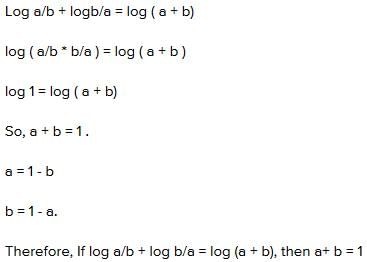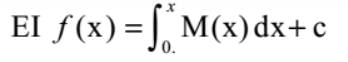Practice Test: Civil Engineering (CE)- 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Practice Test: Civil Engineering (CE)- 1
In each question below are given two statements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II. You have to take the given two statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. Read the conclusion and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the two given statements, disregarding commonly known facts.
Give answer:
- (A) If only conclusion I follows
- (B) If only conclusion II follows
- (C) If either I or II follows
- (D) If neither I nor II follows and
- (E) If both I and II follow.
Statements: All bags are cakes. All lamps are cakes.
Conclusions:
- Some lamps are bags.
- No lamp is bag.
Extreme focus on syllabus and studying for tests has become such a dominant concern of Indian students that they close their minds to anything ___________ to the requirements of the exam.
Select the pair that best expresses a relationship similar to that expressed in the pair:
LIGHT : BLIND
In an exam, the average was found to be 50 marks. After deducting computational errors the marks of the 100 candidates had to be changed from 90 to 60 each and average came down to 45 marks. Total No of candidates who took the exam were.
A solid 4cm cube of wood is coated with red paint on all the six sides. Then the cube is cut into smaller 1cm cubes. How many of these 1cm cubes have no colour on any side?
In deriving the equation for the hydraulic jump in a rectangular channel in terms of the conjugate depths and the initial Froude number.
Pipe A, B and C are kept open and together fill a tank in t minutes. Pipe A is kept open throughout, pipe B is kept open for the first 10 minutes and then closed. Two minutes after pipe B is closed, pipe C is opened and is kept open till the tank is full. Each pipe fills an equal share of the tank. Furthermore, it is known that if pipe A and B are kept open continuously, the tank would be filled completely in t minutes. Find t?
The plastic modulus of a section is 4.8 x 10-4 m3. The shape factor is 1.2. The plastic moment capacity of the section is 120 kN.m. The yield stress of the material is:
MPN index is a measure of one of the following:
Consider the following statements:
1) Strength of concrete cube is inversely proportional to water-cement ratio.
2) A rich concrete mix gives higher strength than a lean concrete mix since it has more cement content.
3) Shrinkage cracks on concrete surface are due to excess water in mix.
Which of the following statements is correct?
Standard 5-day BOD of a waste water sample is nearly x% of the ultimate BOD, where x is:
The dimensions for the flexural rigidity of a beam element in mass (M), length (L) and time (T) is given by:
The superelevation needed for a vehicle travelling at a speed of 60 kmph on a curve of radius 128 m on a surface with a coefficient of friction of 0.15 is:
Which of the following raingauge gives a plot of the accumulated rainfall against the elapsed time?
If the time period between centroid of the rainfall diagram and peak of the hydrograph is 5 hour, using Snyder’s equation the value of the base width of unit hydrograph in hours is?
A river 5 m deep consists of a sand bed with saturated unit weight of 20 kN/m3 . vw = 9.81 kN/m3. The effective vertical stress at 5 m from the top of sand bed is:
A hydraulic model of a spillway is constructed with a scale 1:16. If the prototype discharge is 2048 cumecs, then the corresponding discharge for which the model should be tested is:
A droplet of water at 200C (σ = 0.0728 N/m) has internal pressure 1 kPa greater than that outside it, its diameter is nearly:
A reinforced concrete structure has to be constructed along a sea coast. The minimum grade of concrete to be used as per IS : 456-2000
The order and degree of the differential equation given, is
The probability distribution taken to represent the completion time in PERT analysis is:
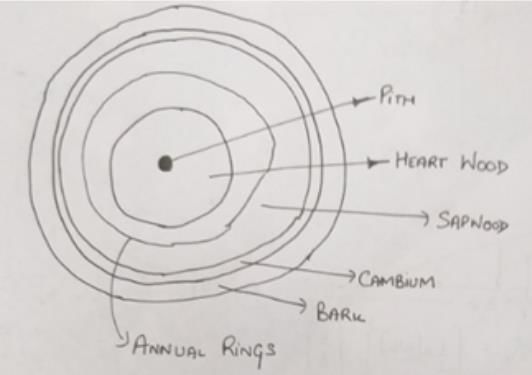
Consider the following statements
1) Cambium layer is between sapwood and heartwood
2) Heartwood is otherwise termed as deadwood
3) Timber used for construction is obtained from heartwood
Which of the following is/are correct statements?
The true bearing of a tower T as observed from station A was 3560 and the magnetic bearing of the same was 40.The back bearing of the line AB when measured with prismatic compass was found to be 2960.Then the true fore bearing of line AB will be _____ degrees.
The degree of static indeterminacy of the rigid frame having 2 internal hinges is as shown in the figure below
If the deformations of the truss-members are as shown in parentheses, the rotation of the member bd is:
The problem of lateral buckling can arise only in those steel beams which have:
The available moisture holding capacity of soil is 15cm per meter depth of soil. If a crop with a root zone of 0.8m and consumptive use of 6 mm/day is to be grown, the frequency of irrigation for restricting the moisture depletion to 60% of available moisture is?
6 boys and 6 girls sit in a row at random. Find the probability that-
1) The boys and girls sit alternately.