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Class 7 exam syllabus.The Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 MCQs are made for Class 7 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 below.
Solutions of Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 questions in English are available as part of our course for Class 7 & Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 solutions in
Hindi for Class 7 course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 7 Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 | 10 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for Class 7 preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Class 7 Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 - Question 1
Which among the following does not belong to the scheduled airline in the public sector?
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 - Question 1
Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 - Question 2
When was the first section of the East Indian Railways inaugurated?
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 - Question 2
Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 - Question 3
The regular itineraries on which sea transport is based are classified as
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 - Question 3
Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 - Question 4
Over which of the following rivers is the world's highest railway bridge in Kashmir being constructed?
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 - Question 4
Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 - Question 5
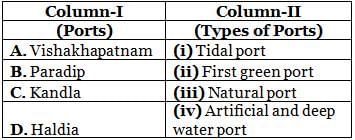
Which of the following zonal headquarters - city combination is incorrect?
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 - Question 5
Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 - Question 6
Which among the following n ational highways are collectively called as the Grand Trunk Road?
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 - Question 6
Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 - Question 7
What is the colour of milestone on all the highways constructed under Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana?
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 - Question 7
Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 - Question 8
Which mode of transpor tation reduces transshipment losses and delays?
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 - Question 8
Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 - Question 9
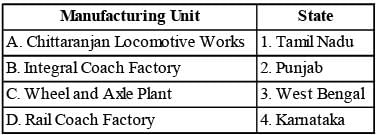
Match the manufacturing units with their locations.
Information about Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Olympiad Test Level 2: Transport System- 2, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF