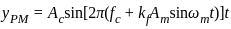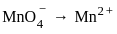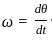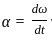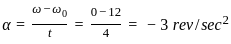RPSC Senior Grade II (Science) Mock Test - 2 - REET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - RPSC Senior Grade II (Science) Mock Test - 2
C60, an allotrope of carbon contains:
The repulsive interaction of electron pairs is maximum in
The photoperiod response of the plants is perceived by the ______.
Magnetic force on a conductor of length 'L' and carrying a current 'I' kept in an external magnetic field 'B' is equal to?
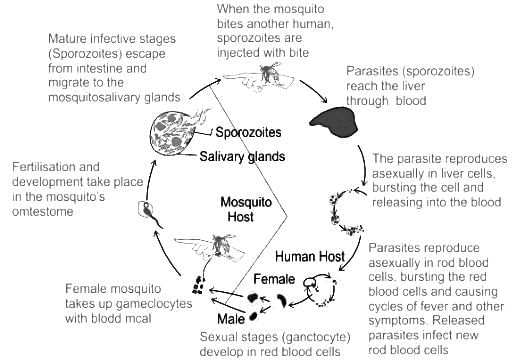
The intermediate host of malaria parasite is
Find the amplitude of the simple harmonic motion obtained by combining the motions
x1 = (2.0 cm) sinωt and x2 = (2.0 cm) sin(ωt + π/3).
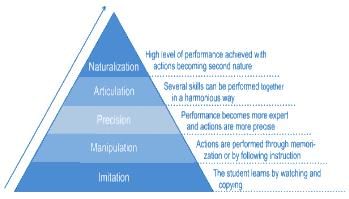
The first level of psychomotor domain is:
Which of the following species is a nucleophile?
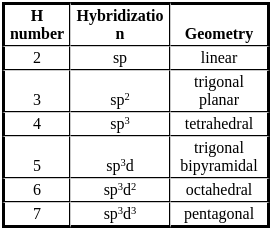
What is the geometry of four sp3 hybrid orbitals is
The role of a science teacher should be to _________.
If in a body, carrying n particles of mass mi and position 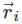 , acceleration due to gravity (gi) does not vary from point to point, then at centre of gravity
, acceleration due to gravity (gi) does not vary from point to point, then at centre of gravity
A plane electromagnetic wave of frequency 100 MHz is travelling in vacuum along the x-direction. At a particular point in space and time, 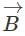 = 2.0 x 10-8
= 2.0 x 10-8 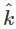 T. (where,
T. (where, 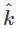 is unit vector along z-direction) What is
is unit vector along z-direction) What is 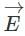 at this point?
at this point?
(speed of light c = 3 x 108 m/s)
If a ball of mass 2 kg with kinetic energy 100 Joule undergoes perfectly elastic collision with a rigid wall, then the speed of ball after collision is
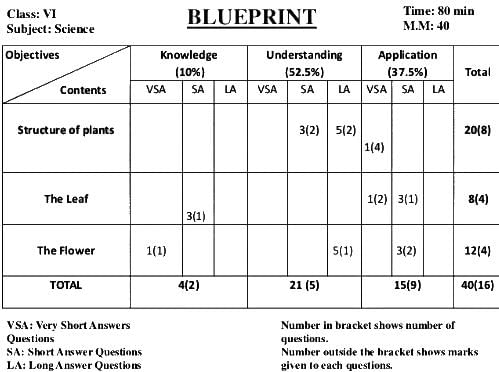
Which information is not available from the blue-print table of a question paper?
If a particle is executing SHM then the direction of the acceleration will be-
A message signal of amplitude Am is superimposed on a carrier wave of amplitude Ac to get frequency modulated wave (FM). The Amplitude of the FM wave will be
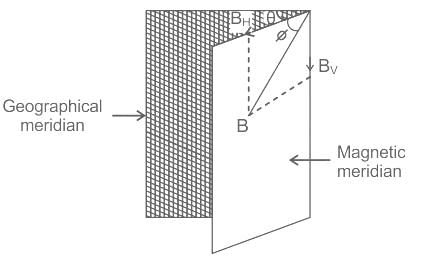
Find the angle of dip at a certain place where the horizontal and vertical components of the earth’s magnetic fields are same.
In the complex ion MLn+6, has five d–electrons and L is a strong field ligand. According to crystal field theory, the magnetic properties of the complex ion correspond to how many unpaired electrons?
The period of a periodic function f(t) = A cos(ωt + φ) is given by __________.
How much charge is required for the reduction of MnO−4 to Mn2+ ?
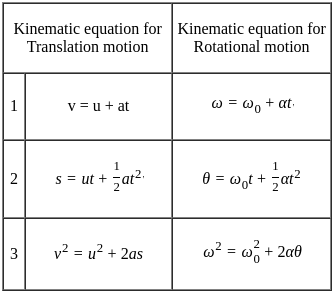
Consider if a wheel is rotating about an axis through its centre at 12 revolutions per second. It is acted on by constant torque opposing its motion for 4 seconds till it comes to rest. In this case the rate of deceleration is _________.
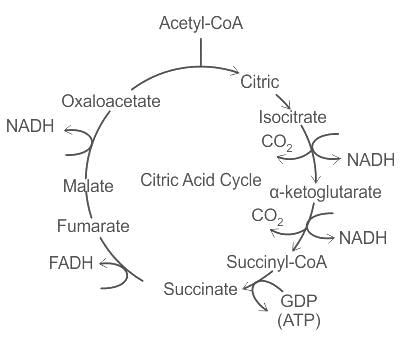
The number of substrate level phosphorylations in one turn of citric acid cycle is



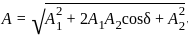 [δ =phase angle between them]
[δ =phase angle between them]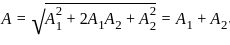
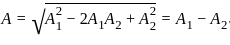
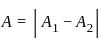
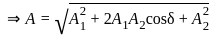
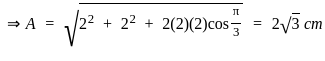
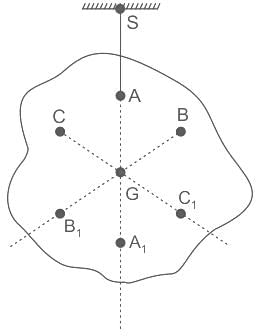
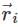 is the position vector of a particle mass m
is the position vector of a particle mass m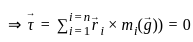 (i)
(i)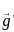 is non zero we may rewrite (i) as:
is non zero we may rewrite (i) as: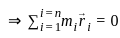 (ii)
(ii)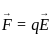
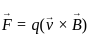
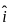 MHz
MHz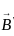
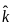
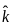
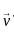 = 3 x 108
= 3 x 108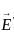
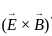
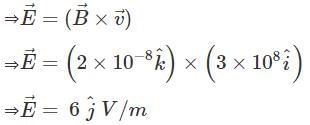
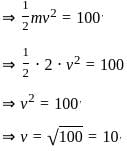
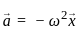
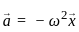
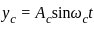
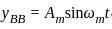
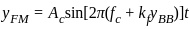 or
or