SRMJEEE Chemistry Mock Test - 6 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - SRMJEEE Chemistry Mock Test - 6
Which of the following will not from a yellow precipitate on heating with an alkaline solution of iodine?
When H₂S gas is passed through the HCl containing aqueous solution of CuCl₂, HgCl₂, BiCl₃ and coCl₂, it does not precipitate out
Electrophile in the case of chlorination of benzene in presence of FeCl₃ is
The greater the s- character in an orbital the ... is its energy
The acid showing salt like character in aqueous solutions is
60 J of heat flows out from 600 g of water at 30°C into surroundings at 25°C.The net entropy change in universe is approximately
A glass bulb is filled with NO₂ gas and immersed in an ice bath at 0°C which becomes colourless after some time . This colourless gas will be
Calculate the heat of formation Δ H of CO (in kcal) from the following data :
C(graphite) + O2(g) → CO2 (g); ΔH = -94K. cal
CO(g) + 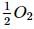 (g) → CO2 (g) ; ΔH = -68K. cal
(g) → CO2 (g) ; ΔH = -68K. cal
Which one of the following reactions occur at the cathode?
Which of the following applies to the reaction,
1. CH₃CH = CHCH₃(major product)
2. CH₂ = CH − CH₂CH₃(minor product)
A compound having the formula NH₂CH₂COOH may behave
A symmetrical molecule has 2 chiral carbon atoms. The no. of isomers is
C-14 has a half-life of 5760 years. 100 mg of a sample containing C-14 is reduced to 25 mg in
Which of the following is used for making horses, shoe heels and stoppers?
In Duma's method, the gas which is collected in Nitrometer is














