Practice Test - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Practice Test
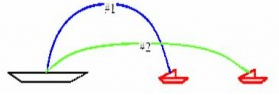
A battle ship simultaneously fires two shells at enemy ships. Both are fired with the same speed but with different directions as shown. If the shells follow the parabolic trajectories shown, which ship gets hit first?
If an object is dropped through the window of a fast running train. Then
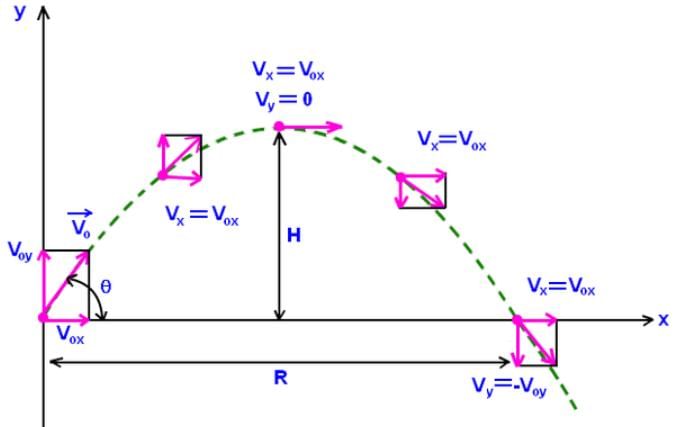
Which statement is true for a ball thrown at 20 degrees with the horizontal, when it is at the highest point in its trajectory?
A man of mass 70 kg stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving upwards with a uniform speed of 10 m s−1, what would be the reading on the scale?
Give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on a stone of mass 0.1 kg lying on the floor of a train which is moving with 1 ms−2 accleration , the stone being at rest relative to the train. Neglect air resistance.
A gas absorbs 200 J of heat and expands by 500 cm3 against a constant pressure of 2 x 105 Nm-2. Change in internal energy is
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-15) This section contains 15 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Which of the following is least likely to behave as Lewis base?
The species present in solution when CO2 dissolved in water, are
[IIT JEE 2006]
The part of the fruit that develops from the ovary wall is called__________.
A scar on the seed coat through which the developing seeds attached to the fruit is called as ________.
A Flower which can be divided into equal vertical halves by more than one plane of division is__________.
Flowers in which only one set of essential organs is present are said to be__________.
Which of the following represents the floral characters of Liliaceae?
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of dicotyledonous seeds?
What is the primary respiratory organ used by frogs when they are in water?