Practice Test: Indian Economy - 1 - UPSC MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Mock Test for UPSC Prelims 2025 - Practice Test: Indian Economy - 1
Which of the following are examples of Economic activities?
- Buying and selling something
- Doing business
- Visiting religious places for prayer
- Giving alms to beggars at places of worship
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Consider the following pairs with reference to different kinds of poor
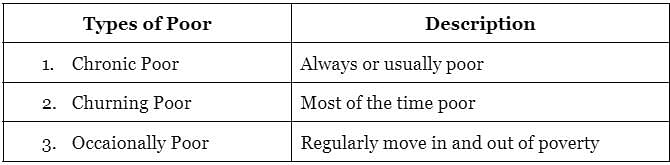
Which of the pairs given above are incorrect?

Which of the pairs given above are incorrect?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Consider the following statements about the Global Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI):
- It has been developed by the Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative and the United Nations Development Programme.
- Health, Education and monthly Income are the three main dimensions covered under MPI.
- A person is multi-dimensionally poor if he is deprived in one-sixth of the weighted indicators
How many of the statements given above are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding the Human Development Index (HDI):
- The HDI encapsulates various dimensions, such as health, education, and standard of living.
- The HDI uses a simple arithmetic mean to aggregate the scores for the three HDI dimension indices.
- The HDI includes the inequalities, poverty, and human security and provides a complete assessment of human development.
- The HDI gives increasing importance to income with rising Gross National Income (GNI).
How many of the statements given above are correct?
Consider the following pairs:
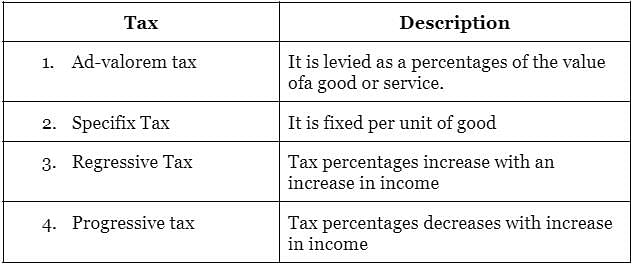
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
The concept of a Poverty line in the form of “Jail cost of living” in pre-independent India was first discussed by who among the following?
Consider the following statements:
- Statement-I : In the given year in India, official poverty lines are higher in some states than in others.
- Statement-II : Price levels of commodities vary from states to states in India.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
Consider the following:
- Lower Inflation in goods and services
- More focus on capital-intensive ways of production
- Urban bias in private investment
How many of the above are causes of income inequality?
Consider the following statements concerning the Indian economy:
- Non-tax Revenue Receipts include profits, interest receipts on loans given, and dividends from entities like PSEs.
- Revenue expenditure, if done by states, directly creates assets.
- Capital Receipts involve recoveries of loans, receipts from asset sales and fresh borrowings.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Consider the following products:
- Alcohol
- Petrol
- Aviation Turbine Fuel
- Natural Gas
How many of the above products are outside the domain of the GST framework?
Which one of the following curves plots the relation between inequality and per capita income?
Consider the following statements regarding the Revenue Deficit in the economy:
- Social sector expenditures, such as expenditure on education, health, and labor welfare, are not considered part of revenue expenditure in India.
- The goal of the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act 2003 was to increase the Revenue Deficit in a sustainable manner.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
In India, which one of the following compiles information on the Periodic Labour Force Survey?
In the context of the Indian economy, consider the following statements:
- Labor force refers to the number of persons actually working or willing to work.
- Workforce refers to the number of persons who are actually working and it does not include those who are willing to work but not working.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Consider the following statements:
- Angel Tax is levied when the Initial Public Offer by a listed company is oversubscribed.
- Windfall Tax is a virtual tax as a result of the withdrawal of subsidies by the government.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Which of the following organisations came up with the ‘State of Inequality in India report’?
Consider the following statements:
- Fiscal Deficit is the difference between the government’s total receipts and total expenditures.
- The concept of Budget Deficit rather than Fiscal deficit is widely used in the Economy in recent times.
- Monetized Deficit refers to the purchase of government bonds by the central bank to finance the spending needs of the government.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and Gross National Product (GNP) in the context of the globalised economy:
- GDP primarily focuses on where the output is produced, while GNP emphasises who produced it.
- China's GNP was historically higher than its GDP, but now it is catching up with it’s GDP due to the Belt and Road Initiative.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
With reference to the Indian economy, which of the following denotes the difference between the fiscal deficit and the interest payment?
Many a times we read about “Circuit Breakers” in share markets. They are temporary measures which halt the trading on which of the following occasion?
With reference to the ‘T+0 Settlement Cycle’ that was recently introduced in Indian Stock Market,
consider the following statements:
1. The shares are transferred to the buyer’s account and funds are deposited in the seller’s account on
the same day of the trade.
2. It is applicable only for trades executed before 05:00 p.m.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding deficit financing in the economy:
- Deficit financing means generating funds to finance the deficit which results from excess expenditure over revenue.
- The Reserve Bank of India can print money and supply credit in deficit financing.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Consider the following events from the first to the last:
- Introduction of the Regional Rural Banks
- Introduction of the Lead Bank Scheme
- Establishment of the State Bank of India
- Nationalisation of 14 major banks in India
Select the correct chronological order(past to present) using the code given below:
Consider the following statements:
1. Credit bureaus are organizations that collect, analyze, and maintain credit data on borrowers, businesses, and organizations.
2.They are licensed by the Securities and Exchange Board of India.
3. Only one Credit reports can only be provided to borrowers and government agencies.
How many statements given above is/are correct?
With reference to the ‘Coffee Board’ in India, consider the following statements:
1. It is a statutory body functioning under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
2. Its head office is situated in Bengaluru.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Gini index or Gini Coefficient is used to measure which of the following?
Which of the following activities are undertaken by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS)?
- Product Certification Scheme
- Hall Marking Scheme
- Laboratory Recognition Scheme
- Sale of Indian Standards
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Which of the following is the primary objective of the Financial Services Institutions Bureau?
Consider the following statements regarding structural inflation:
- It is a short term inflation due to temporary mismatch in the demand and supply.
- Inefficient distribution and storage facilities is a major cause of such type of inflation.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
With reference to the ‘Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)’, consider the following statements:
- They were established under the Kelkar committee recommendations.
- They were established with the goal of providing credit and financial services to rural areas.
- They are jointly owned by the Central Government, State Government, and a sponsor bank.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
|
16 videos|4 docs|70 tests
|
|
16 videos|4 docs|70 tests
|

















