Political Science: CUET Mock Test - 1 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Political Science: CUET Mock Test - 1
Which organisation came into existence in April 1949?
According to the States Reorganization Commission, "in the formation of the new states" only which issue should not become the only basis?
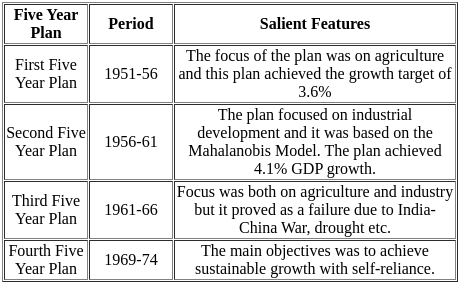
Which among the following is based on the Harrod-Domar Model?
The Green Revolution delivered only a moderate agricultural growth, mainly a rise in:
What was the main symbol of the collapse of the communist bloc in 1989?
Which reforms were introduced by Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union?
What was the immediate consequence of the Gorbachev reforms in the Soviet Union?
In what year did the Soviet Union disintegrate?
How did the end of the Cold War affect global power dynamics?
Which two organizations have emerged as alternative centers of power after the Cold War?
What is the main impact of China’s economic rise?
Which of the following is a key feature of the European Union?
How did ASEAN’s approach differ from the EU's?
What challenge to the unipolar world system is mentioned in the passage?
The fifth general election to Lok Sabha were held in _______.
Indira Gandhi got the Congress Working Committee to adopt a Ten Point Programme in ______.
Use of English language was strongly opposed by the
The first three Lok Sabha elections of 1952, 1957 and 1962 were dominated by the Congress Party under the leadership of:
The Indian leader who is the first recipient of the Bharat Ratna Award is
The constitution of India came into effect on the
Which waterway separates India from Sri Lanka?
The lndo-Sri Lanka Peace Accord was entered into under the leadership of
In East Pakistan the popular struggle against West Pakistan domination was led by
The Constitution of India provides for the safeguard of cultural and educational rights of minorities under fundamental rights of Article
The island country that received both diplomatic and financial aid from the Soviet Union was