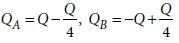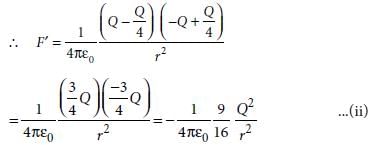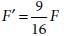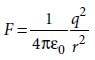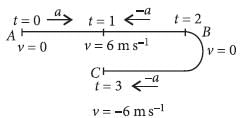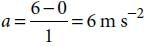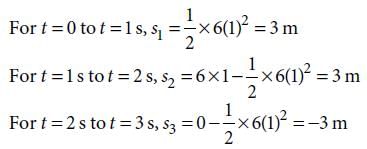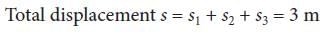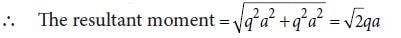Practice Test - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Practice Test
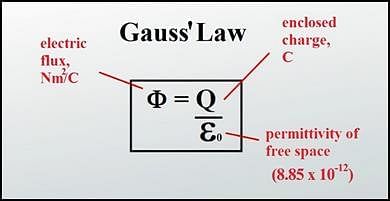
A point charge of 2.0 μC is at the centre of a cubic Gaussian surface 9.0 cm on edge. What is the net electric flux through the surface?
Two identical conductors of copper and aluminium are placed in an identical electric field. The magnitude of induced charge in the aluminium will be:
A hollow spherical conductor of radius 2m carries a charge of 500 μ C. Then electric field strength at its surface is
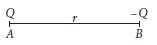
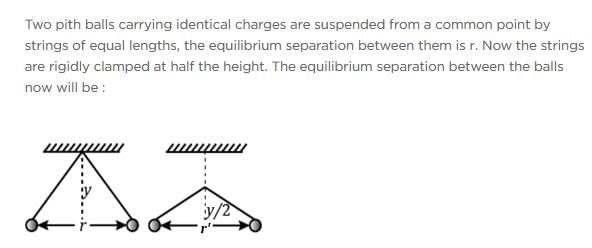
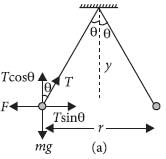
Two point charges A and B, having charges +Q and –Q respectively, are placed at certain distance apart and force acting between them is F. If 25% charge of A is transferred to B, then force between the charges becomes
Under the influence of the coulomb field of charge +Q, a charge −q is moving around it in an elliptical orbit. Find out the correct statement(s).
A toy car with charge q moves on a frictionless horizontal plane surface under the influence of a uniform electric field 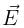 . Due to the force
. Due to the force 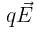 , its velocity increases from 0 to 6 m s–1 in one second duration. At that instant the direction of the field is
, its velocity increases from 0 to 6 m s–1 in one second duration. At that instant the direction of the field is
reversed. The car continues to move for two more seconds under the influence of this field. The average velocity and the average speed of the toy car between 0 to 3 seconds are respectively
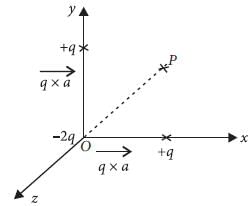
Three point charges +q, –2q and +q are placed at points (x = 0, y = a, z = 0), (x = 0, y = 0, z = 0) and (x = a, y = 0, z = 0) respectively. The magnitude and direction of the electric dipole moment vector of this charge assembly are
Trioxalato aluminate (III) and tetrafluorido-borate (III) ions are respectively :
Which of the ligand can show linkage isomerism and acts as flexidentate ligand:
From the stability constant (hypothetical values), given below, predict which is the strongest ligand:
Skeletal muscle bundles [fascicles] are held together by a common connective tissue layer called:
Read the following :
i. The synovial joints ischaracterised by the presence of a fluid filled synovial cavity between the articulating surfaces of the two bones.
ii. Saddle is a type of synovial joint
Tracheal tube divides into right and left bronchi at the level of :
The specialised patch of modified heart muscles from where contraction initiates is/are :
Which of the following blood components play a major role in blood coagulation?
In the systemic circulation, the blood vessel that carries blood from the intestine to the liver is named: