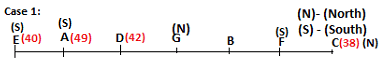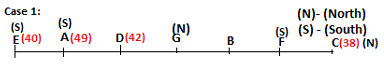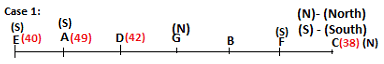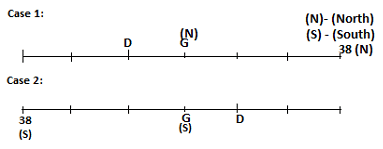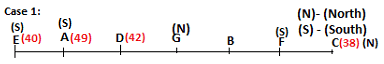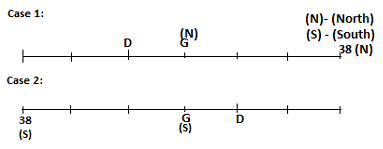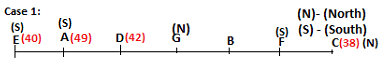RBI Assistant Mains Mock Test - 8 - Bank Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - RBI Assistant Mains Mock Test - 8
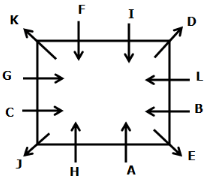
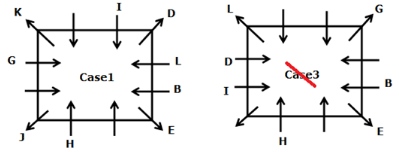
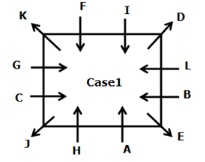
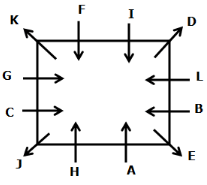
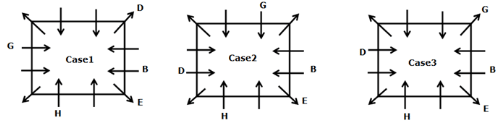
Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the given question.
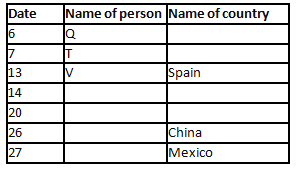
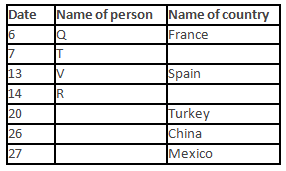
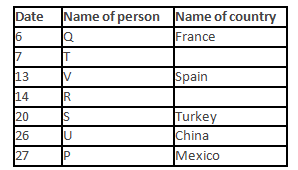
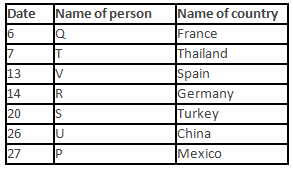
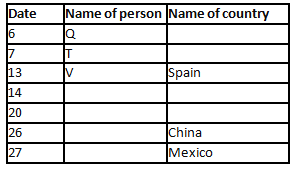
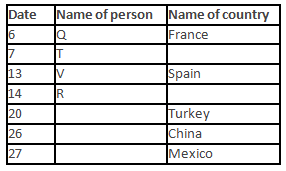
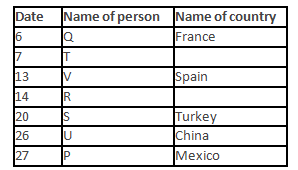
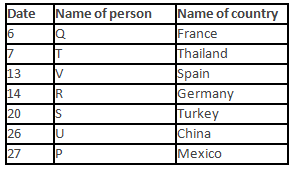
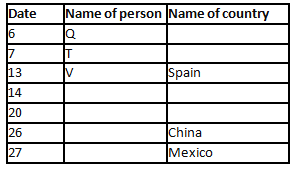
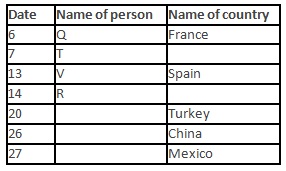
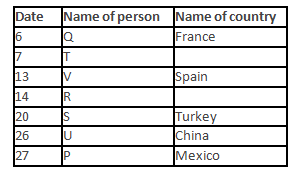
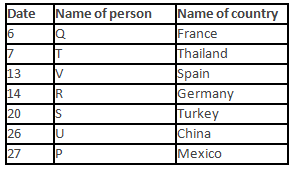
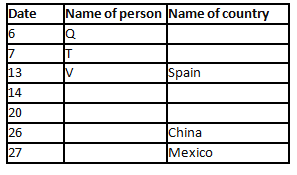
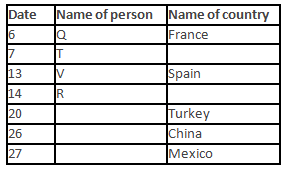
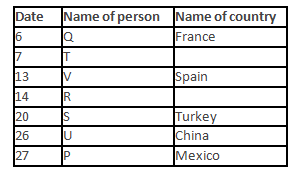
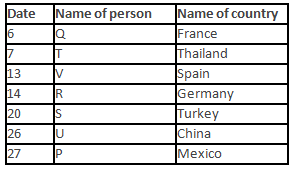
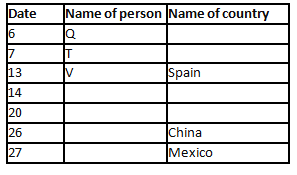
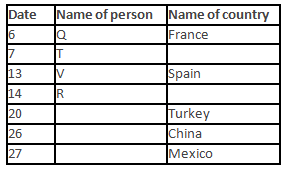
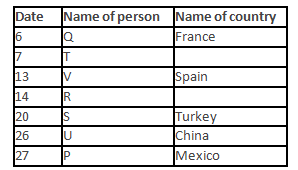
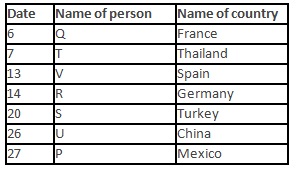
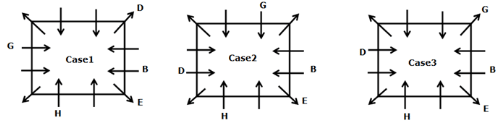
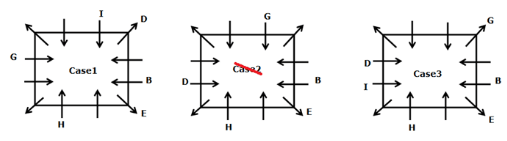
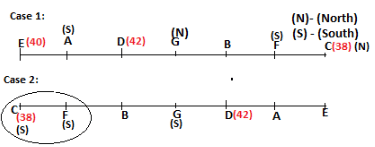
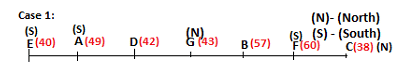
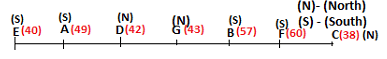
A meeting by the head office of ABC company was organised in India in January and after the meeting, seven persons from different countries went back to their own countries in March on different dates viz. 6th, 7th, 13th, 14th, 20th, 26th and 27th.
The person from China went back to his country on 26th March. V went to Spain on 13th March. Q went to his country immediately before T. Q did not go on a day after V. The one who went to Mexico did not go on or before 20th March. The person from Turkey went back to his country immediately after R. T was not from Germany. The one who went to France did not go immediately before or after V. U did not go on 27th March and he was not from Turkey. S went back to his country on one of the days before P. R was not from Thailand.
On which date did U go back to his country?
Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the given question.
A meeting by the head office of ABC company was organised in India in January and after the meeting, seven persons from different countries went back to their own countries in March on different dates viz. 6th, 7th, 13th, 14th, 20th, 26th and 27th.
The person from China went back to his country on 26th March. V went to Spain on 13th March. Q went to his country immediately before T. Q did not go on a day after V. The one who went to Mexico did not go on or before 20th March. The person from Turkey went back to his country immediately after R. T was not from Germany. The one who went to France did not go immediately before or after V. U did not go on 27th March and he was not from Turkey. S went back to his country on one of the days before P. R was not from Thailand.
The person who went back on 27th March was from which country?
Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the given question.
A meeting by the head office of ABC company was organised in India in January and after the meeting, seven persons from different countries went back to their own countries in March on different dates viz. 6th, 7th, 13th, 14th, 20th, 26th and 27th.
The person from China went back to his country on 26th March. V went to Spain on 13th March. Q went to his country immediately before T. Q did not go on a day after V. The one who went to Mexico did not go on or before 20th March. The person from Turkey went back to his country immediately after R. T was not from Germany. The one who went to France did not go immediately before or after V. U did not go on 27th March and he was not from Turkey. S went back to his country on one of the days before P. R was not from Thailand.
Which of the following countries was U from?
Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the given question.
A meeting by the head office of ABC company was organised in India in January and after the meeting, seven persons from different countries went back to their own countries in March on different dates viz. 6th, 7th, 13th, 14th, 20th, 26th and 27th.
The person from China went back to his country on 26th March. V went to Spain on 13th March. Q went to his country immediately before T. Q did not go on a day after V. The one who went to Mexico did not go on or before 20th March. The person from Turkey went back to his country immediately after R. T was not from Germany. The one who went to France did not go immediately before or after V. U did not go on 27th March and he was not from Turkey. S went back to his country on one of the days before P. R was not from Thailand.
Which of the following is true?
Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the given question.
A meeting by the head office of ABC company was organised in India in January and after the meeting, seven persons from different countries went back to their own countries in March on different dates viz. 6th, 7th, 13th, 14th, 20th, 26th and 27th.
The person from China went back to his country on 26th March. V went to Spain on 13th March. Q went to his country immediately before T. Q did not go on a day after V. The one who went to Mexico did not go on or before 20th March. The person from Turkey went back to his country immediately after R. T was not from Germany. The one who went to France did not go immediately before or after V. U did not go on 27th March and he was not from Turkey. S went back to his country on one of the days before P. R was not from Thailand.
Which of following options is the odd one out?
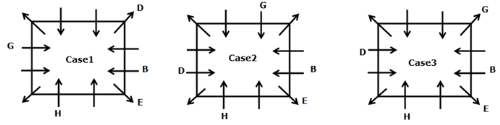
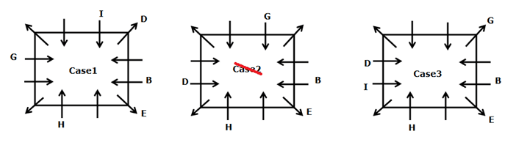
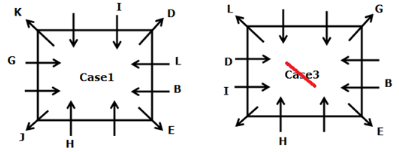
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions
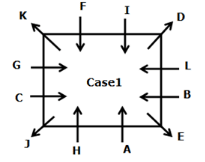
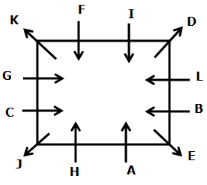
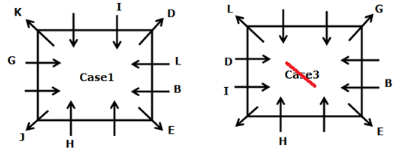
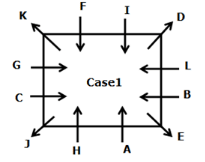
Twelve persons- A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, and L are sitting on the square table but not necessarily in the same order. One person sits on each corner of the table and faces opposite to the center whereas two persons sit on each side of the table and face the center. The consecutive alphabetically named person does not sit together.
H sits third to the left of B who does not sit on the corner of the table. B sits immediate left of E, Vice versa. G sits fourth to the left of D who doesn’t sit adjacent to H. The number of persons sit between G and H is the same as the number of persons sit between G and I. L sits second to the left of I. J sits fourth to the right of the one who sits immediate right of K. K and H are not immediate neighbors. J does not sit on the side of the table. A and G are not immediate neighbors.
Who among the following person sits third to the right of J?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions
Twelve persons- A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, and L are sitting on the square table but not necessarily in the same order. One person sits on each corner of the table and faces opposite to the center whereas two persons sit on each side of the table and face the center. The consecutive alphabetically named person does not sit together.
H sits third to the left of B who does not sit on the corner of the table. B sits immediate left of E, Vice versa. G sits fourth to the left of D who doesn’t sit adjacent to H. The number of persons sit between G and H is the same as the number of persons sit between G and I. L sits second to the left of I. J sits fourth to the right of the one who sits immediate right of K. K and H are not immediate neighbors. J does not sit on the side of the table. A and G are not immediate neighbors.
What is the position of B with respect to the one who sits immediate right of H?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions
Twelve persons- A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, and L are sitting on the square table but not necessarily in the same order. One person sits on each corner of the table and faces opposite to the center whereas two persons sit on each side of the table and face the center. The consecutive alphabetically named person does not sit together.
H sits third to the left of B who does not sit on the corner of the table. B sits immediate left of E, Vice versa. G sits fourth to the left of D who doesn’t sit adjacent to H. The number of persons sit between G and H is the same as the number of persons sit between G and I. L sits second to the left of I. J sits fourth to the right of the one who sits immediate right of K. K and H are not immediate neighbors. J does not sit on the side of the table. A and G are not immediate neighbors.
How many persons sit between E and the one who sits immediate left of I when counted from the left of E?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions
Twelve persons- A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, and L are sitting on the square table but not necessarily in the same order. One person sits on each corner of the table and faces opposite to the center whereas two persons sit on each side of the table and face the center. The consecutive alphabetically named person does not sit together.
H sits third to the left of B who does not sit on the corner of the table. B sits immediate left of E, Vice versa. G sits fourth to the left of D who doesn’t sit adjacent to H. The number of persons sit between G and H is the same as the number of persons sit between G and I. L sits second to the left of I. J sits fourth to the right of the one who sits immediate right of K. K and H are not immediate neighbors. J does not sit on the side of the table. A and G are not immediate neighbors.
Who among the following persons faces the same direction?
I. DE
II. LB
III. JH
Directions: Study the following information and answer the question given below.
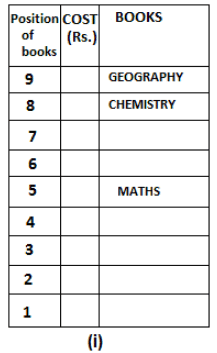
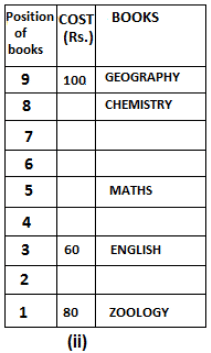
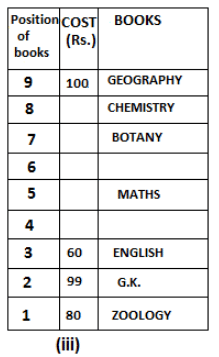
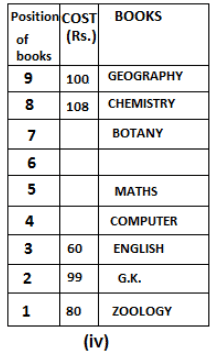
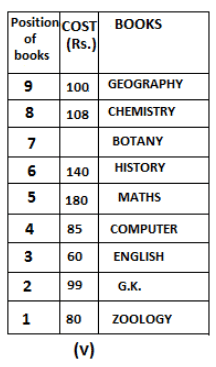
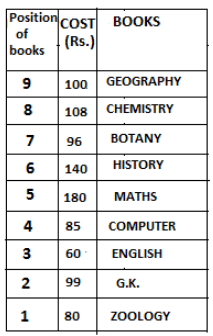
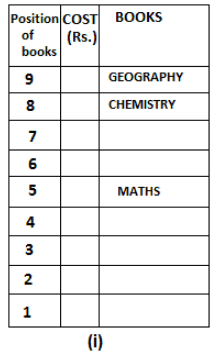
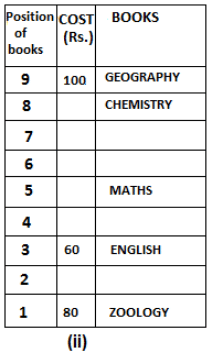
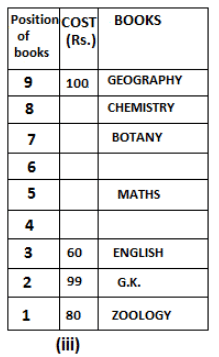
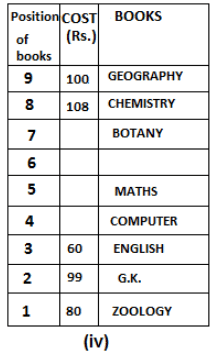
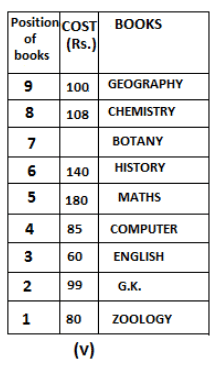
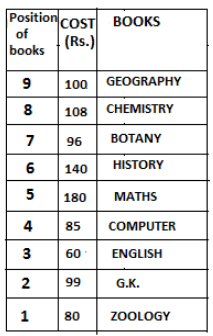
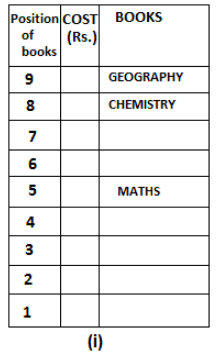
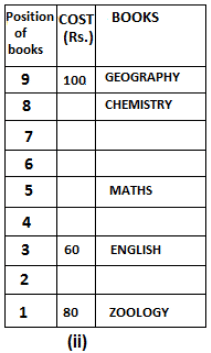
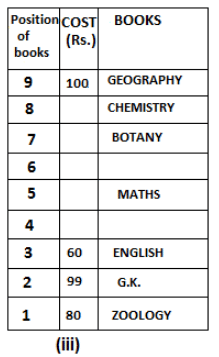
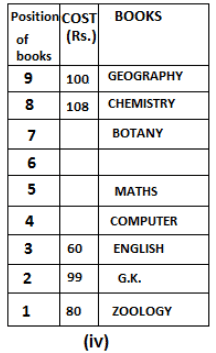
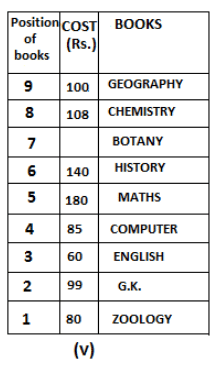
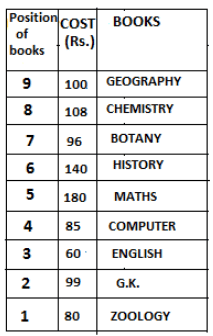
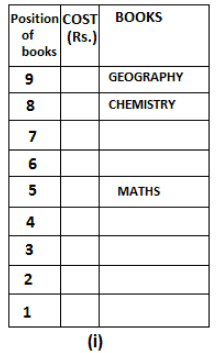
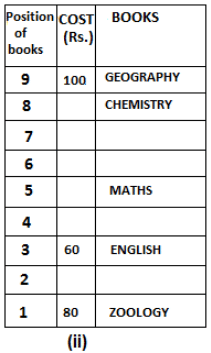
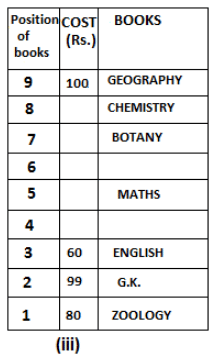
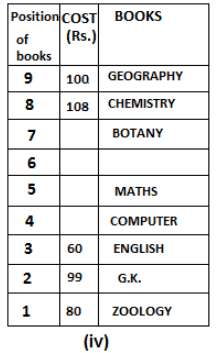
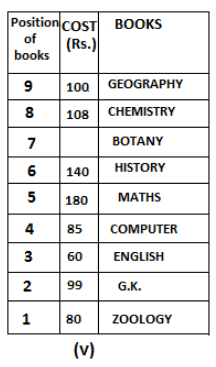
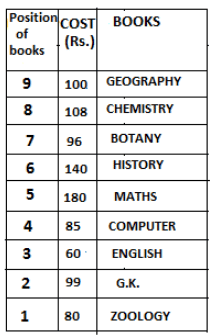
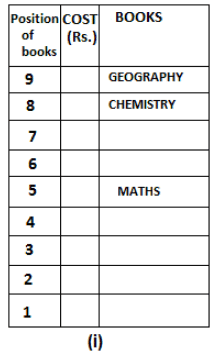
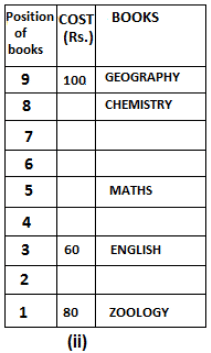
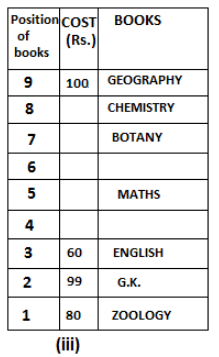
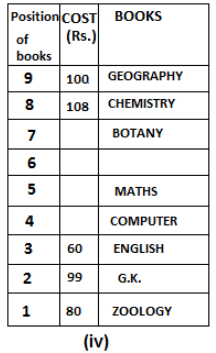
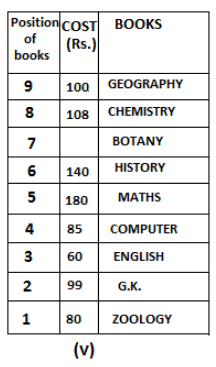
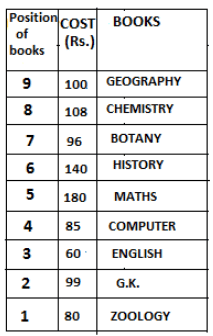
Nine books are kept one above another in such a way that the book which is kept at lowermost position is numbered as 1 and the one above it is numbered 2 and so on, till 9 which is at the uppermost position. Each book has a different cost. The cost of each book is equal to a multiple of the book which is kept immediately above it. E.g: The cost of book kept at position 1 is a multiple of 2 i.e. 2, 4, 6 ... and so on and the cost of the book which is kept at position 9 is a multiple of 10 i.e. 10, 20, 30 ... and so on. No book is of the same cost.
Maths book is kept 3 places below Chemistry book. English book is not kept at position 4. The cost of English book is Rs. 60. English book is kept two places above Zoology book. The cost of Geography book is 1.25 times of the cost of Zoology book. The cost of Botany book is a multiple of 12, but is between 90 to 100. The cost of Chemistry book is Rs. 8 more than the cost of Geography book. Cost of Zoology book is Rs. 20 more than that of English book. Number of books kept above Botany book is 1 more than the number of books kept below G.K. book. The cost of G.K. book is Re. 1 less than the cost of Geography book. Computer book is neither kept at position 5 nor at position 6. Geography book is kept at the top and Chemistry book is kept either immediately above it or immediately below it. First digit (the digit at 100s place) of the cost of Maths and Chemistry books is the same, but the second and third digits of the cost of chemistry book are interchanged to get the second and third digits of the cost of Maths book. The cost of History book is the sum of the cost of English and Zoology books. The cost of Computer book is Rs. 5 less than half the cost of Maths book.
The cost of which of the following books is the highest?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the question given below.
Nine books are kept one above another in such a way that the book which is kept at lowermost position is numbered as 1 and the one above it is numbered 2 and so on, till 9 which is at the uppermost position. Each book has a different cost. The cost of each book is equal to a multiple of the book which is kept immediately above it. E.g: The cost of book kept at position 1 is a multiple of 2 i.e. 2, 4, 6 ... and so on and the cost of the book which is kept at position 9 is a multiple of 10 i.e. 10, 20, 30 ... and so on. No book is of the same cost.
Maths book is kept 3 places below Chemistry book. English book is not kept at position 4. The cost of English book is Rs. 60. English book is kept two places above Zoology book. The cost of Geography book is 1.25 times of the cost of Zoology book. The cost of Botany book is a multiple of 12, but is between 90 to 100. The cost of Chemistry book is Rs. 8 more than the cost of Geography book. Cost of Zoology book is Rs. 20 more than that of English book. Number of books kept above Botany book is 1 more than the number of books kept below G.K. book. The cost of G.K. book is Re. 1 less than the cost of Geography book. Computer book is neither kept at position 5 nor at position 6. Geography book is kept at the top and Chemistry book is kept either immediately above it or immediately below it. First digit (the digit at 100s place) of the cost of Maths and Chemistry books is the same, but the second and third digits of the cost of chemistry book are interchanged to get the second and third digits of the cost of Maths book. The cost of History book is the sum of the cost of English and Zoology books. The cost of Computer book is Rs. 5 less than half the cost of Maths book.
What is the cost (in Rs.) of History book?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the question given below.
Nine books are kept one above another in such a way that the book which is kept at lowermost position is numbered as 1 and the one above it is numbered 2 and so on, till 9 which is at the uppermost position. Each book has a different cost. The cost of each book is equal to a multiple of the book which is kept immediately above it. E.g: The cost of book kept at position 1 is a multiple of 2 i.e. 2, 4, 6 ... and so on and the cost of the book which is kept at position 9 is a multiple of 10 i.e. 10, 20, 30 ... and so on. No book is of the same cost.
Maths book is kept 3 places below Chemistry book. English book is not kept at position 4. The cost of English book is Rs. 60. English book is kept two places above Zoology book. The cost of Geography book is 1.25 times of the cost of Zoology book. The cost of Botany book is a multiple of 12, but is between 90 to 100. The cost of Chemistry book is Rs. 8 more than the cost of Geography book. Cost of Zoology book is Rs. 20 more than that of English book. Number of books kept above Botany book is 1 more than the number of books kept below G.K. book. The cost of G.K. book is Re. 1 less than the cost of Geography book. Computer book is neither kept at position 5 nor at position 6. Geography book is kept at the top and Chemistry book is kept either immediately above it or immediately below it. First digit (the digit at 100s place) of the cost of Maths and Chemistry books is the same, but the second and third digits of the cost of chemistry book are interchanged to get the second and third digits of the cost of Maths book. The cost of History book is the sum of the cost of English and Zoology books. The cost of Computer book is Rs. 5 less than half the cost of Maths book.
What is the difference between the cost of Maths and Computer books?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the question given below.
Nine books are kept one above another in such a way that the book which is kept at lowermost position is numbered as 1 and the one above it is numbered 2 and so on, till 9 which is at the uppermost position. Each book has a different cost. The cost of each book is equal to a multiple of the book which is kept immediately above it. E.g: The cost of book kept at position 1 is a multiple of 2 i.e. 2, 4, 6 ... and so on and the cost of the book which is kept at position 9 is a multiple of 10 i.e. 10, 20, 30 ... and so on. No book is of the same cost.
Maths book is kept 3 places below Chemistry book. English book is not kept at position 4. The cost of English book is Rs. 60. English book is kept two places above Zoology book. The cost of Geography book is 1.25 times of the cost of Zoology book. The cost of Botany book is a multiple of 12, but is between 90 to 100. The cost of Chemistry book is Rs. 8 more than the cost of Geography book. Cost of Zoology book is Rs. 20 more than that of English book. Number of books kept above Botany book is 1 more than the number of books kept below G.K. book. The cost of G.K. book is Re. 1 less than the cost of Geography book. Computer book is neither kept at position 5 nor at position 6. Geography book is kept at the top and Chemistry book is kept either immediately above it or immediately below it. First digit (the digit at 100s place) of the cost of Maths and Chemistry books is the same, but the second and third digits of the cost of chemistry book are interchanged to get the second and third digits of the cost of Maths book. The cost of History book is the sum of the cost of English and Zoology books. The cost of Computer book is Rs. 5 less than half the cost of Maths book.
Which of the following books is numbered 7?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the question given below.
Nine books are kept one above another in such a way that the book which is kept at lowermost position is numbered as 1 and the one above it is numbered 2 and so on, till 9 which is at the uppermost position. Each book has a different cost. The cost of each book is equal to a multiple of the book which is kept immediately above it. E.g: The cost of book kept at position 1 is a multiple of 2 i.e. 2, 4, 6 ... and so on and the cost of the book which is kept at position 9 is a multiple of 10 i.e. 10, 20, 30 ... and so on. No book is of the same cost.
Maths book is kept 3 places below Chemistry book. English book is not kept at position 4. The cost of English book is Rs. 60. English book is kept two places above Zoology book. The cost of Geography book is 1.25 times of the cost of Zoology book. The cost of Botany book is a multiple of 12, but is between 90 to 100. The cost of Chemistry book is Rs. 8 more than the cost of Geography book. Cost of Zoology book is Rs. 20 more than that of English book. Number of books kept above Botany book is 1 more than the number of books kept below G.K. book. The cost of G.K. book is Re. 1 less than the cost of Geography book. Computer book is neither kept at position 5 nor at position 6. Geography book is kept at the top and Chemistry book is kept either immediately above it or immediately below it. First digit (the digit at 100s place) of the cost of Maths and Chemistry books is the same, but the second and third digits of the cost of chemistry book are interchanged to get the second and third digits of the cost of Maths book. The cost of History book is the sum of the cost of English and Zoology books. The cost of Computer book is Rs. 5 less than half the cost of Maths book.
How many books are kept above English book?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
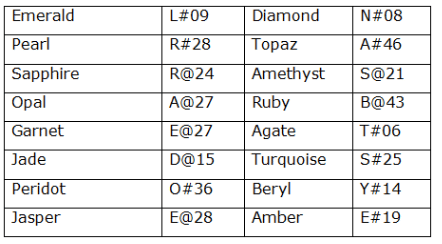
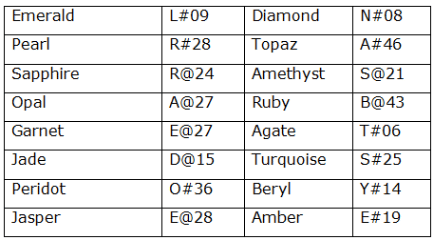
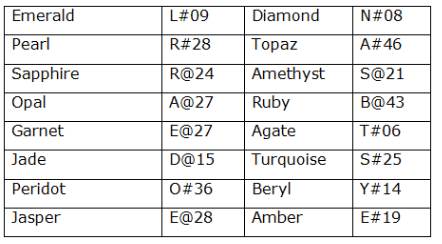
In a certain code language
‘ Emerald Diamond Pearl Topaz ’ means ‘ L#09 N#08 R#28 A#46 ’,
‘ Sapphire Amethyst Opal Ruby ’ means ‘ R@24 S@21 A@27 B@43 ’,
‘ Garnet Agate Jade Turquoise ’ means ‘ E@27 T#06 D@15 S#25 ’,
‘Peridot Beryl Jasper Amber ’ means ‘ O#36 Y#14 E@28 E#19 ’
What does "B@43" represent in a code language?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
In a certain code language
‘ Emerald Diamond Pearl Topaz ’ means ‘ L#09 N#08 R#28 A#46 ’,
‘ Sapphire Amethyst Opal Ruby ’ means ‘ R@24 S@21 A@27 B@43 ’,
‘ Garnet Agate Jade Turquoise ’ means ‘ E@27 T#06 D@15 S#25 ’,
‘Peridot Beryl Jasper Amber ’ means ‘ O#36 Y#14 E@28 E#19 ’
What is the logic used to find a number in the given language?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
In a certain code language
‘ Emerald Diamond Pearl Topaz ’ means ‘ L#09 N#08 R#28 A#46 ’,
‘ Sapphire Amethyst Opal Ruby ’ means ‘ R@24 S@21 A@27 B@43 ’,
‘ Garnet Agate Jade Turquoise ’ means ‘ E@27 T#06 D@15 S#25 ’,
‘Peridot Beryl Jasper Amber ’ means ‘ O#36 Y#14 E@28 E#19 ’
What is the code for ‘Jasper Jade’ in the given language?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
In a certain code language
‘ Emerald Diamond Pearl Topaz ’ means ‘ L#09 N#08 R#28 A#46 ’,
‘ Sapphire Amethyst Opal Ruby ’ means ‘ R@24 S@21 A@27 B@43 ’,
‘ Garnet Agate Jade Turquoise ’ means ‘ E@27 T#06 D@15 S#25 ’,
‘Peridot Beryl Jasper Amber ’ means ‘ O#36 Y#14 E@28 E#19 ’
What does "R@24 R#28 T#06" represent in a code language?
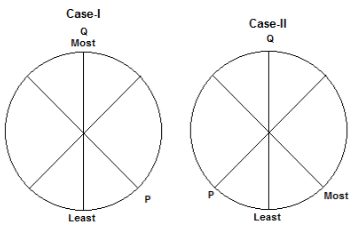
Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the question that follows.
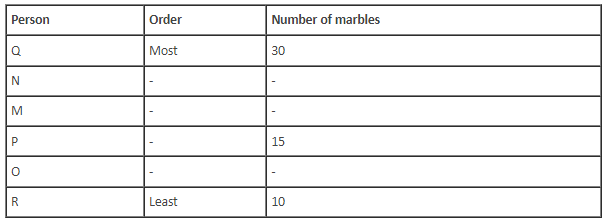
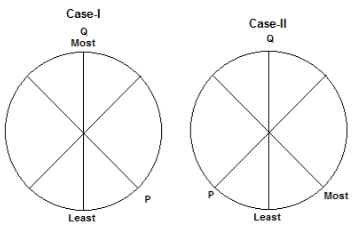
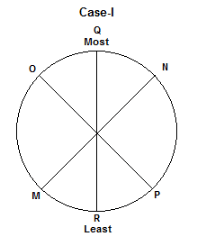
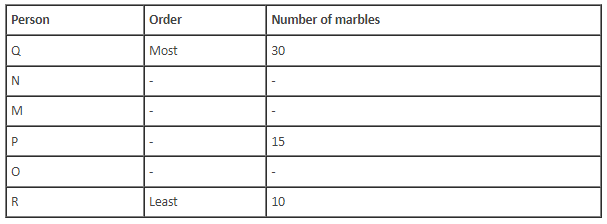
Six children M, N, O, P, Q and R are sitting around a circular table. They all have different number of marbles. O does not have more marbles than P. P is an immediate neighbour of the one who has the least number of marbles. M has more marbles than P but fewer marbles than N. Q is sitting opposite to the one who has the least number of marbles. P has 5 more marbles than R. M is second to the left of P. The difference between the number of marbles with Q and with R is 20. O is not an immediate neighbour of P and does not have the least number of marbles. The most number of marbles with a child is 30. P is sitting second to the left of the one who has the most number of marbles. Either M or R has the least number of marbles.
How many children sit between the one who has the least number of marbles and N, when counted from the right of N?
Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the question that follows.
Six children M, N, O, P, Q and R are sitting around a circular table. They all have different number of marbles. O does not have more marbles than P. P is an immediate neighbour of the one who has the least number of marbles. M has more marbles than P but fewer marbles than N. Q is sitting opposite to the one who has the least number of marbles. P has 5 more marbles than R. M is second to the left of P. The difference between the number of marbles with Q and with R is 20. O is not an immediate neighbour of P and does not have the least number of marbles. The most number of marbles with a child is 30. P is sitting second to the left of the one who has the most number of marbles. Either M or R has the least number of marbles.
What is the possible number of marbles with O?
Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the question that follows.
Six children M, N, O, P, Q and R are sitting around a circular table. They all have different number of marbles. O does not have more marbles than P. P is an immediate neighbour of the one who has the least number of marbles. M has more marbles than P but fewer marbles than N. Q is sitting opposite to the one who has the least number of marbles. P has 5 more marbles than R. M is second to the left of P. The difference between the number of marbles with Q and with R is 20. O is not an immediate neighbour of P and does not have the least number of marbles. The most number of marbles with a child is 30. P is sitting second to the left of the one who has the most number of marbles. Either M or R has the least number of marbles.
Who among the following has the second most number of marbles?
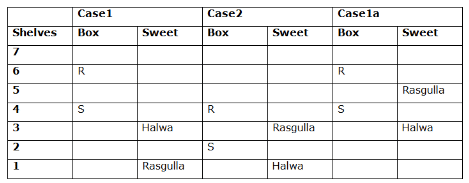
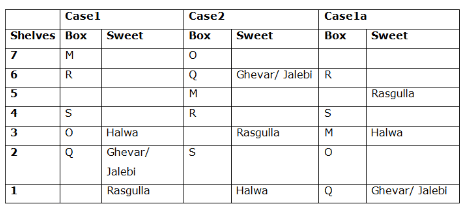
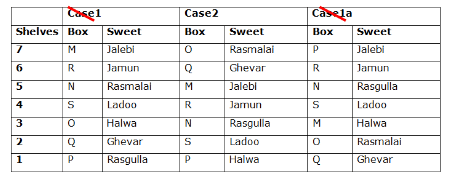
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions
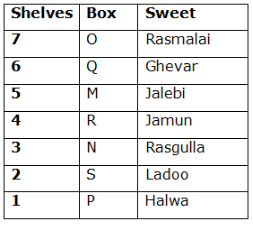
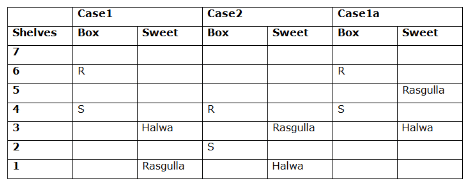
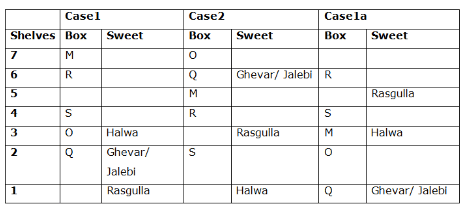
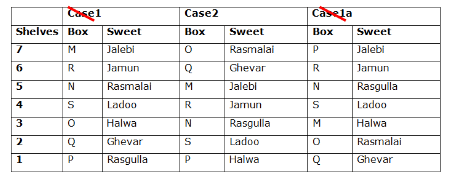
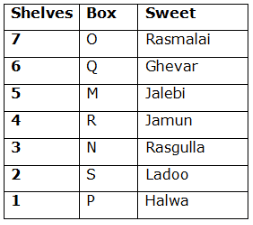
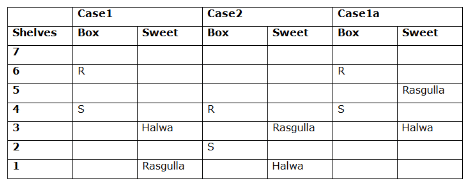
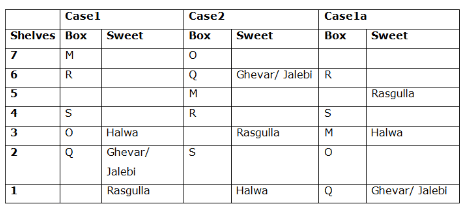
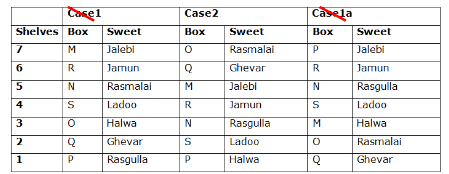
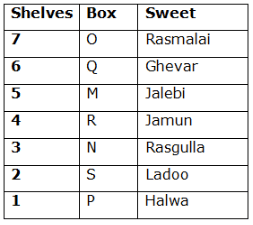
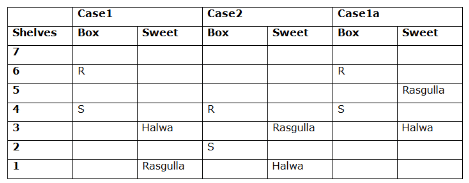
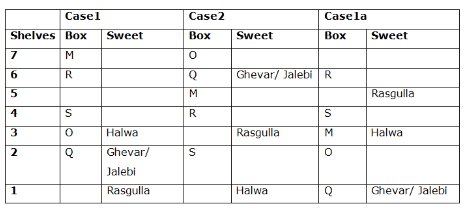
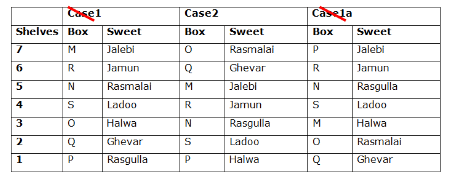
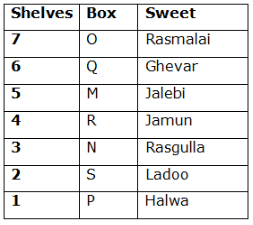
Seven boxes- M, N, O, P, Q, R, and S are kept one above another in the seven different shelves such that the lowermost shelf is numbered as one and the topmost shelf is numbered as seven. Each box has different sweets- Rasmalai, Ghevar, Jalebi, Halwa, Rasgulla, Ladoo, and Jamun. All the information is not necessarily in the same order.
Box R is kept immediately below the box which is kept three boxes above S. Box S is kept on an even-numbered shelf. The Halwa box is kept immediately below S. Only one box is kept between the Halwa box and the Rasgulla box. The number of boxes kept above the Rasgulla box is the same as the number of the box kept below M. Box O is kept immediately above box Q. Box Q has either Ghevar or Jalebi. Box N is kept immediately above the Ladoo box. Box R neither has Ladoo nor Jalebi. The Jalebi box is kept immediately above the Jamun box. Box M neither has Jamun nor Halwa. Box N does not have Rasmalai.
Which of the following box is kept on the second shelf?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions
Seven boxes- M, N, O, P, Q, R, and S are kept one above another in the seven different shelves such that the lowermost shelf is numbered as one and the topmost shelf is numbered as seven. Each box has different sweets- Rasmalai, Ghevar, Jalebi, Halwa, Rasgulla, Ladoo, and Jamun. All the information is not necessarily in the same order.
Box R is kept immediately below the box which is kept three boxes above S. Box S is kept on an even-numbered shelf. The Halwa box is kept immediately below S. Only one box is kept between the Halwa box and the Rasgulla box. The number of boxes kept above the Rasgulla box is the same as the number of the box kept below M. Box O is kept immediately above box Q. Box Q has either Ghevar or Jalebi. Box N is kept immediately above the Ladoo box. Box R neither has Ladoo nor Jalebi. The Jalebi box is kept immediately above the Jamun box. Box M neither has Jamun nor Halwa. Box N does not have Rasmalai.
If box O is related to Ghevar, box R is related to Rasgulla, then which of the following box is related to Halwa?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions
Seven boxes- M, N, O, P, Q, R, and S are kept one above another in the seven different shelves such that the lowermost shelf is numbered as one and the topmost shelf is numbered as seven. Each box has different sweets- Rasmalai, Ghevar, Jalebi, Halwa, Rasgulla, Ladoo, and Jamun. All the information is not necessarily in the same order.
Box R is kept immediately below the box which is kept three boxes above S. Box S is kept on an even-numbered shelf. The Halwa box is kept immediately below S. Only one box is kept between the Halwa box and the Rasgulla box. The number of boxes kept above the Rasgulla box is the same as the number of the box kept below M. Box O is kept immediately above box Q. Box Q has either Ghevar or Jalebi. Box N is kept immediately above the Ladoo box. Box R neither has Ladoo nor Jalebi. The Jalebi box is kept immediately above the Jamun box. Box M neither has Jamun nor Halwa. Box N does not have Rasmalai.
Which of the following sweet does the box N have?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions
Seven boxes- M, N, O, P, Q, R, and S are kept one above another in the seven different shelves such that the lowermost shelf is numbered as one and the topmost shelf is numbered as seven. Each box has different sweets- Rasmalai, Ghevar, Jalebi, Halwa, Rasgulla, Ladoo, and Jamun. All the information is not necessarily in the same order.
Box R is kept immediately below the box which is kept three boxes above S. Box S is kept on an even-numbered shelf. The Halwa box is kept immediately below S. Only one box is kept between the Halwa box and the Rasgulla box. The number of boxes kept above the Rasgulla box is the same as the number of the box kept below M. Box O is kept immediately above box Q. Box Q has either Ghevar or Jalebi. Box N is kept immediately above the Ladoo box. Box R neither has Ladoo nor Jalebi. The Jalebi box is kept immediately above the Jamun box. Box M neither has Jamun nor Halwa. Box N does not have Rasmalai.
Which of the following combination is true?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the question given below.
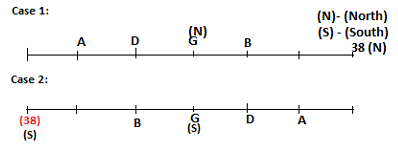
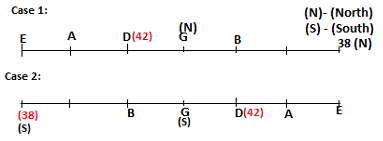
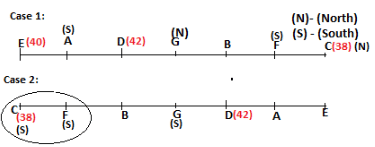
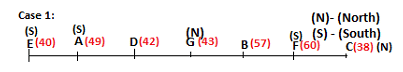
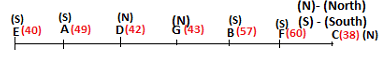
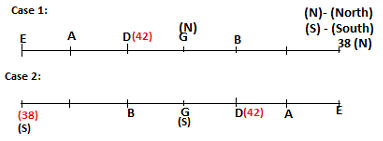
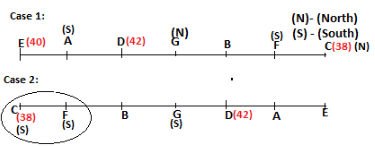
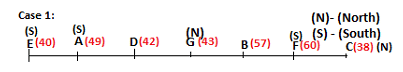
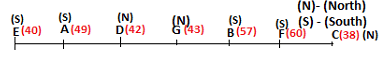
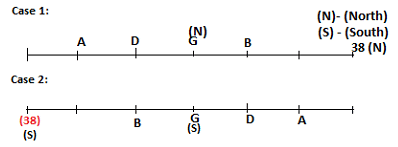
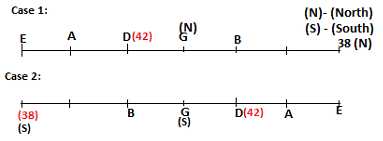
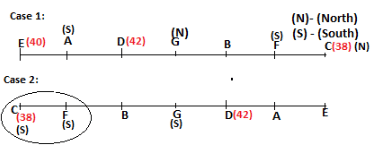
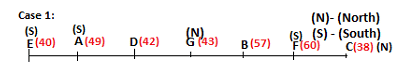
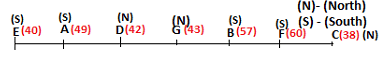
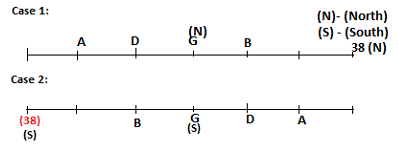
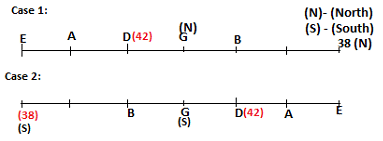
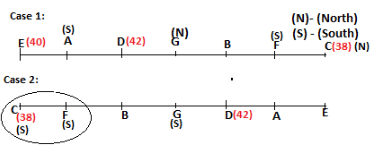
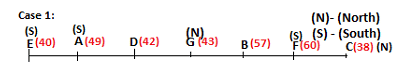
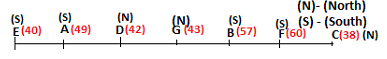
Seven persons A, B, C, D, E, F and G are sitting in a row, such that some of them are facing South and some of them are facing North. They all have different weights. The person whose weight is an odd number does not sit immediately to the left of the person whose weight is also an odd number. D faces opposite direction than the direction faced by A. G is sitting in the middle of the row. Two persons are sitting between A and B. C is facing North and sits at one of the extreme ends to the immediate left of F. The person whose weight is 40 kg sits immediately to the right of A. G faces the same direction as the one whose weight is 38 kg. Either A or B is a neighbour of G. E's weight is not 38 kg. The one whose weight is 43 kg and the one whose weight is 57 kg are immediate neighbours. Two persons are sitting between E and G. The one whose weight is 42 kg sits to the immediate left of G. F's weight is 3 kg more than B's weight. D is sitting third from one of the extreme ends and fourth to the left of the one whose weight is 38 kg. The one whose weight is 49 kg sits immediately to the left of E. Two persons are sitting between the one whose weight is 57 kg and the one whose weight is 49 kg. B is not a neighbour of D and faces the same direction as the direction faced by E.
Who is sitting third to the left of G?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the question given below.
Seven persons A, B, C, D, E, F and G are sitting in a row, such that some of them are facing South and some of them are facing North. They all have different weights. The person whose weight is an odd number does not sit immediately to the left of the person whose weight is also an odd number. D faces opposite direction than the direction faced by A. G is sitting in the middle of the row. Two persons are sitting between A and B. C is facing North and sits at one of the extreme ends to the immediate left of F. The person whose weight is 40 kg sits immediately to the right of A. G faces the same direction as the one whose weight is 38 kg. Either A or B is a neighbour of G. E's weight is not 38 kg. The one whose weight is 43 kg and the one whose weight is 57 kg are immediate neighbours. Two persons are sitting between E and G. The one whose weight is 42 kg sits to the immediate left of G. F's weight is 3 kg more than B's weight. D is sitting third from one of the extreme ends and fourth to the left of the one whose weight is 38 kg. The one whose weight is 49 kg sits immediately to the left of E. Two persons are sitting between the one whose weight is 57 kg and the one whose weight is 49 kg. B is not a neighbour of D and faces the same direction as the direction faced by E.
Which of the following options represents people facing South?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the question given below.
Seven persons A, B, C, D, E, F and G are sitting in a row, such that some of them are facing South and some of them are facing North. They all have different weights. The person whose weight is an odd number does not sit immediately to the left of the person whose weight is also an odd number. D faces opposite direction than the direction faced by A. G is sitting in the middle of the row. Two persons are sitting between A and B. C is facing North and sits at one of the extreme ends to the immediate left of F. The person whose weight is 40 kg sits immediately to the right of A. G faces the same direction as the one whose weight is 38 kg. Either A or B is a neighbour of G. E's weight is not 38 kg. The one whose weight is 43 kg and the one whose weight is 57 kg are immediate neighbours. Two persons are sitting between E and G. The one whose weight is 42 kg sits to the immediate left of G. F's weight is 3 kg more than B's weight. D is sitting third from one of the extreme ends and fourth to the left of the one whose weight is 38 kg. The one whose weight is 49 kg sits immediately to the left of E. Two persons are sitting between the one whose weight is 57 kg and the one whose weight is 49 kg. B is not a neighbour of D and faces the same direction as the direction faced by E.
Who is sitting to the immediate left of the one whose weight is 57 kg?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the question given below.
Seven persons A, B, C, D, E, F and G are sitting in a row, such that some of them are facing South and some of them are facing North. They all have different weights. The person whose weight is an odd number does not sit immediately to the left of the person whose weight is also an odd number. D faces opposite direction than the direction faced by A. G is sitting in the middle of the row. Two persons are sitting between A and B. C is facing North and sits at one of the extreme ends to the immediate left of F. The person whose weight is 40 kg sits immediately to the right of A. G faces the same direction as the one whose weight is 38 kg. Either A or B is a neighbour of G. E's weight is not 38 kg. The one whose weight is 43 kg and the one whose weight is 57 kg are immediate neighbours. Two persons are sitting between E and G. The one whose weight is 42 kg sits to the immediate left of G. F's weight is 3 kg more than B's weight. D is sitting third from one of the extreme ends and fourth to the left of the one whose weight is 38 kg. The one whose weight is 49 kg sits immediately to the left of E. Two persons are sitting between the one whose weight is 57 kg and the one whose weight is 49 kg. B is not a neighbour of D and faces the same direction as the direction faced by E.
Who weighs 42 kg?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the question given below.
Seven persons A, B, C, D, E, F and G are sitting in a row, such that some of them are facing South and some of them are facing North. They all have different weights. The person whose weight is an odd number does not sit immediately to the left of the person whose weight is also an odd number. D faces opposite direction than the direction faced by A. G is sitting in the middle of the row. Two persons are sitting between A and B. C is facing North and sits at one of the extreme ends to the immediate left of F. The person whose weight is 40 kg sits immediately to the right of A. G faces the same direction as the one whose weight is 38 kg. Either A or B is a neighbour of G. E's weight is not 38 kg. The one whose weight is 43 kg and the one whose weight is 57 kg are immediate neighbours. Two persons are sitting between E and G. The one whose weight is 42 kg sits to the immediate left of G. F's weight is 3 kg more than B's weight. D is sitting third from one of the extreme ends and fourth to the left of the one whose weight is 38 kg. The one whose weight is 49 kg sits immediately to the left of E. Two persons are sitting between the one whose weight is 57 kg and the one whose weight is 49 kg. B is not a neighbour of D and faces the same direction as the direction faced by E.
How many persons are sitting between E and the one whose weight is 60 kg?